中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (13): 3435-3445.doi: 10.12307/2026.143
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
间充质干细胞及外泌体治疗支气管肺发育不良
黄 佳1,2,严清艳1,2,杨 星1,2,朱晓萍1,3,罗红芳1,2
- 1贵州医科大学临床医学院儿科学教研室,贵州省贵阳市 550004;2贵州医科大学第二附属医院儿科,贵州省凯里市 556000;3贵州医科大学附属医院儿科,贵州省贵阳市 550004
-
接受日期:2025-08-05出版日期:2026-05-08发布日期:2025-12-26 -
通讯作者:罗红芳,主任医师,硕士研究生导师,贵州医科大学临床医学院儿科学教研室,贵州省贵阳市 550004;贵州医科大学第二附属医院儿科,贵州省凯里市 556000; 共同通讯作者:朱晓萍,主任医师,博士研究生导师,贵州医科大学临床医学院儿科学教研室,贵州省贵阳市 550004;贵州医科大学附属医院儿科,贵州省贵阳市 550004 -
作者简介:黄佳,女,1999年生,硕士,主要从事儿童呼吸疾病的基础与临床研究。 -
基金资助:贵州省科技厅社会发展攻关项目(黔科合支撑[2020]4Y124号),项目负责人:朱晓萍
Mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes in treatment of bronchopulmonary dysplasia
Huang Jia1, 2, Yan Qingyan1, 2, Yang Xing1, 2, Zhu Xiaoping1, 3, Luo Hongfang1, 2
- 1Department of Pediatrics, School of Clinical Medicine, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Pediatrics, Second Affiliated Hospital, Guizhou Medical University, Kaili 556000, Guizhou Province, China; 3Department of Pediatrics, Affiliated Hospital, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Accepted:2025-08-05Online:2026-05-08Published:2025-12-26 -
Contact:Luo Hongfang, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Pediatrics, School of Clinical Medicine, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; Department of Pediatrics, Second Affiliated Hospital, Guizhou Medical University, Kaili 556000, Guizhou Province, China Co-corresponding author: Zhu Xiaoping, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Pediatrics, School of Clinical Medicine, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; Department of Pediatrics, Affiliated Hospital, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Huang Jia, MS, Department of Pediatrics, School of Clinical Medicine, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; Department of Pediatrics, Second Affiliated Hospital, Guizhou Medical University, Kaili 556000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Social Development Key Project of Guizhou Provincial Department of Science and Technology, No. [2020]4Y124 (to ZXP)
摘要:
文题释义:
间充质干细胞:是一类具有多向分化潜能的成体干细胞,能在特定条件下分化为多种细胞类型,如成骨细胞、软骨细胞、肺泡上皮细胞、血管内皮细胞等,还能分泌多种生长因子、细胞因子和外泌体,在组织损伤修复中具有重要的调节作用。支气管肺发育不良:是一种以肺泡发育受限、肺组织结构简化、肺血管发育不良以及肺功能异常为主要表现的新生儿肺部疾病。
摘要
背景:间充质干细胞及其外泌体可通过抗氧化、抗炎、促进血管新生和抑制肺纤维化等机制,有效缓解肺损伤,促进肺组织修复和功能重建,从而在一定程度上改善支气管肺发育不良的病程和预后。
目的:综述间充质干细胞及其外泌体在支气管肺发育不良中的研究现状。
方法:由第一作者检索中国知网、PubMed数据库,文献检索时限为各数据库建库至2025年3月,以“间充质干细胞,外泌体,支气管肺发育不良,纳米水凝胶,作用机制”为中文检索词,以“mesenchymal stem cells, exosomes,bronchopulmonary dysplasia,nanohydrogels,mechanism of action”为英文检索词,最终选取符合标准的85篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:①间充质干细胞及其外泌体可介导多种治疗机制,包括缓解氧化应激反应、促进血管生成与血管修复、抑制肺纤维化进程、抗细胞凋亡、调节细胞自噬、参与免疫调节、炎症反应抑制等,在支气管肺发育不良防治中展现出良好的应用前景,有望成为该病的重要治疗策略之一。②在传统给药方式下,间充质干细胞及其外泌体难以在肺部实现长期滞留,从而限制了对受损组织的持续修复能力。近年来,水凝胶等工程化生物材料的引入为此问题提供了新的解决思路。水凝胶不仅能够实现外泌体在肺组织中的缓释释放,还可在一定程度上使其免受肺内炎症微环境的影响,从而提升其生物稳定性和治疗效能。因此,基于水凝胶的干细胞及外泌体递送系统有望成为未来支气管肺发育不良治疗研究的热点方向。
中图分类号:
引用本文
黄 佳, 严清艳, 杨 星, 朱晓萍, 罗红芳. 间充质干细胞及外泌体治疗支气管肺发育不良[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(13): 3435-3445.
