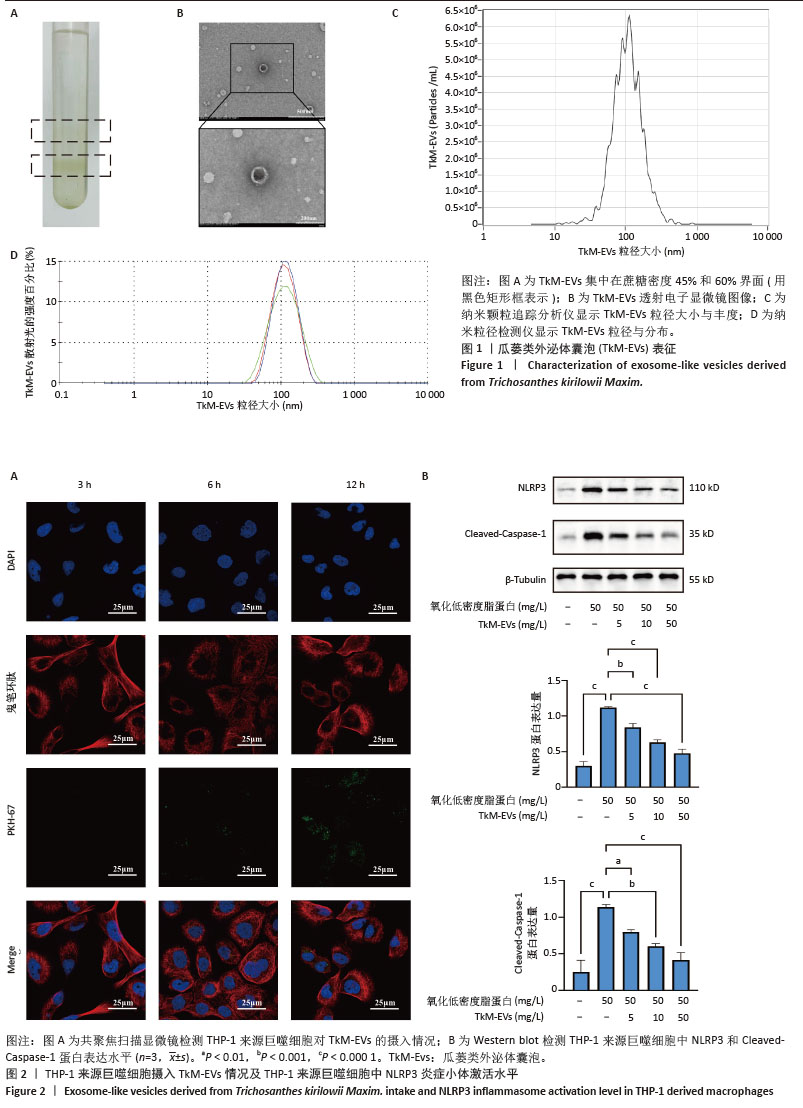
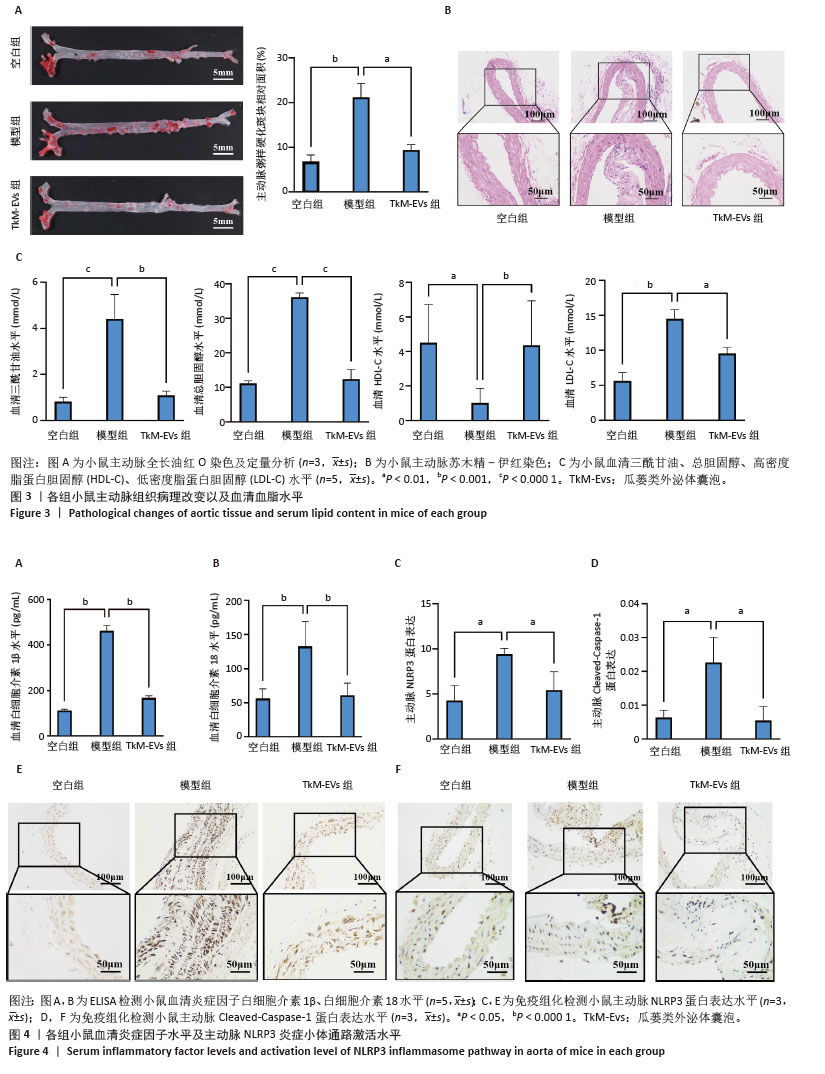
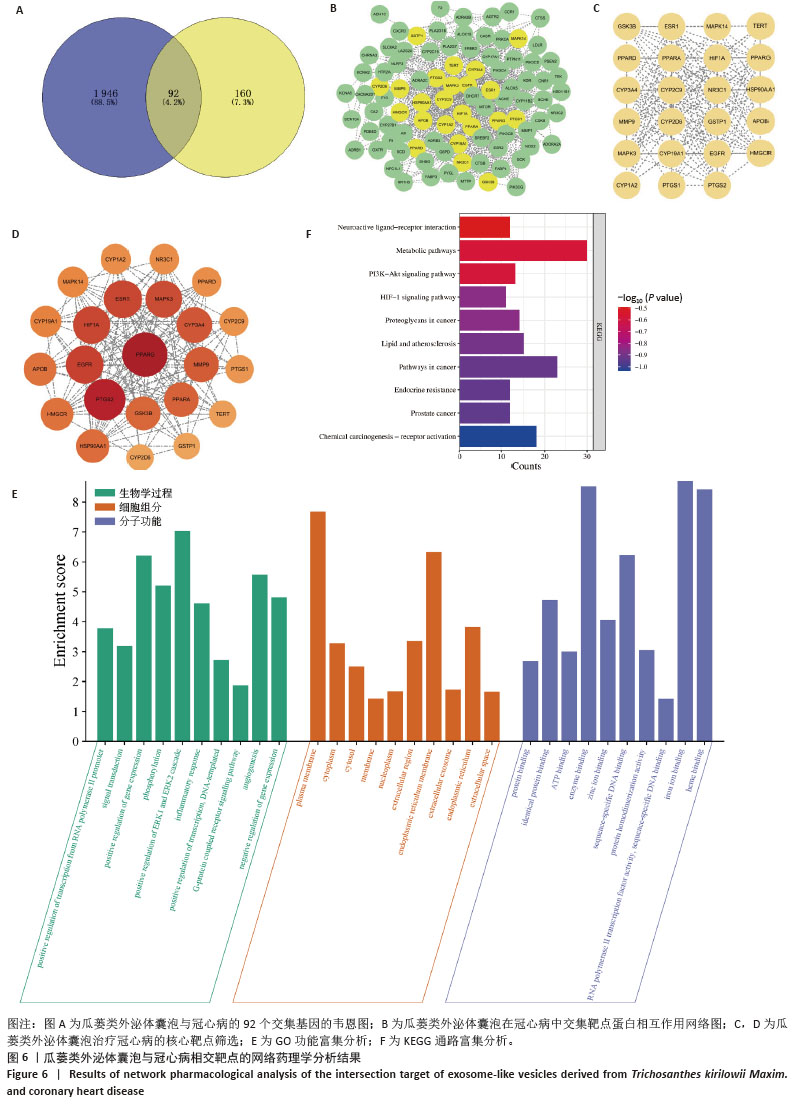
[1] RADDATZ MA, PERSHAD Y, PARKER AC, et al. Clonal Hematopoiesis of Indeterminate Potential and Cardiovascular Health. Cardiol Clin. 2025;43(1):13-23.
