[1] 王奕璁,姜保国. 骨与关节损伤[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2014:866.
[2] 廖怀章,姚共和.经皮多针阶梯形排列固定治疗不稳定型尺桡骨干骨折疗效观察[J].中医正骨,2008,20(3):7-9+11.
[3] MODE BR, KELLAM JF, FOSTER PD, et al. Immediate internal fixation of open fractures of the diaphysis of the forearm. J Bone Joint Surg. 1986;68:1008-1017.
[4] 李庭,孙志坚,姚东晨,等.成人桡骨远端骨折诊断与治疗循证指南(2024)[J].骨科临床与研究杂志,2024,9(5):257-274.
[5] LIU Z, YANG J, CHEN Y, et al. P311 facilitates the angiogenesis and wound healing function of MSCs by increasing VEGF production. Front Immunol. 2022;13:821932.
[6] 熊恒恒,聂伟志.钛制弹性钉和锁定接骨板固定锁骨中段骨折的有限元分析[J].骨科,2024,15(6):524-528.
[7] 普布顿珠,扎西平措,旦增欧珠,等.高海拔地区应用克氏针髓内固定治疗儿童尺桡骨干双骨折的临床疗效[J].中国骨伤,2023, 36(7):619-622.
[8] 任建国,周杰,周超云,等.弹性髓内钉微创闭合复位内固定治疗小儿尺桡骨干骨折76例[J].实用手外科杂志,2023,37(2): 179-180+229.
[9] 孙滨,李琳琳,孙卫强,等.闭合复位经皮穿针内固定治疗尺桡骨远端不稳定性骨折[J].中医正骨,2024,36(12):70-74.
[10] 谢晓飞.髓内针与接骨板治疗成人尺桡骨干骨折的临床疗效分析[D].大连:大连医科大学,2018.
[11] 刘振宇,高化,李亚东,等.髓内钉内固定治疗尺桡骨骨干骨折的并发症分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019,34(11): 1219-1220.
[12] SHARMA A. A study of titanium elastic nailing in forearm fractures in elderly patients. J Orthop Spine Trauma. 2024;10(2):82-86.
[13] MENA A, WOLLSTEIN R, YANG J. Development of a finite element model of the human wrist joint with radial and ulnar axial force distribution and radiocarpal contact validation. J Biomech Eng. 2025; 147(3):031006.
[14] KIM YW, LEE SK, AN YS. Distal blocking screw augmentation in ulnar intramedullary nail fixation of adult forearm diaphyseal fractures. J Orthop Surg. 2024;32(3):10225536241295520.
[15] 夏长江, 袁志峰, 方宁. 基于尺桡骨三维有限元模型分析桡骨远端骨折的生物力学特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(6):893-897.
[16] LEWIS GS, MISCHLER D, WEE H, et al. Finite element analysis of fracture fixation. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2021;19(4):403-416.
[17] 李宁,杨涵,黄秋悦,等.3D打印钛合金个性化骨盆假体静态分析[J].医用生物力学,2017,32(6):487-493.
[18] JÌRA J, JÌROVÁ J. Computational modelling of stress state during hand treatment. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng. 2020;2:431-438.
[19] HOPF JC, MEHLER D, NOWAK TE, et al. Nailing of diaphyseal ulna fractures in adults-biomechanical evaluation of a novel implant in comparison with locked plating. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1): 158-164.
[20] ZHANG Y, SHAO Q, YANG C, et al. Finite element analysis of different locking plate fixation methods for the treatment of ulnar head fracture. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):191-195.
[21] PRAMUDITA JA, HIROKI W, YODA T, et al. Variations in strain distribution at distal radius under different loading conditions. Life. 2022;12(5):74.
[22] 谢强. 前侧钢板结合后外侧螺钉踝关节融合的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(35):5697-5702.
[23] 陈国富,梁军波,张传毅,等.克氏针撑开辅助复位弹性钉固定治疗儿童难复性桡骨下1/3骨折[J].中国骨伤,2022,35(8):752-756.
[24] BREKELMANS WAM, POORT HW, SLOOFF T. A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts. Acta Orthop Scand. 1972; 43(5):301-317.
[25] PENG Y, DU X, HUANG L, et al. Optimizing bone cement stiffness for vertebroplasty through biomechanical effects analysis based on patient-specific three-dimensional finite element modeling. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2018;56(11):2137-2150.
[26] LONG Z, ZHOU J, XIONG L, et al. Finite element study on three osteotomy methods for treating thoracolumbar osteoporotic fracture vertebral collapse complicated with neurological dysfunction. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024;103(7):e36987.