Huang Jia, Yan Qingyan, Yang Xing, Zhu Xiaoping, Luo Hongfang. Mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes in treatment of bronchopulmonary dysplasia[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(13): 3435-3445.
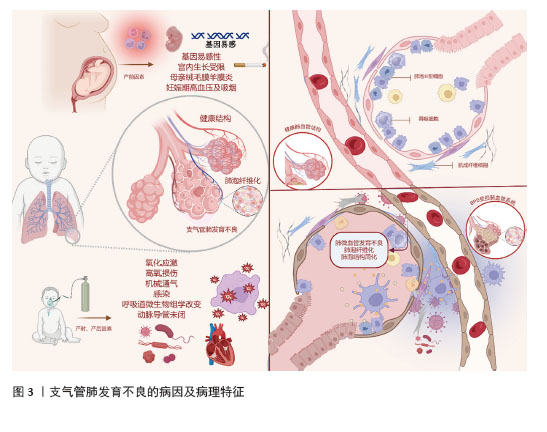
2.1 支气管肺发育不良概述 支气管肺发育不良最早由NORTHWAY等[3]于1967年提出,是一种复杂的多因素引起的肺损伤综合征。支气管肺发育不良的发生与产前、产时和产后3个阶段的多种因素密切相关,见图3。产前阶段的主要影响因素包括遗传易感性、宫内发育受限、母体绒毛膜羊膜炎、妊娠期高血压以及孕妇吸烟等[4];产时因素主要是胎龄和出生体质量,研究显示,早产儿胎龄越小、体质量越轻,发生支气管肺发育不良的概率越高,因此这两项指标被广泛认为是最具预测价值的危险因素[5];产后阶段则受氧化应激、高浓氧暴露、机械通气、感染、呼吸道菌群失调和动脉导管未闭等因素影响,这些因素容易引起肺部炎症、氧化应激损伤及实质纤维化,从而促使支气管肺发育不良的发生。支气管肺发育不良的主要特征为肺生长停滞、肺泡结构简化、血管发育受损和肺功能异常,对于肺仍处于肺管期向囊泡期过渡阶段的早产儿而言,这些病理改变会导致气体交换障碍,并引发严重的呼吸系统疾病。一项随访研究发现,支气管肺发育不良患儿不仅在婴儿期肺功能受损,哮喘患病率增加,同时还会对儿童期乃至成年期的肺功能产生深远影响[6]。据统计,在胎龄为22-24周的新生儿中,近80%被诊断患有支气管肺发育不良[7]。该疾病在早期死亡率较高,晚期则可能导致呼吸系统、循环系统乃至神经系统的长期并发症,严重影响患儿的生存预后和生活质量[8]。目前,针对支气管肺发育不良的治疗手段较为有限,常用药物包括外源性肺泡表面活性物质、抗氧化剂、糖皮质激素、抗氧化剂、维生素A、咖啡因、大环内酯类抗生素、利尿剂等[9]。然而,由于支气管肺发育不良牵涉复杂的病理生理机制,目前的治疗方案尚不能够完全预防或阻止肺损伤的进展,间充质干细胞作为未分化的基础细胞,能够在特定条件下诱导为修复受损或破坏组织所需的特定细胞类型,并具备自我更新能力[10]。在支气管肺发育不良的治疗中,间充质干细胞显示出了巨大的潜力。
2.2 间充质干细胞及其外泌体在支气管肺发育不良中的潜在治疗作用
2.2.1 抗氧化应激 支气管肺发育不良是一种由出生时过早暴露于高氧环境所诱发的疾病。尽管胎儿的肺通常在子宫内低氧环境中发育,但对于极低出生体质量的婴儿而言,长期接受机械通气,或仅仅因暴露于相对较高的环境氧浓度,再加之肺部内源性抗氧化系统尚未发育成熟,使其更容易受到氧化应激损伤,从而加重支气管肺发育不良的发生和发展[11]。在肺间质中,脂肪成纤维细胞通过提供中性脂质,支持Ⅱ型肺泡上皮细胞合成磷脂,这一过程对未成熟胎儿肺部表面活性剂的合成至关重要。然而,氧化应激可诱导脂肪成纤维细胞向肌成纤维细胞转分化,导致Ⅱ型肺泡上皮细胞合成和分泌表面活性剂的能力下降[12]。此外,氧化应激还会诱导Ⅱ型肺泡上皮细胞过度凋亡并抑制其增殖,进一步阻碍肺泡上皮损伤的修复,影响肺泡的结构和功能恢复,从而加剧支气管肺发育不良的病理进程[13]。