[2] GUSEV E, SARAPULTSEV A. Atherosclerosis and Inflammation: Insights from the Theory of General Pathological Processes. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(9):7910.
[3] RUIZ-LEON AM, LAPUENTE M, ESTRUCH R, et al. Clinical Advances in Immunonutrition and Atherosclerosis: A Review. Front Immunol. 2019;10:837.
[4] LIBBY P. The changing landscape of atherosclerosis. Nature. 2021; 592(7855):524-533.
[5] MACH F, BAIGENT C, CATAPANO AL, et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur Heart J. 2020;41(1):111-188.
[6] HERNANDO-REDONDO J, NIÑO OC, FITÓ M. Atherogenic low-density lipoprotein and cardiovascular risk. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2025;36(1):8-13.
[7] ITABE H, OBAMA T. The Oxidized Lipoproteins In Vivo: Its Diversity and Behavior in the Human Circulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(6):5747.
[8] LI Z, GUO J, BI L. Role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in autoimmune diseases. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;130:110542.
[9] KELLEY N, JELTEMA D, DUAN Y, et al. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: An Overview of Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(13):3328.
[10] FU JN, WU H. Structural Mechanisms of NLRP3 Inflammasome Assembly and Activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2023;41:301-316.
[11] HA MT, PHAN TN, KIM JA, et al. Trichosanhemiketal A and B: Two 13,14-seco-13,14-epoxyporiferastanes from the root of Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim. Bioorg Chem. 2019;83:105-110.
[12] HU XQ, SONG H, LI N, et al. Identification and analysis of miRNAs differentially expressed in male and female Trichosanthes kirilowii maxim. BMC Genomics. 2023;24(1):81.
[13] ZHANG Y, WANG K, HUANG Q, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of an alpha-amylase inhibitor (TkAAI) gene from Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim. Biotechnol Lett. 2022;44(10):1127-1138.
[14] HOU Z, ZHU L, MENG R, et al. Hypolipidemic and antioxidant activities of Trichosanthes kirilowii maxim seed oil and flavonoids in mice fed with a high-fat diet. J Food Biochem. 2020;44(8):e13272.
[15] 鲍友利,曹寅,吴鸿飞. “瓜蒌-薤白”药对诱导自噬抑制NLRP3炎症小体激活减轻RAW264.7巨噬细胞炎症反应[J].中国中药杂志, 2023,48(10):2820-2828.
[16] MU N, LI J, ZENG L, et al. Plant-Derived Exosome-Like Nanovesicles: Current Progress and Prospects. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:4987-5009.
[17] CUI LS, PERINI G, PALMIERI V, et al. Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as a Novel Frontier in Cancer Therapeutics. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(16):1331.
[18] BUZAS EI. The roles of extracellular vesicles in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2023;23(4):236-250.
[19] ZHANG B, SIM WK, SHEN TL, et al. Engineered EVs with pathogen proteins: promising vaccine alternatives to LNP-mRNA vaccines. J Biomed Sci. 2024;31(1):9.
[20] WU J, MA Y, CHEN Y. Extracellular vesicles and COPD: foe or friend? J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):147.
[21] COLY PM, BOULANGER CM. Role of extracellular vesicles in atherosclerosis: An update. J Leukoc Biol. 2022;111(1):51-62.
[22] SHARMA S, MAHANTY M, RAHAMAN SG, et al. Avocado-derived extracellular vesicles loaded with ginkgetin and berberine prevent inflammation and macrophage foam cell formation. J Cell Mol Med. 2024;28(7):e18177.
[23] ZHANG S, XIA J, ZHU Y, et al. Establishing Salvia miltiorrhiza-Derived Exosome-like Nanoparticles and Elucidating Their Role in Angiogenesis. Molecules. 2024;29(7):1599.
[24] NIU W, XIAO Q, WANG X, et al. A Biomimetic Drug Delivery System by Integrating Grapefruit Extracellular Vesicles and Doxorubicin-Loaded Heparin-Based Nanoparticles for Glioma Therapy. Nano Lett. 2021;21(3):1484-1492.