[27] BELYTSCHKO T, KULAK RF, SCHULTZ AB, et al. Finite element stress analysis of an intervertebral disc. J Biomech. 1974;7(3):277-285.
[28] 胡家栋. 骨科生物力学有限元分析头10年工作综述[J]. 力学进展, 1986(1):98-34.
[29] LIU J, MUSTAFA AK, LEES VC, et al. Analysis and validation of a 3D finite element model for human forearm fracture. Int J Numer Methods Biomed Eng. 2022;38(9):e3617
[30] LIANG C, JIANG F, KAWAGUCHI D, et al. A Biomechanical Simulation of Forearm Flexion Using the Finite Element Approach. Bioengineering. 2023; 11(1): 23.
[31] LEVYTSKYI AF, TERPYLOVSKYI YR, YARESKO OV. Biomechanical features of single-bone osteosynthesis of diaphyseal fractures in children by the titanium elastic nails. World Med Biol. 2022;18(80):103-108.
[32] 王刚,高化,刘振宇,等.闭合复位弹性髓内钉内固定治疗成人桡骨干骨折疗效观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2025,40(3):322-324.
[33] 文玉伟,朱丹江,王强,等.弹性髓内钉治疗学龄前儿童股骨干骨折的疗效及预后分析[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2023,12(11):806-811.
[34] 郭月超,张玉舰,王哲,等. 弹性髓内针治疗儿童桡骨颈骨折的方案选择[J].河北医药,2019,41(9):1391-1393,1397.
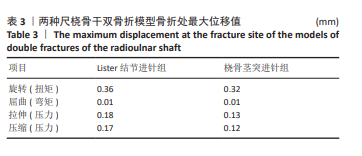
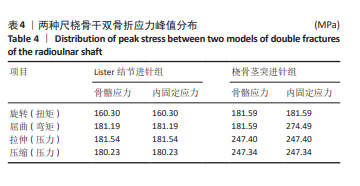
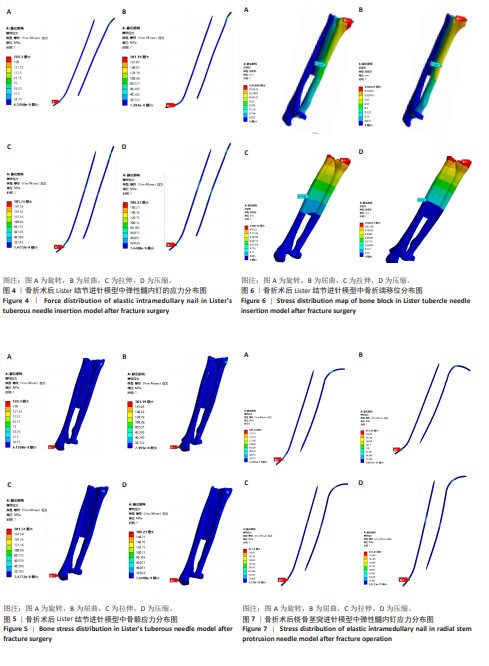
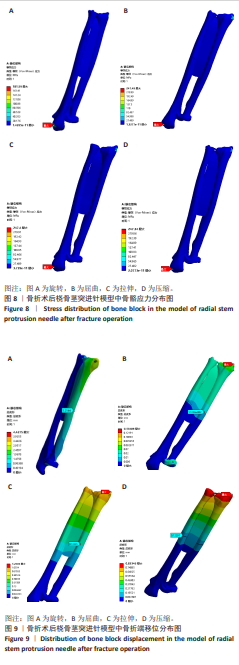
[35] 廖怀章,刘绪银,孙燕.经Lister结节穿针多针阶梯形排列髓内弹性固定的3D有限元分析[J].中医正骨,2009,21(11):11-16.
[36] 储涛,孙军.儿童尺桡骨骨干骨折弹性髓内钉闭合复位内固定中手术时间对预后的影响分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021, 36(1):90-91.
[37] 王浩,何红英,张建政,等.髓内钉治疗成人前臂双骨折的疗效分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2023,29(7):631-634.
[38] 王刚,高化,刘振宇,等.闭合复位弹性髓内钉内固定治疗成人桡骨干骨折疗效观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2025,40(3):322-324.
[39] 李忠贤,姬宇程,翁羽洁,等.蒙医整骨治疗尺桡骨骨折力学原理的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(21):3293-3298.
[40] 杨振,张恩水,曾昱源,等.髓内钉和钢板3种固定组合治疗成人前臂双骨干骨折生物力学三维有限元分析[J].山东医药,2022, 62(36):26-31. |