氧气含量已被证明能够调节多种间充质干细胞的生长和分化。然而,在高氧暴露和机械通气条件下,肺部常驻间充质干细胞的功能会受到抑制。来自支气管肺发育不良新生儿气管抽吸样本的肺间充质干细胞显示,血小板衍生生长因子受体α和血管内皮生长因子等与肺泡发育及修复相关的生长因子表达水平明显下降[14-15]。相比之下,在缺氧环境下培养的骨髓间充质干细胞表现出更高的存活率、集落形成能力和分化潜力[16-18]。这表明氧化应激可能导致婴儿肺组织内常驻干细胞减少或功能障碍,从而影响肺泡的修复和再生。基于此,补充外源性干细胞及其衍生物成为支气管肺发育不良治疗的潜在策略。研究发现,与正常胎肺间充质干细胞相比,在缺氧条件下培养的人脐带间充质干细胞能够分泌相似水平的肺保护蛋白和生长因子,甚至在某些情况下其分泌水平更高。因此,移植人脐带间充质干细胞有望用于对抗高氧暴露对常驻肺细胞的损害[16]。然而,由于人脐带间充质干细胞未曾经历高氧环境,其在移植到接受高氧通气的肺部之后是否会遭受与常驻肺间充质干细胞相同的氧化应激损伤,目前尚缺乏明确的研究结论。
线粒体在细胞能量代谢和氧化应激中发挥核心作用,其结构、动力学、DNA完整性以及氧化代谢功能与支气管肺发育不良的发生密切相关[12]。研究表明,高氧暴露会导致线粒体损伤,从而成为肺结构简化和支气管肺发育不良发生的重要致病因素[19]。高氧环境不仅抑制肺线粒体的生物能量功能,还损害肺损伤动物模型的肺泡发育[20]。线粒体DNA对氧化损伤极为敏感,高氧诱导的线粒体DNA损伤会抑制大鼠肺外植体的分支形态发生,从而影响肺泡成熟。在早产儿中,血管内皮细胞的线粒体生物能量功能障碍、活性氧生成紊乱以及线粒体DNA损伤会破坏正常的肺部发育[21]。因此,线粒体功能不仅可能影响支气管肺发育不良的发生发展,还可作为支气管肺发育不良早产儿长期预后和死亡率的重要预测因子[22]。针对线粒体损伤的修复策略已成为支气管肺发育不良研究的重要方向。间充质干细胞可通过外泌体主动分泌线粒体,并将其转移至受体细胞,从而实现线粒体功能的恢复。这一机制为受损肺细胞提供健康线粒体,促进细胞功能修复,并改善肺组织的生理状态[23-24]。研究表明,在急性呼吸窘迫综合征动物模型中,间充质干细胞衍生外泌体可通过线粒体转移改善损伤肺组织的肺泡-毛细血管屏障功能[25]。此外,骨髓间充质干细胞可依赖间隙连接蛋白43介导的肺泡附着及线粒体转移,恢复肺泡的生物能量学平衡,从而减轻脂多糖诱导的急性肺损伤[26]。同时,间充质干细胞还能通过旁分泌信号分子及外泌体促进受损肺细胞的线粒体复制,进一步增强肺组织的修复能力[23-24]。
