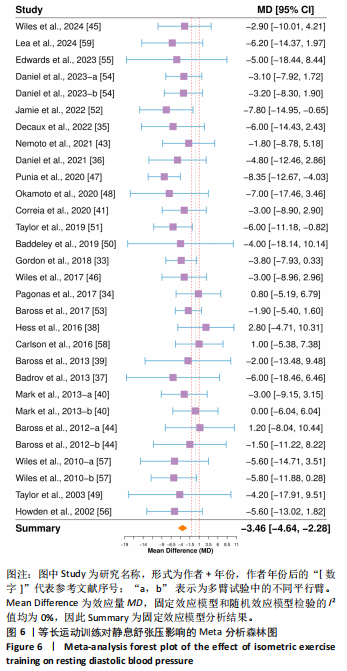
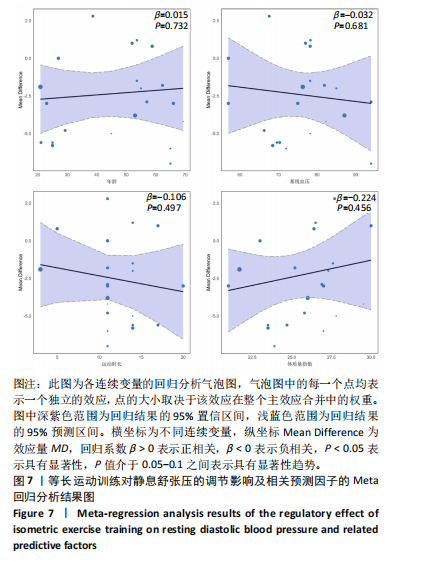
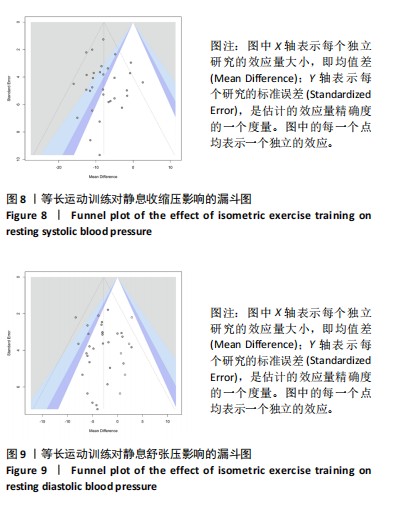
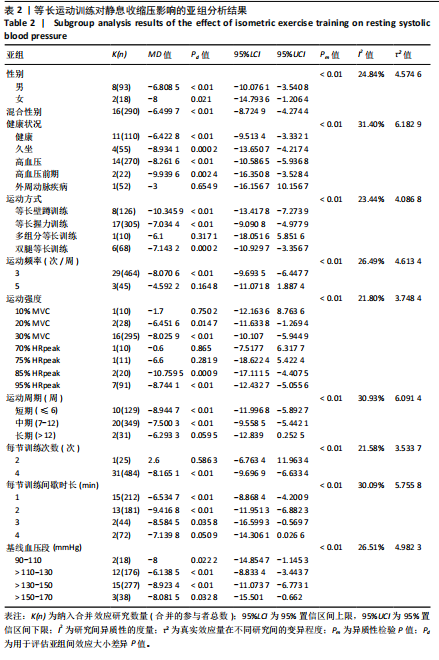
[1] JOSEPH P, LEONG D, MCKEE M, et al. Reducing the global burden of cardiovascular disease, part 1: the epidemiology and risk factors. Circulation Res. 2017;121(6):677-694.
[2] LEONG DP, JOSEPH PG, MCKEE M, et al. Reducing the global burden of cardiovascular disease, part 2: prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease. Circulation Res. 2017;121(6):695-710.
[3] ZHOU B, BENTHAM J, DI CESARE M, et al. Worldwide trends in blood pressure from 1975 to 2015: a pooled analysis of 1479 population-based measurement studies with 19.1 million participants. Lancet. 2017;389(10064):37-55.
[4] THOM SM, CRUICKSHANK K, STANTON A, et al. Differential impact of blood pressure–lowering drugs on central aortic pressure and clinical outcomes. Circulation. 2006;113:1213-1225.
[5] WANG G, GROSSE SD, SCHOOLEY MW. Conducting research on the economics of hypertension to improve cardiovascular health. Am J Prev Med. 2017;53(6): S115-S117.
[6] ASSIRI GA, SHEBL NA, MAHMOUD MA, et al. What is the epidemiology of medication errors, error-related adverse events and risk factors for errors in adults managed in community care contexts? A systematic review of the international literature. BMJ Open. 2018;8(5):e019101.
