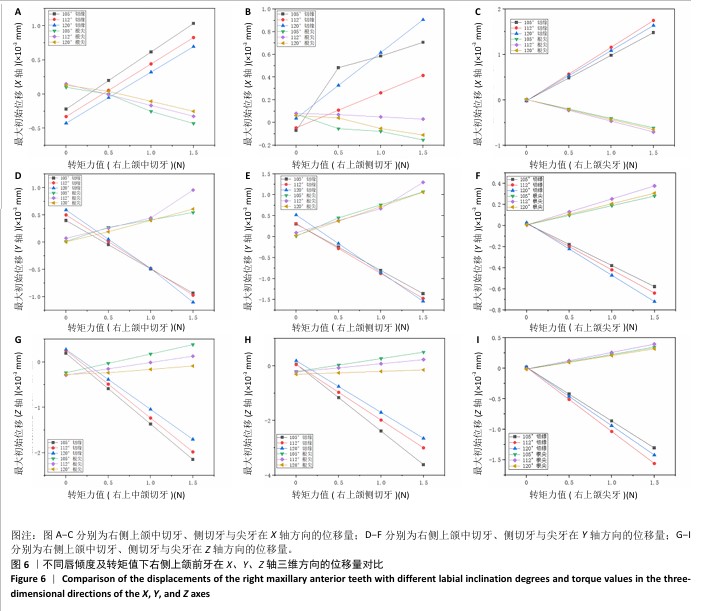
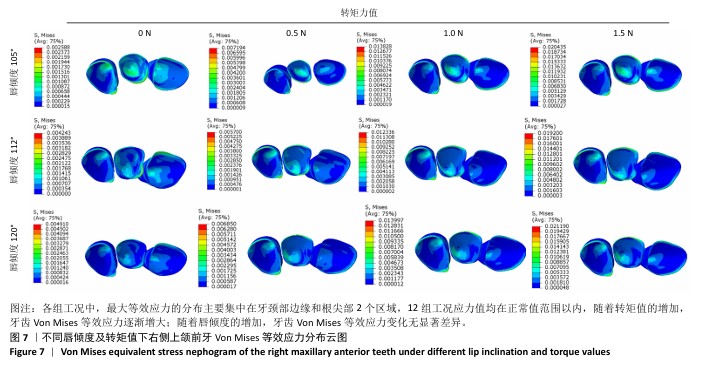
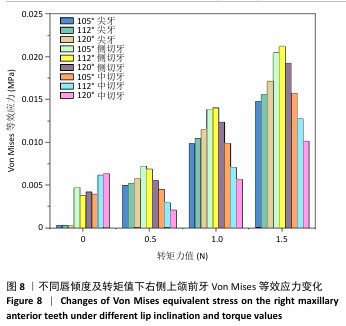
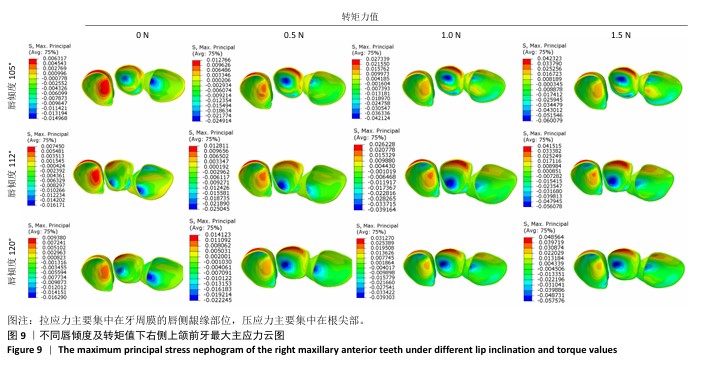
[1] IMAMURA Y, SATO Y, KITAGAWA N, et al. Influence of occlusal loading force on occlusal contacts in natural dentition. J Prosthodont Res. 2015;59(2):113-120.
[2] LIU JK, TSAI MY. Relationship between morphologic malocclusion and temporomandibular disorders in orthodontic patients prior to treatment. Funct Orthod. 1997;14(5):13-16.
[3] KHAYAT N, WINOCUR E, KEDEM R, et al. The prevalence of temporomandibular disorders and dental attrition levels in patients with posterior crossbite and/or deep bite: A preliminary prospective study. Pain Res Manag. 2021;2021:8827895.
[4] BHATEJA NK, FIDA M, SHAIKH A. Deep bite malocclusion: Exploration of the skeletal and dental factors. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2016; 28(3):449-454.
[5] YUN S, PARK JH, CHANG NY, et al. Craniomaxillofacial changes using high-pull J-hook headgear and mini-implant anchorage in adolescents: A structural superimposition method. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2021;45(6):433-440.
[6] ALRBATA RH, MOMANI MQ, AL-TARAWNEH AM, et al. Optimal force magnitude loaded to orthodontic microimplants: A finite element analysis. Angle Orthod. 2016;86(2):221-226.