2.2.2 促进血管生成和血管修复 在支气管肺发育不良患儿中,血管生成受抑制被认为是导致肺泡简化的主要机制,肺微血管发育不良使毛细血管密度降低,血液循环横截面积减小,最后导致气体交换表面积减小。因此,促进肺血管生成和修复血管损伤是缓解支气管肺发育不良的关键。血管内皮生长因子是一种高度特异性的血管内皮细胞有丝分裂原,是血管生成的中心调节因子。血管内皮生长因子还能促进Ⅱ型肺泡上皮细胞的生长和分化,而这些细胞正是合成和分泌肺表面活性物质的关键细胞类型。因此,血管内皮生长因子在调节血管生成和肺泡发育中发挥重要作用[27]。间充质干细胞及其外泌体可通过调控血管内皮生长因子表达参与血管损伤的修复过程。ZHANG等[28]发现,来自人脐带间充质干细胞的外泌体可激活磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白途径,通过上调缺氧诱导因子1α(一种已知的血管内皮生长因子合成调节因子)来增强血管内皮生长因子的表达,促进血管生成。值得注意的是,联合应用超氧化物歧化酶拟似剂四甲基哌啶与外泌体的治疗策略,能够进一步增强上述促血管生成和修复的效果[29]。CHOU等[30]通过动物实验发现,在支气管肺发育不良大鼠模型中,连续每日经气管给予肺表面活性剂联合人脐带间充质干细胞可显著上调血管内皮生长因子和血小板衍生生长因子受体蛋白的表达水平,缓解高氧诱导下的肺泡形成障碍及血管生成受损。值得注意的是,较高剂量的人脐带间充质干细胞相较于低剂量更有效地增强了治疗效果,表明间充质干细胞对修复效果具有剂量依赖性,间充质干细胞联合治疗策略在促进支气管肺发育不良的肺部血管及结构发育方面具有显著潜力。非编码RNA家族作为内皮细胞功能的关键调节因子,在血管生成过程中发挥着重要作用[31]。基因分析结果表明,间充质干细胞外泌体富含大量促进血管生成的miRNA[32]。QU等[33]发现,源自人脐带间充质干细胞外泌体的miR-126-3p通过靶向磷酸肌醇3激酶调节亚基2/磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白信号途径来启动血管生成程序,在体外实验中,miR-126-3p能显著增强血管生成因子信号,进一步促进血管生成。此外,研究还表明,来源于人脐带间充质干细胞的外泌体所携带的miR-126-3p在大鼠体内表现出抗细胞凋亡作用,凸显了其在治疗中的潜力和应用前景。B型利钠肽(B-type natriuretic peptide,BNP)是一种具有刺激内皮细胞再生作用的新生血管因子。MOREIRA等[34]的研究显示,通过鼻内途径给予新生大鼠人脐带组织来源间充质干细胞可显著上调B型利钠肽编码基因NPPB的表达,进而改善支气管肺发育不良动物模型的肺泡发育和肺血管生成。此外,在深Ⅱ度烧伤的大鼠模型中,研究发现人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体能够通过递送血管生成素2,显著增强血管生成[35]。
2.2.3 抗纤维化 纤维化是指在炎症反应或组织损伤过程中,纤维结缔组织及细胞外基质成分(如胶原蛋白和纤连蛋白)在病变区域及其周围组织中的异常沉积,最终导致不可逆的瘢痕形成,并持续损害器官功能[36],肺纤维化是支气管肺发育不良患儿的显著病理特征之一。间充质干细胞及其衍生的外泌体能够减少细胞外基质过度沉积以及促进组织再生,在抑制和修复肺纤维化过程中发挥了关键作用,显示出良好的治疗潜力。