[7] WHELTON PK, CAREY RM, ARONOW WS, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: executive summary: a report of the american college of cardiology/american heart association task force on clinical practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018; 71(19):2199-2269.
[8] HALLAL PC, DUMITH SC, REICHERT FF, et al. Cross-sectional and longitudinal associations between physical activity and blood pressure in adolescence: birth cohort study. J Phys Act Health. 2011;8(4):468-474.
[9] DE SOUZA VIEIRA V, DA COSTA AGUIAR S, CAMPOS MC, et al. Light-intensity physical activity and sedentary behavior are associated with blood pressure levels in adolescents. Pediatr Exerc Sci. 2024; 1(aop):1-9.
[10] GUAN T, CAO M, ZHENG C, et al. Dose-response association between physical activity and blood pressure among Chinese adults: a nationwide cross-sectional study. J Hypertens. 2024;42(2):360-370.
[11] STAMATAKIS E, GALE J, BAUMAN A, et al. Sitting time, physical activity, and risk of mortality in adults. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019; 73(16):2062-2072.
[12] DIAZ KM, SHIMBO D. Physical activity and the prevention of hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2013;15:659-668.
[13] CORNELISSEN VA, SMART NA. Exercise training for blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Heart Assoc. 2013;2(1):e004473.
[14] BÖRJESSON M, ONERUP A, LUNDQVIST S, et al. Physical activity and exercise lower blood pressure in individuals with hypertension: narrative review of 27 RCTs. Br J Sports Med. 2016;50(6):356-361.
[15] ARNETT DK, BLUMENTHAL RS, ALBERT MA, et al. 2019 ACC/AHA guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019; 74(10):1376-1414.
[16] SCHULTZ MG, CURRIE KD, HEDMAN K, et al. The identification and management of high blood pressure using exercise blood pressure: current evidence and practical guidance. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(5):2819.
[17] CLARKE SL. Hypertension in adults: initial evaluation and management. Am Fam Physician. 2023;108(4):352-359.
[18] MILLAR PJ, MCGOWAN CL, CORNELISSEN VA, et al. Evidence for the role of isometric exercise training in reducing blood pressure: potential mechanisms and future directions. Sports Med. 2014;44:345-356.
[19] EDWARDS JJ, COLEMAN DA, RITTI-DIAS RM, et al. Isometric exercise training and arterial hypertension: an updated review. Sports Med. 2024;54(6):1459-1497.
[20] EDWARDS JJ, DEENMAMODE AHP, GRIFFITHS M, et al. Exercise training and resting blood pressure: a large-scale pairwise and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Br J Sports Med. 2023;57(20):1317-1326.
[21] KELLEY GA, KELLEY KS, STAUFFER BL. Isometric exercise and inter-individual response differences on resting systolic and diastolic blood pressure in adults: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Blood Pressure. 2021;30(5):310-321.
[22] HANDFORD HJ, PARMENTER BJ, MCLEOD KA, et al. The effectiveness and safety of isometric resistance training for adults with high blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hypertens Res. 2021;44(11):1373-1384.
[23] BAFFOUR-AWUAH B, PEARSON MJ, DIEBERG G, et al. Isometric resistance training to manage hypertension: systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2023;25(4):35-49.
[24] PAGE MJ, MCKENZIE JE, BOSSUYT PM, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n71.
[25] HIGGINS JP. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Cochrane Collaboration and John Wiley & Sons Ltd. 2008.
[26] CUMPSTON M, LI T, PAGE MJ, et al. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: a new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;2019(10): ED000142.
[27] HIGGINS JPT, SAVOVIĆ J, PAGE MJ, et al. Assessing risk of bias in a randomized trial. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; 2019:205-228.
[28] DERSIMONIAN R, LAIRD N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clin Trials. 1986; 7(3):177-188.
[29] MOSTAFAEI H, GHOJAZADEH M, HAJEBRAHIMI S. Fixed-effect versus random-effects models for meta-analyses: fixed-effect models. Eur Urol Focus. 2023; 9(5):691-692.
[30] NAKAGAWA S, NOBLE DWA, SENIOR AM, et al. Meta-evaluation of meta-analysis: ten appraisal questions for biologists. BMC Biol. 2017;15:1-14.
[31] BINNEY ZO, MANSOURNIA MA. Methods matter: (mostly) avoid categorising continuous data-a practical guide. Br J Sports Med. 2024;58(5):241-243.
[32] RICO-GONZÁLEZ M, PINO-ORTEGA J, CLEMENTE F, et al. Guidelines for performing systematic reviews in sports science. Biol Sport. 2022;39(2):463-471.
[33] GORDON BDH, THOMAS EV, WARREN-FINDLOW J, et al. A comparison of blood pressure reductions following 12-weeks of isometric exercise training either in the laboratory or at home. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2018;12(11):798-808.
