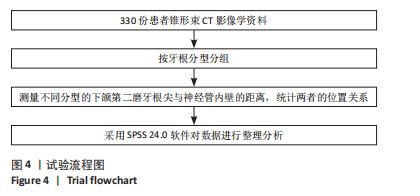
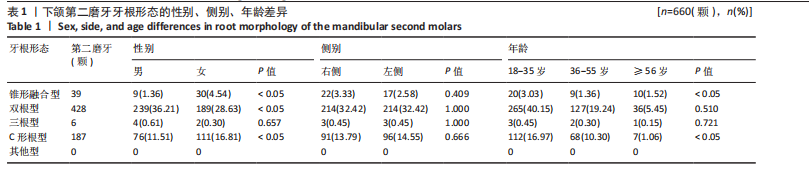
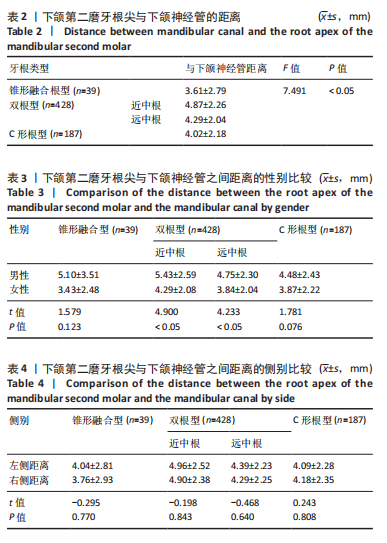
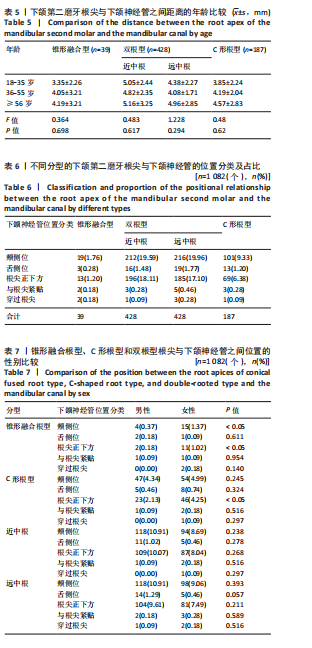
[1] 蓝炎涛, 张丽霞.下颌第三磨牙阻生类型与第二磨牙远中邻面龋坏的相关性研究[J]. 现代医院,2021,21(1):159-161+164.
[2] DEEPA K, UJJWAL K, ARCHANA M, et al. Association of Prevalence of Dental Caries in Mandibular Second Molar with Impacted Third Molar.J Nepal Health Res Counc. 2021;19(2):259-263.
[3] 冯璐, 张岚, 黄定明. 中国西部地区人群下颌后牙与下牙槽神经管距离关系的三维研究[C].中华口腔医学会牙体牙髓病学专业委员会第十四次全国牙体牙髓病学学术大会论文汇编,2022.
[4] Kovisto T, Ahmad M, Bowles WR. Proximity of the Mandibular Canal to the Tooth Apex. J Endod. 2011;37(3):311-315.
[5] CHONG BS, QUINN A, PAWAR RR, et al. The anatomical relationship between the roots of mandibular second molars and the inferior alveolar nerve. Int Endod J. 2015;48(6):549-555.
[6] PATEL R, CLARKSON E. Implant surgery update for the general practitioner: dealing with common postimplant surgery complications. Dent Clin North Am. 2021;65(1):125-134.
[7] CEBRIÁN F, PEÑA-CARDELLES JF, AKHONDI S, et al. Inferior alveolar nerve damage related to dental implant placement. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2025;7:27125.
[8] 庞显卓, 薛明. 下颌后牙区显微根尖手术中颏神经的管理[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2023,16(5):526-529.
[9] BADR O, TALAL Z. Mental Nerve Anterior Loop Detection in Panoramic and Cone Beam Computed Tomography Radiograph for Safe Dental Implant Placement.Cureus.2022;14(10): e30687-e30687.