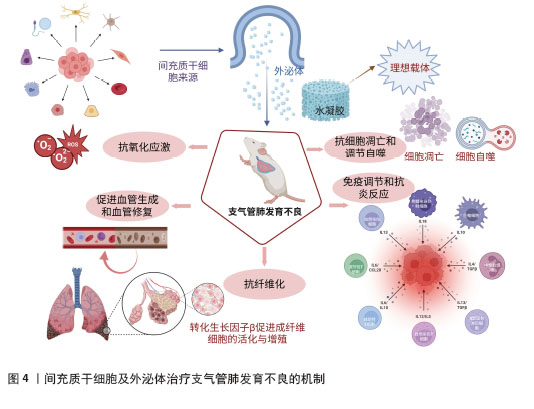
转化生长因子β在炎症调节、细胞增殖与分化以及组织修复等过程中发挥着多种稳态调控作用[37]。大量研究表明,转化生长因子β能够促进成纤维细胞的活化与增殖,导致细胞外基质过度沉积,是肺纤维化形成的主要驱动因子之一[38],见图4。转化生长因子β表达水平的升高常与肺纤维化的严重程度密切相关[39]。肿瘤坏死因子α刺激基因6通过抑制转化生长因子β信号通路来调节成纤维细胞的生长,从而发挥抗纤维化作用[40],GONG等[41]发现间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞在炎症环境下共培养,其肿瘤坏死因子α刺激基因6分泌增加,从而减轻转化生长因子β所介导的纤维化。此外,来源于人脐带间充质干细胞的外泌体中富含的miRNA let-7i-5p可通过靶向调控转化生长因子β受体1/Smad3信号通路,有效抑制成纤维细胞活化,缓解二氧化硅诱导的肺纤维化[42]。SUN等[43-44]进一步发现,间充质干细胞来源外泌体所携带的miRNA let-7 不仅可减少胶原纤维的沉积、转化生长因子β及抗纤维化肝细胞生长因子的表达,还可抑制抗凋亡基因 Bcl-2、铁死亡相关蛋白及线粒体DNA损伤标志物的表达,从而在多个水平上发挥抗纤维化作用,其中核因子E2相关因子2信号通路参与了上述过程。内皮-间充质转化是指内皮细胞丧失其特有的细胞标志和功能,转而获得间充质细胞表型和特性的生物学过程,是特发性肺纤维化的致病机制。ZHAO等[45]的研究发现,人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体分泌的miR-218能够通过下调表观遗传转录抑制因子甲基化CpG结合蛋白2来抑制转化生长因子β1诱导的内皮-间充质转化,延缓肺纤维化进展。
2.2.4 抗细胞凋亡和调节自噬 由于早产儿抗氧化系统功能失调,体内过量的活性氧无法及时消耗,从而攻击生物膜并传播脂质过氧化连锁反应,最后导致细胞凋亡[46]。因此,靶向抑制细胞凋亡是一种具有潜力的支气管肺发育不良治疗策略。CHEN等[47]证实,间充质干细胞来源外泌体可通过激活血管内皮生长因子-血管内皮生长因子受体2介导的蛋白激酶B和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶/细胞外调节蛋白激酶信号通路,有效抑制木瓜蛋白酶诱导的肺血管内皮细胞的凋亡。此外,YANG等[48]的研究表明,间充质干细胞来源外泌体还可通过调控磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白信号通路中凋亡相关蛋白的表达,在体外有效预防高氧诱导的Ⅱ型肺泡上皮细胞凋亡。RNA通过转录后调节基因表达在各种生物学功能(包括细胞凋亡、增殖和分化)中发挥关键作用[49]。SUI等[50]发现,骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体携带的长链非编码RNA-p21可通过上调沉默信息调节因子1的表达,抑制肺上皮细胞凋亡,从而修复脓毒症诱导的肺损伤。尽管间充质干细胞及其外泌体在多种疾病模型中已被证实具有抗凋亡作用,但其在支气管肺发育不良相关肺损伤中的具体机制仍有待深入研究。