[34] PAGONAS N, VLATSAS S, BAUER F, et al. Aerobic versus isometric handgrip exercise in hypertension: a randomized controlled trial. J Hypertens. 2017;35(11):2199-2206.
[35] DECAUX A, EDWARDS JJ, SWIFT HT, et al. Blood pressure and cardiac autonomic adaptations to isometric exercise training: a randomized sham‐controlled study. Physiological Reports. 2022;10(2):e15112.
[36] BADDELEY-WHITE DS, WOOD CN, MCGOWAN CLM, et al. Blood pressure-lowering efficacy of a 6-week multi-modal isometric exercise intervention. Blood Pressure Monit. 2021;26(1):30-38.
[37] BADROV MB, HORTON S, MILLAR PJ, et al. Cardiovascular stress reactivity tasks successfully predict the hypotensive response of isometric handgrip training in hypertensives. Psychophysiology. 2013; 50(4):407-414.
[38] HESS NCL, CARLSON D, INDER JD, et al. Clinically meaningful blood pressure reductions with low intensity isometric handgrip exercise: a randomized trial. 2016. 2016;65(3):46146-46148.
[39] BAROSS AW, WILES JD, SWAINE IL. Double-leg isometric exercise training in older men. Open Access J Sports Med. 2013;4:33-40.
[40] BADROV MB, BARTOL CL, DIBARTOLOMEO MA, et al. Effects of isometric handgrip training dose on resting blood pressure and resistance vessel endothelial function in normotensive women. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2013;113:2091-2100.
[41] CORREIA A, OLIVEIRA PL, FARAH BQ, et al. Effects of isometric handgrip training in patients with peripheral artery disease: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020;9(4):e013596.
[42] PALMEIRA AC, FARAH BQ, SILVA GO, et al. Effects of isometric handgrip training on blood pressure among hypertensive patients seen within public primary healthcare: a randomized controlled trial. Sao Paulo Med J. 2021;139(6):648-656.
[43] NEMOTO Y, SATOH T, TAKAHASHI T, et al. Effects of isometric handgrip training on home blood pressure measurements in hypertensive patients: a randomized crossover study. Intern Med. 2021;60(14): 2181-2188.
[44] BAROSS AW, WILES JD, SWAINE IL. Effects of the intensity of leg isometric training on the vasculature of trained and untrained limbs and resting blood pressure in middle‐aged men. Int J Vasc Med. 2012;2012(1):964697.
[45] WILES JD, SANTER E, REES-ROBERTS M, et al. Feasibility study to assess the delivery of a novel isometric exercise intervention for people with high blood pressure in a healthcare setting. medRxiv. 2024;2024:24302961.
[46] WILES JD, GOLDING N, COLEMAN D. Home-based isometric exercise training induced reductions in resting blood pressure. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2017;117:83-93.
[47] PUNIA S, KULANDAIVELAN S. Home‐based isometric handgrip training on RBP in hypertensive adults-Partial preliminary findings from RCT. Physiotherapy Res Int. 2020;25(1):e1806.
[48] OKAMOTO T, HASHIMOTO Y, KOBAYASHI R. Isometric handgrip training reduces blood pressure and wave reflections in East Asian, non-medicated, middle-aged and older adults: a randomized control trial. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2020;32:1485-1491.
[49] TAYLOR AC, MCCARTNEY N, KAMATH MV, et al. Isometric training lowers resting blood pressure and modulates autonomic control. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2003;35(2):251-256.
[50] BADDELEY-WHITE DS, MCGOWAN CL, HOWDEN R, et al. Blood pressure lowering effects of a novel isometric exercise device following a 4-week isometric handgrip intervention. Open Access J Sports Med. 2019;10:89-98.
[51] TAYLOR KA, WILES JD, COLEMAN DA, et al. Neurohumoral and ambulatory haemodynamic adaptations following isometric exercise training in unmedicated hypertensive patients. J Hypertens. 2019; 37(4):827-836.
[52] O’DRISCOLL JM, EDWARDS JJ, COLEMAN DA, et al. One year of isometric exercise training for blood pressure management in men: a prospective randomized controlled study. J Hypertens. 2022;40(12):2406-2412.
[53] BAROSS AW, HODGSON DA, PADFIELD SL, et al. Reductions in resting blood pressure in young adults when isometric exercise is performed while walking. J Sports Med. 2017;2017(1):7123834.
[54] COHEN DD, AROCA-MARTINEZ G, CARREÑO-ROBAYO J, et al. Reductions in systolic blood pressure achieved by hypertensives with three isometric training sessions per week are maintained with a single session per week. J Clin Hypertens. 2023;25(4):380-387.