[25] KIM J, LI S, ZHANG S, et al. Plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles and their therapeutic activities. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2022;17(1):53-69.
[26] MADRIGAL-MATUTE J, FERNANDEZ-GARCIA CE, BLANCO-COLIO LM, et al. Thioredoxin-1/peroxiredoxin-1 as sensors of oxidative stress mediated by NADPH oxidase activity in atherosclerosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015;86:352-361.
[27] EL HADRI K, MAHMOOD DF, COUCHIE D, et al. Thioredoxin-1 promotes anti-inflammatory macrophages of the M2 phenotype and antagonizes atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012;32(6):1445-1452.
[28] KHARE HA, BINDERUP T, HAG AMF, et al. Longitudinal imaging of murine atherosclerosis with 2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-D-glucose and [18F]-sodium fluoride in genetically modified Apolipoprotein E knock-out and wild type mice. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):22983.
[29] WANG LH, GU ZW, LI J, et al. Isorhynchophylline inhibits inflammatory responses in endothelial cells and macrophages through the NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023;23(1):80.
[30] GUPTA D, ZICKLER AM, EL ANDALOUSSI S. Dosing extracellular vesicles. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;178:113961.
[31] FENG WJ, TENG YT, ZHONG QP, et al. Biomimetic Grapefruit-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Safe and Targeted Delivery of Sodium Thiosulfate against Vascular Calcification. Acs Nano. 2023;17(24):24773-24789.
[32] LI M, HOU XF, ZHANG J, et al. Applications of HPLC/MS in the analysis of traditional Chinese medicines. J Pharm Anal. 2011;1(2):81-91.
[33] 吴希泽,康健,李越,等.基于“浊气归心,淫精于脉”理论运用HPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS和网络药理学探讨抵挡汤防治动脉粥样硬化和高脂血症的作用机制[J].中国中药杂志,2023,48(5):1352-1369.
[34] LIAN MQ, CHNG WH, LIANG J, et al. Plant-derived extracellular vesicles: Recent advancements and current challenges on their use for biomedical applications. J Extracell Vesicles. 2022;11(12):e12283.
[35] NEMATI M, SINGH B, MIR RA, et al. Plant-derived extracellular vesicles: a novel nanomedicine approach with advantages and challenges. Cell Commun Signal. 2022;20(1):69.
[36] CHEN Y, CUI FC, WU XY , et al. The expression and clinical significance of serum exosomal-long non-coding RNA DLEU1 in patients with cervical cancer. Ann Med. 2025;57(1):2442537.
[37] ALDALI F, DENG CC, NIE MB, et al. Advances in therapies using mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes for treatment of peripheral nerve injury: state of the art and future perspectives. Neural Regen Res. 2025;20(11):3151-3171.
[38] ZHAO Y, ZHANG YD, LIU X, et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of plasma exosomes reveals the functional contribution of N-acetyl-alpha-glucosaminidase to Parkinson’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2025; 20(10):2998-3012.
[39] YIN WJ, MA HY, QU Y, et al. Exosomes: the next-generation therapeutic platform for ischemic stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2025;20(5):1221-1235.
[40] WU GQ, SU TY, ZHOU P, et al. Engineering M2 macrophage-derived exosomes modulate activated T cell cuproptosis to promote immune tolerance in rheumatoid arthritis. Biomaterials. 2025:315:122943.
[41] JIANG MY, ZHANG K, MENG JF, et al. Engineered exosomes in service of tumor immunotherapy: From optimizing tumor-derived exosomes to delivering CRISPR/Cas9 system. Int J Cancer. 2025;156(5):898-913.
[42] RAIMONDO S, URZÌ O, MERAVIGLIA S, et al. Anti-inflammatory properties of lemon-derived extracellular vesicles are achieved through the inhibition of ERK/NF-kappaB signalling pathways. J Cell Mol Med. 2022;26(15):4195-4209.
[43] LI ZF, WANG HZ, YIN HR, et al. Arrowtail RNA for ligand display on ginger exosome-like nanovesicles to systemic deliver siRNA for cancer suppression. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):14644.
[44] QIAO ZZ, ZHANG K, LIU J, et al. Biomimetic electrodynamic nanoparticles comprising ginger-derived extracellular vesicles for synergistic anti-infective therapy. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):7164.