[10] MARYAM J, SAEED R, FARNAZ J, et al. Anatomic Features of C-shaped Mandibular Second Molars in a Selected Iranian Population Using CBCT.Iran Endod J. 2018;13(1):120-125.
[11] ADIBI S, PAKNAHAD M. Comparison of cone-beam computed tomography and osteometric examination in preoperativeassessment of the proximity of the mandibular canal to the apices of the teeth. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;55(3):246-250.
[12] ALMANSOUR MI, AL-ZUBAIDI SM, ENIZY AS, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of root and root canal morphology of mandibular second molars in a Saudi subpopulation evaluated by cone-beam computed tomography. BMC Oral Health. 2022;22(1):267.
[13] 吴康汝, 吴新智,张振标.人体测量方法[M].北京:科学出版社, 1984:12-13.
[14] MICHAŁ P, ALEKSANDRA P, KRZYSZTOF S, et al. The influence of age, sex, and tooth type on the anatomical relationship between tooth roots and the mandibular canal. Imaging Sci Dent. 2021;51(4):373-382.
[15] 谢霓, 王九龙, 朱友家. 下颌第二磨牙牙根及根管形态学研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2015,31(7):415-417.
[16] 邵俊杰, 倪洁丽, 李琥, 等. 下颌神经管结构、位置与分支的CBCT影像研究[J]. 口腔生物医学,2018,9(3):148-151.
[17] SABER SM, SEOUD MAE, SADAT SMAE, et al. Root and canal morphology of mandibular second molars in an Egyptian subpopulation: a cone-beam computed tomography study. BMC Oral Health. 2023;23(1):217.
[18] ZHANG R, WANG H, TIAN YY, et al. Use of cone-beam computed tomography to evaluate root and canal morphology of mandibular molars in Chinese individuals. Int Endod J. 2011;44(11):990-999.
[19] SENAN EM, MADFA AA, ALHADAINY HA. Root and Canal Configuration of Mandibular First Molars in a Yemeni Population: A Cone-beam Computed Tomography. Eur Endod J. 2020;5(1):10-17.
[20] ANDRES T, REINHILDE J, PAUL L, et al.Characterization of mandibular molar root and canal morphology using cone beam computed tomography and its variability in Belgian and Chilean population samples. Imaging Sci Dent. 2015;45(2):95-101.
[21] YANG L, HAN J, WANG Q, et al. Variations of root and canal morphology of mandibular second molars in Chinese individuals:a cone-beam computed tomography study. BMC Oral Health. 2022;22(1): 274.
[22] 袁曦玉, 孟凡琦, 马丽, 等. 维吾尔族成人下颌第二磨牙牙根及根管形态的CBCT研究[J]. 口腔颌面修复学杂志,2023,24(3):199-205.
[23] GUO Q, WANG Q, YANG Y, et al. Root and root canal morphology of mandibular second permanent molars in the Gansu province population: A CBCT study. Aust Endod J. 2023:49 Suppl 1:27-32.
[24] 黎祺, 黄少宏. 岭南地区广府民系人群下颌第二恒磨牙牙根和根管形态的锥形束CT研究[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志,2019,46(6):640-649.
[25] SRIVASTAVA S, ALHARBI HM, ALHARBI AS, et al. Assessment of the Proximity of the Inferior Alveolar Canal with the Mandibular Root Apices and Cortical Plates—A Retrospective Cone Beam Computed Tomographic Analysis.J Pers Med. 2022;12(11):1784.
[26] SHOKRY SM, ALSHAIB SA, AL MOHAIMEED ZZ, et al. Assessment of the Inferior Alveolar Nerve Canal Course Among Saudis by Cone Beam Computed Tomography (Pilot Study).J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2019;18(3):452-458.
[27] 杨偲偲, 程波, 尹苗, 等. 下颌第一、第二磨牙与神经管相对位置的CBCT影像分析[J]. 口腔医学研究,2024,40(9):810-815.
[28] BÜRKLEIN S, GRUND C, SCHÄFER E. Relationship between Root Apices and the Mandibular Canal: A Cone-beam Computed Tomographic Analysis in a German Population. J Endod. 2015;41(10):1696-1700.