[55] EDWARDS JJ, JALALUDEEN N, BEQIRI A, et al. The effect of isometric exercise training on arterial stiffness: a randomized crossover controlled study. Physiol Rep. 2023;11(10):e15690.
[56] HOWDEN R, LIGHTFOOT JT, BROWN SJ, et al. The effects of isometric exercise training on resting blood pressure and orthostatic tolerance in humans. Exp Physiol. 2002; 87(4):507-515.
[57] WILES JD, COLEMAN DA, SWAINE IL. The effects of performing isometric training at two exercise intensities in healthy young males. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010;108:419-428.
[58] CARLSON DJ, INDER J, PALANISAMY SKA, et al. The efficacy of isometric resistance training utilizing handgrip exercise for blood pressure management: a randomized trial. Medicine. 2016;95(52):e5791.
[59] LEA J WD, O’DRISCOLL JM, WILES JD. The implementation of a home-based isometric wall squat intervention using ratings of perceived exertion to select and control exercise intensity: a pilot study in normotensive and pre-hypertensive adults. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2024;124(1):281-293.
[60] CAHU RODRIGUES SL, FARAH BQ, SILVA G, et al. Vascular effects of isometric handgrip training in hypertensives. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2020;42(1):24-30.
[61] LOPEZ-VALENCIANO A, RUIZ-PEREZ I, AYALA F, et al. Updated systematic review and meta-analysis on the role of isometric resistance training for resting blood pressure management in adults. J Hypertens. 2019;37(7):1320-1333.
[62] EDWARDS J, DE CAUX A, DONALDSON J, et al. Isometric exercise versus high-intensity interval training for the management of blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2022; 56(9):506-514.
[63] CARLSON DJ, DIEBERG G, HESS NC, et al. Isometric exercise training for blood pressure management: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mayo Clin Proc. 2014;89(3):327-334.
[64] EDWARDS JJ, WILES J, O’DRISCOLL J. Mechanisms for blood pressure reduction following isometric exercise training: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hypertens. 2022;40(11):2299-2306.
[65] GLASER S, FRIEDRICH N, KOCH B, et al. Exercise blood pressure and heart rate reference values. Heart Lung Circ. 2013; 22(8):661-667.
[66] DEVEREUX GR, WILES JD, HOWDEN R. Immediate post-isometric exercise cardiovascular responses are associated with training-induced resting systolic blood pressure reductions. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2015;115:327-333.
[67] BETZ HH, EISENMANN JC, LAURSON KR, et al. Physical activity, BMI, and blood pressure in US youth: NHANES 2003-2006. Pediatr Exerc Sci. 2018;30(3):418-425.
[68] DE MEDEIROS REGO ML, CABRAL DAR, DA COSTA KG, et al. Systolic blood pressure mediates the association between body mass index and inhibitory control in children. Biol Psychol. 2020;157:107988.
[69] CONEGLIAN JC, BARCELOS GT, BANDEIRA A CN, et al. Acute blood pressure response to different types of isometric exercise: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023;24(2):60.
[70] DE OLIVEIRA PC, LEHNEN AM, WACLAWOWSKY G. Effect of isometric exercise on blood pressure in prehypertensive and hypertensive individuals: protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Syst Rev. 2022;11(1):100.
[71] DEVEREUX GR, WILES JD, SWAINE I. Markers of isometric training intensity and reductions in resting blood pressure. J Sports Sci. 2011;29(7):715-724.
[72] ENOKA RM, DUCHAITEAU J. Muscle fatigue: what, why and how it influences muscle function. J Physiol. 2008;586(1):11-23.
[73] SWIFT HT, O’DRISCOLL JM, COLEMAN DD, et al. Acute cardiac autonomic and haemodynamic responses to leg and arm isometric exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2022;122(4):975-985.
[74] ALMEIDA JPAS, BESSA M, LOPES LTP, et al. Isometric handgrip exercise training reduces resting systolic blood pressure but does not interfere with diastolic blood pressure and heart rate variability in hypertensive subjects: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Hypertens Res. 2021;44(9):1205-1212.
[75] ETTEHAD D, EMDIN CA, KIRAN A, et al. Blood pressure lowering for prevention of cardiovascular disease and death: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2016;387(10022):957-967.
[76] STRANDBERG TE, PITKÄLÄ K. What is the most important component of blood pressure: systolic, diastolic or pulse pressure? Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2003;12(3):293-297.
[77] TIAN Z, VOLLMER BARBOSA C, LANG H, et al. Efficacy of pharmacological and interventional treatment for resistant hypertension: a network meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Res. 2024;120(1):108-119.
[78] FLACK JM, ADEKOLA B. Blood pressure and the new ACC/AHA hypertension guidelines. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2020;30(3):160-164.
|