[45] KANG SJ, LEE JH, RHEE WJ. Engineered plant-derived extracellular vesicles for targeted regulation and treatment of colitis-associated inflammation. Theranostics. 2024;14(14):5643-5661.
[46] WATABE N, SUBSOMWONG P, YAMANE K, et al. Exosome-like nanoparticles from Arbutus unedo L. mitigate LPS-induced inflammation via JAK-STAT inactivation. Food Funct. 2024;15(22):11280-11290.
[47] BIAN YP, LI WZ, JIANG XQ, et al. Garlic-derived exosomes carrying miR-396e shapes macrophage metabolic reprograming to mitigate the inflammatory response in obese adipose tissue. J Nutr Biochem. 2023;113:109249.
[48] AL-HAWARY SIS, JASIM SA, ROMERO-PARRA RM, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome pathway in atherosclerosis: Focusing on the therapeutic potential of non-coding RNAs. Pathol Res Pract. 2023;246:154490.
[49] XUE Z, ZHANG Z, LIU H, et al. lincRNA-Cox2 regulates NLRP3 inflammasome and autophagy mediated neuroinflammation. Cell Death Differ. 2019;26(1):130-145.
[50] HAO H, CAO L, JIANG C, et al. Farnesoid X Receptor Regulation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome Underlies Cholestasis-Associated Sepsis. Cell Metab. 2017;25(4):856-867. e5.
[51] CHEN Y, QIN X, AN Q, et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Directly Promote Inflammation by Canonical NLRP3 and Non-canonical Caspase-11 Inflammasomes. EBioMedicine. 2018;32:31-42.
[52] SHARMA BR, KANNEGANTI TD. NLRP3 inflammasome in cancer and metabolic diseases. Nat Immunol. 2021;22(5):550-559.
[53] TANASE DM, VALASCIUC E, GOSAV EM, et al. Portrayal of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Atherosclerosis: Current Knowledge and Therapeutic Targets. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(9):8162.
[54] WU P, WU W, ZHANG S, et al. Therapeutic potential and pharmacological significance of extracellular vesicles derived from traditional medicinal plants. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1272241.
[55] LIU X, LOU K, ZHANG Y, et al. Unlocking the Medicinal Potential of Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: current Progress and Future Perspectives. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024;19:4877-4892.
[56] KIM M, PARK JH. Isolation of Aloe saponaria-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Investigation of Their Potential for Chronic Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(9):1905.
[57] 丁杨,胡容. NLRP3炎症小体激活及调节机制的研究进展[J].药学进展,2018,42(4):294-302.
[58] LUCAFÒ M, GRANATA S, BONTEN EJ, et al. Hypomethylation of NLRP3 gene promoter discriminates glucocorticoid-resistant from glucocorticoid-sensitive idiopathic nephrotic syndrome patients. Clin Transl Sci. 2021;14(3):964-975.
[59] JIAO Y, YAN Z, YANG A. Mitochondria in innate immunity signaling and its therapeutic implications in autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1160035.
[60] WU Y, NI T, ZHANG M, et al. Treatment with β-Adrenoceptor Agonist Isoproterenol Reduces Non-parenchymal Cell Responses in LPS/D-GalN-Induced Liver Injury. Inflammation. 2024;47(2):733-752.
[61] LIAO X, CHANG E, TANG X, et al. Cardiac macrophages regulate isoproterenol-induced Takotsubo-like cardiomyopathy. JCI Insight. 2022;7(3):e156236.
[62] RONG J, HAN C, HUANG Y, et al. Inhibition of xanthine oxidase alleviated pancreatic necrosis via HIF-1α-regulated LDHA and NLRP3 signaling pathway in acute pancreatitis. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024;14(8): 3591-3604.
[63] MA J, CHEN L, ZHU X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-21a-5p promotes M2 macrophage polarization and reduces macrophage infiltration to attenuate atherosclerosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021;53(9):1227-1236.
[64] AL-AHMADI W, WEBBERLEY TS, JOSEPH A, et al. Pro-atherogenic actions of signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 serine 727 phosphorylation in LDL receptor deficient mice via modulation of plaque inflammation. FASEB J. 2021;35(10):e21892.
[65] JAIPERSAD AS, LIP GY, SILVERMAN S, et al. The role of monocytes in angiogenesis and atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(1):1-11.
[66] XIAO X, XU M, YU H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles mitigate oxidative stress-induced senescence in endothelial cells via regulation of miR-146a/Src. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):354. |