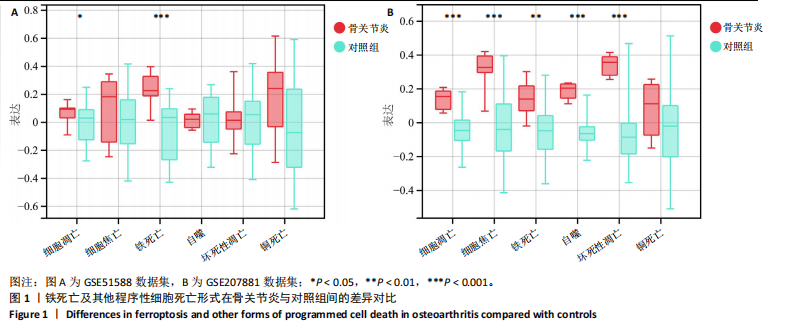
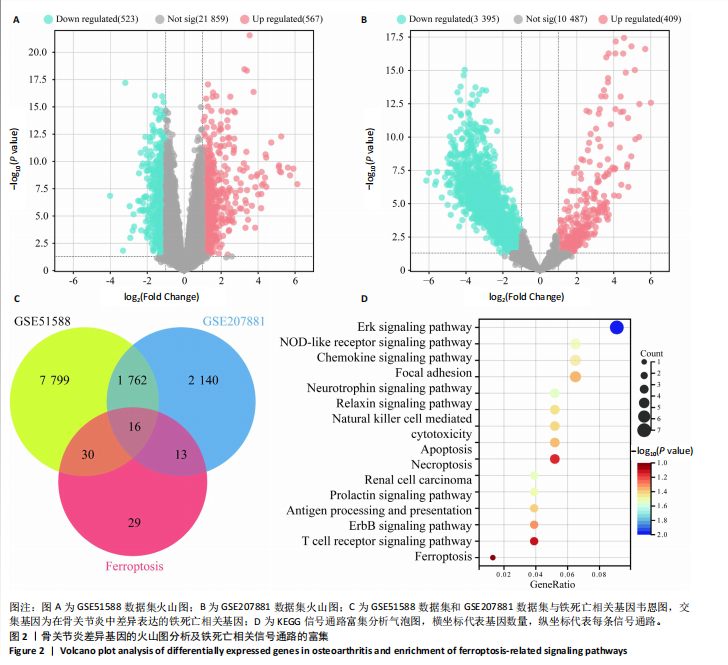
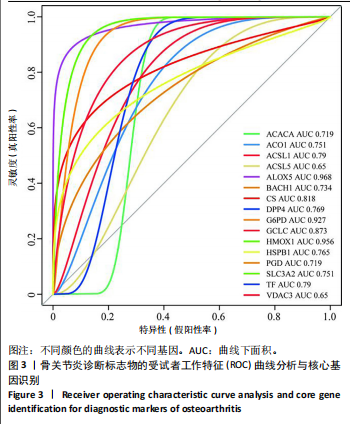
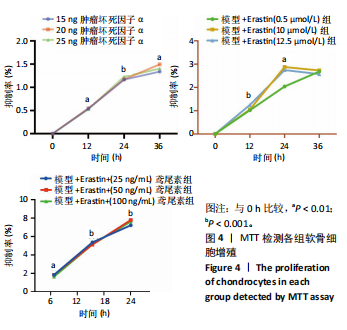
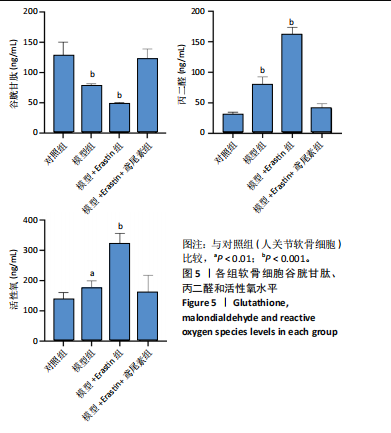
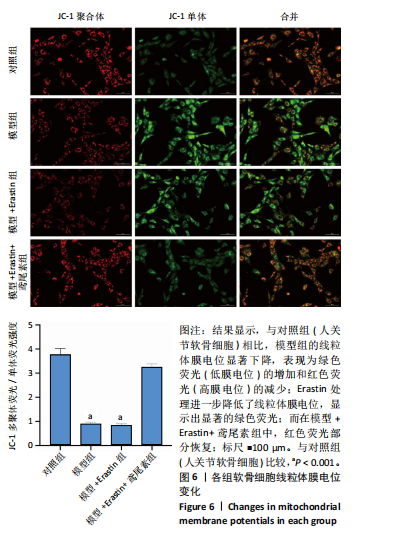
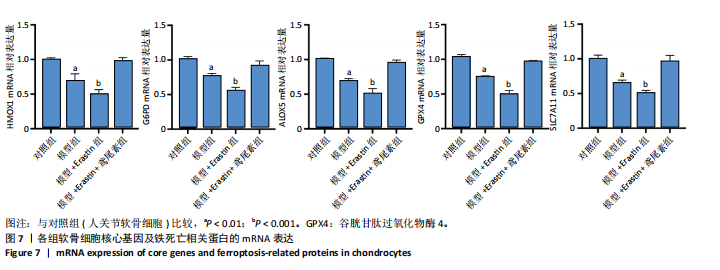
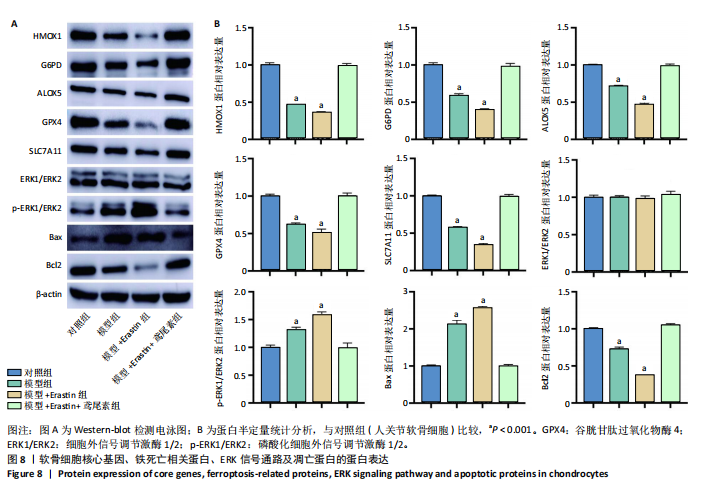
[1] HU S, LI Y, ZHANG X, et al. Increasing burden of osteoarthritis in China: trends and projections from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Med Sci Monit. 2024;30:e942626.
[2] HOLYOAK DT, TIAN YF, VAN DER MEULEN MC, et al. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, Mouse Models, and Nanoparticle Injectable Systems for Targeted Treatment. Ann Biomed Eng. 2016;44(6):2062-2075.
[3] EKMAN B, NERO H, LOHMANDER LS, et al. Costing analysis of a digital first-line treatment platform for patients with knee and hip osteoarthritis in Sweden. Plos one.2020;15(8):e0236342.
[4] XU Y, YANG Z, DAI T, et al. Characteristics and time points to inhibit ferroptosis in human osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):21592.
[5] CHANG S, TANG M, ZHANG B, et al. Ferroptosis in inflammatory arthritis: a promising future. Front Immunol. 2022;13:955069.
[6] HU Y, WANG Y, LIU S, et al. The Potential Roles of Ferroptosis in Pathophysiology and Treatment of Musculoskeletal Diseases-Opportunities, Challenges, and Perspectives. J Clin Med. 2023; 12(6):2125.
[7] ZHAO R, CHEN Y, WANG D, et al. Role of irisin in bone diseases. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1212892.
[8] ROGGIO F, PETRIGNA L, TROVATO B, et al. The role of lubricin, irisin and exercise in the prevention and treatment of osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(6):5126.
[9] AL-HETTY HRAK, ABDULAMEER SJ, ALGHAZALI MW, et al. The role of ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. J Membr Biol. 2023;256(3):223-228.