[29] KOIVISTO T, CHIONA D, MILROY LL, et al. Mandibular Canal Location: Cone-beam Computed Tomography Examination. J Endod. 2016;42(7):1018-1021.
[30] DAGER MM, MCNAMARA JA, BACCETTI T, et al. Aging in the craniofacial complex. Angle Orthod. 2008;78(3):440-444.
[31] 高璇. 下颌第二磨牙根尖与下颌管间距离及相关因素的研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2022.
[32] CASTRO R, GUIVARC’H M, FOLETTI JM, et al. Endodontic-related inferior alveolar nerve injuries: A review and a therapeutic flow chart.J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;119(5):412-418.
[33] 高璇, 李霞. 牙髓相关性下牙槽神经损伤的原因及诊治研究进展[J]. 山东医药,2022,62(24):98-101.
[34] MATTHIAS P, ANSELM P. Permanent mimic musculature and nerve damage caused by sodium hypochlorite: a case report. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008;106(3):e80-83.
[35] BERK KM, ECEM DG. Inferior alveolar nerve injury due to the extrusion of calcium hydroxide during endodontic treatment: A case report.Aust Endod J. 2022;48(2):342-346.
[36] LIU H, LI Y, SHEN Y. Persistent paresthesia of inferior alveolar nerve after accidental extrusion of calcium hydroxide paste containing iodoform into the mandibular canal.J Dent Sci. 2024;19(1):720-721.
[37] ALMASLAMANI M, ALHASSAWI S, PRASAD P, et al. Diagnosis and Management of Inferior Alveolar Nerve Injury Caused by Calcium Hydroxide Extrusion during Root Canal Treatment: Case Report. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024;16(Suppl 5):S4900-S4904.
[38] 唐蓓, 赵文俊, 王虎, 等. 根管超填导致下牙槽神经损伤2例[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2020,47(3):293-296.
[39] 廖洪林, 方仲瀚, 张艳艳, 等.牙种植术后三叉神经创伤性神经病理性疼痛的诊断与防治[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志,2023,50(6):729-738.
[40] TURKYILMAZ I. Persistent numbness of the lower lip and chin due to inferior alveolar nerve injury after implant placement: A clinical report. Prim Dent J. 2024;13(4):66-68.
[41] 蔡锋, 高文鼎, 程志刚. 种植体损伤下牙槽神经1例及文献回顾[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2024,40(2):117-118.
[42] NAVOT G, EYAL R, LARS B, et al. Medico-legal aspects of altered sensation following endodontic treatment: a retrospective case series.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011;112(1):126-131.
[43] 禹雯怡, 余海波, 陈娇, 等. 根管治疗相关的下牙槽神经损伤及治疗流程研究进展[J]. 临床口腔医学杂志,2024,40(4):248-250.
[44] 宋海龙, 许东亮. 基于反应范围模型探讨牙列缺损种植治疗患者神经损伤的影响因素[J].罕少疾病杂志,2025,32(5):49-52.
[45] 刘云通, 刘畅, 高丽钞, 等. 术后下牙槽神经功能障碍的研究进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志,2023,50(4):479-484.
[46] DE ABREU JM, NUNES T, ALMIRO PA,et al. Health-Related Quality of Life with Iatrogenic Inferior Alveolar Nerve Injuries Treated with Photobiomodulation: A Comparative Study. J Clin Med. 2024;13(23):7237.
[47] 谈松, 胡小洪. 高压氧治疗在牙槽神经损伤中的应用效果[C]第六届上海国际护理大会论文汇编(下),2024:133.
[48] 祝颂松, 王旭东, 杨学文,等. 下颌支矢状骨劈开术并发症防治的专家共识[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志,2022,40(3):247-254.
[49] ALHARBI G, RAO JKD, ALNAIM T,et al. Efficacy of low-level laser therapy and microsurgery on neurosensory recovery following inferior alveolar and lingual nerve injuries: A systematic review. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2024;14(5):631-637.
|