[7] BARDIDEH E, TAMIZI G, SHAFAEE H, et al. The effects of intrusion of anterior teeth by skeletal anchorage in deep bite patients; a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomimetics (Basel, Switzerland). 2023;8(1): 101.
[8] 施则安,夏恺,罗良语,等.无托槽隐形矫治器联合微种植体内收并压低上前牙的三维有限元分析[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志,2022, 40(5):589-596.
[9] 康芙嘉,张茜雅,余磊,等.微种植体辅助无托槽隐形矫治器压低上颌前牙的三维有限元分析[J].口腔医学,2023,43(9):796-802.
[10] XIAO T, SU J Y, LEI J, et al. Effectiveness of different intrusion modes of maxillary anterior teeth with mini-implants in clear aligner treatment: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. BMC Oral Health. 2024; 24(1):758.
[11] JAIN A, PRASANTHA GS, MATHEW S, et al. Analysis of stress in periodontium associated with orthodontic tooth movement: A three dimensional finite element analysis. Comput Method. Biomech Biomed Engin. 2021;24(16):1841-1853.
[12] YANG PZ, BAI LY, ZHANG HX, et al. Efficacy of a four-curvature auxiliary arch at preventing maxillary central incisor linguoclination during orthodontic treatment: A finite element analysis. BMC Oral Health. 2023;23(1):144.
[13] KAWAMURA J, PARK JH, KOJIMA Y, et al. Biomechanical analysis for total distalization of the maxillary dentition: A finite element study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2021;160(2):259-265.
[14] JI L, LI B, WU X. Evaluation of biomechanics using different traction devices in distalization of maxillary molar with clear aligners: A finite element study. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2023;26(5): 559-567.
[15] WEI Z, YU X, XU X, et al. Experiment and hydro-mechanical coupling simulation study on the human periodontal ligament. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2014;113(3):749-756.
[16] MCGUINNESS NJ, WILSON AN, JONES ML, et al. A stress analysis of the periodontal ligament under various orthodontic loadings. Eur J Orthod. 1991;13(3):231-242.
[17] PITHON MM. Spontaneous correction of accentuated retraction of maxillary central incisors after autogenous graft in midline, mesialization, and lingual torque of incisor roots. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2018;38(Suppl):s67-s77.
[18] LI Y, XIAO S, JIN Y, et al. Stress and movement trend of lower incisors with different IMPA intruded by clear aligner: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. Prog Orthod. 2023;24(1): 5.
[19] PAPAGEORGIOU SN, KEILIG L, VANDEVSKA-RADUNOVIC V, et al. Torque differences due to the material variation of the orthodontic appliance: A finite element study. Prog Orthod. 2017;18(1): 6.
[20] THOTE AM, UDDANWADIKER RV, SHARMA K, et al. Optimum force system for intrusion and extrusion of maxillary central incisor in labial and lingual orthodontics. Comput Biol Med. 2016;69:112-119.
[21] ZHAO W, LOU Y, YAN W. Evaluation of stress and displacement of maxillary canine during the single canine retraction in the maxillary first premolar extraction cases- a finite element study. Clin Oral Investig. 2024;28(3):206.
[22] BURSTONE CR. Deep overbite correction by intrusion. Am J Orthod. 1977;72(1):1-22.
[23] RICKETTS RM. Bioprogressive therapy as an answer to orthodontic needs. Part II. Am J Orthod. 1976;70(4):359-397.
[24] MOGA RA, OLTEANU CD, BOTEZ M, et al. Assessment of the maximum amount of orthodontic force for PDL in intact and reduced periodontium (part I). Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(3):1889.
[25] LIAO Z, CHEN J, LI W, et al. Biomechanical investigation into the role of the periodontal ligament in optimising orthodontic force: A finite element case study. Arch Oral Biol. 2016;66:98-107.
[26] ABBING A, KORETSI V, ELIADES T, et al. Duration of orthodontic treatment with fixed appliances in adolescents and adults: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Prog Orthod. 2020;21(1):37.
[27] BAESHEN HA. The effect of partial corticotomy on the rate of maxillary canine retraction: Clinical and radiographic study. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland). 2020;25(20):4837.
[28] CATTANEO PM, CORNELIS MA. Orthodontic tooth movement studied by finite element analysis: An update. What can we learn from these simulations? Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2021;19(2):175-181.
[29] WOOD SA, STRAIT DS, DUMONT ER, et al. The effects of modeling simplifications on craniofacial finite element models: The alveoli (tooth sockets) and periodontal ligaments. J Biomech. 2011;44(10): 1831-1838.
[30] KAWAMURA J, OJIMA K, NANDA R. Effect of attachment type on distal bodily movement of the maxillary canine in aligner orthodontics: A finite element study. Angle. Orthod. 2023;93(5):566-571. |