[10] YAO X, SUN K, YU S, et al. Chondrocyte ferroptosis contribute to the progression of osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. 2020;27:33-43.
[11] GUO Z, LIN J, SUN K, et al. Deferoxamine alleviates osteoarthritis by inhibiting chondrocyte ferroptosis and activating the Nrf2 pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:791376.
[12] ZHANG S, XU J, SI H, et al. The role played by ferroptosis in osteoarthritis: evidence based on iron dyshomeostasis and lipid peroxidation. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(9):1668.
[13] LIU Y, ZHANG Z, FANG Y, et al. Ferroptosis in osteoarthritis: current understanding. J Inflamm Res. 2024;17:8471-8486.
[14] TAO L, WANG J, WANG K, et al. Exerkine FNDC5/irisin‐enriched exosomes promote proliferation and inhibit ferroptosis of osteoblasts through interaction with Caveolin‐1. Aging Cell. 2024;23(8):e14181.
[15] ASKARI H, RAJANI SF, POOREBRAHIM M, et al. A glance at the therapeutic potential of irisin against diseases involving inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis: an introductory review. Pharmacol Res. 2018;129:44-55.
[16] TIAN L, LIU Q, WANG X, et al. Fighting ferroptosis: Protective effects of dexmedetomidine on vital organ injuries. Life Sci. 2024;354:122949.
[17] RAYEGO-MATEOS S, MARQUEZ-EXPOSITO L, BASANTES P, et al. CCN2 activates RIPK3, NLRP3 inflammasome, and NRF2/oxidative pathways linked to kidney inflammation. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023;12(8):1541.
[18] KONG K, YANG Y, CHANG Y, et al. A Ubiquitin‐Competitive Strategy Based on the Element Microenvironment to Treat Osteoarthritis. Adv Funct Mater. 2024;34(51):2409707.
[19] HAN J, ZHAN L, HUANG Y, et al. Moderate mechanical stress suppresses chondrocyte ferroptosis in osteoarthritis by regulating NF-κB p65/GPX4 signaling pathway. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):5078.
[20] LI X, ZHU X, WU H, et al. Roles and mechanisms of irisin in attenuating pathological features of osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9: 703670.
[21] JIA S, YANG Y, BAI Y, et al. Mechanical stimulation protects against chondrocyte pyroptosis through irisin-induced suppression of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signal pathway in osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022; 10:797855.
[22] LI X, LIU Y, LIU Q, et al. Recombinant human irisin regulated collagen II, matrix metalloproteinase‑13 and the Wnt/β‑catenin and NF‑κB signaling pathways in interleukin‑1β‑induced human SW1353 cells. Exp Ther Med. 2020;19(4):2879-2886.
[23] JIA S, YU Z, BAI L. Exerkines and osteoarthritis. Front Physiol. 2023;14: 1302769.
[24] POSA F, ZERLOTIN R, ARIANO A, et al. Irisin role in chondrocyte 3D culture differentiation and its possible applications. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(2):585.
[25] LIU Y, HOU M, PAN Z, et al. Arctiin-reinforced antioxidant microcarrier antagonizes osteoarthritis progression. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022; 20(1):303.
[26] AMIRKHIZI F, HAMEDI-SHAHRAKI S, RAHIMLOU M. Dietary total antioxidant capacity is associated with lower disease severity and inflammatory and oxidative stress biomarkers in patients with knee osteoarthritis. J Health Popul Nutr. 2023;42(1):104.
[27] NING K, WANG Z, ZHANG X. Exercise-induced modulation of myokine irisin in bone and cartilage tissue—Positive effects on osteoarthritis: A narrative review. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:934406.
[28] ROGGIO F, PETRIGNA L, TROVATO B, et al. The role of lubricin, irisin and exercise in the prevention and treatment of osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(6):5126.
[29] LV J, ZHANG H, CHEN N. Exercise Mimetic Pills for Chronic Diseases Based on Autophagy. Exercise, Autophagy and Chronic Diseases. 2021: 247-260.
[30] GUBERT C, HANNAN A J. Exercise mimetics: harnessing the therapeutic effects of physical activity. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021;20(11):862-879.
|