自噬是一种细胞自我降解机制,通过将细胞内的有害或受损组分运送至溶酶体进行降解,从而维持细胞内环境的稳态[51]。适度自噬水平可以促进细胞功能和体内平衡,从而延长细胞寿命并改善肺部健康[52]。LI等[53]发现,支气管肺发育不良模型新生大鼠自噬标志物轻链3β水平上调,表明自噬可能在支气管肺发育不良的发展中发挥作用。尽管确切的机制尚不清楚,但已有研究表明自噬在间充质干细胞介导的肺组织再生中发挥关键作用,见图3。SURESHBABU等[54]的一项研究证明,哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白的调控关联蛋白(regulatory-associated protein of mechanistic target of rapamycin,RPTOR)作为高氧诱导的急性肺损伤和新生儿支气管肺发育不良的潜在治疗靶点,靶向抑制哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白的调控关联蛋白可增强新生小鼠的自噬活性并减少细胞凋亡,从而有效预防高氧诱导的肺损伤。WEI等[55]发现,人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体携带的miR-377-3p能够通过靶向抑制哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白的调控关联蛋白,诱导体内外自噬,从而改善脂多糖诱导的急性肺损伤。此外,过表达miR-377-3p的骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体相较于人胎肺成纤维细胞来源外泌体,在抑制支气管肺泡灌洗液中炎症因子方面表现出更强的效果,并显著增强自噬水平。
2.2.5 免疫调节和抗炎反应 免疫失衡和炎症反应是影响支气管肺发育不良疾病发展的重要病理生理过程,对支气管肺发育不良动物模型肺免疫细胞的转录组学分析显示,与趋化因子介导的信号传导和免疫细胞趋化相关的基因显著上调,同时与多种T淋巴细胞功能相关的基因则呈下调趋势[56]。间充质干细胞通过调节免疫反应和拮抗炎症可延缓支气管肺发育不良[23]。具体而言,间充质干细胞可以通过细胞接触和旁分泌机制来调节免疫细胞的功能。一方面,间充质干细胞通过细胞表面表达程序性死亡配体1和Fas配体等免疫抑制特性分子,与免疫细胞表面的受体结合,从而抑制免疫细胞的活性,导致其功能丧失[57];另一方面,间充质干细胞还可以直接作用于免疫细胞,抑制其活性和增殖。间充质干细胞能够调节多种免疫细胞的功能,包括中性粒细胞、调节性T细胞、效应T细胞、巨噬细胞和树突状细胞[58],这些细胞在多种炎症性肺病的发生机制中起重要作用。因此,间充质干细胞通过调控先天性及适应性免疫系统中的淋巴细胞,发挥免疫调节和抗炎作用。
树突状细胞和间充质干细胞之间的相互作用可使树突状细胞形成耐受性表型,并诱导炎性M1巨噬细胞极化为免疫抑制性M2巨噬细胞,从而促进某些抗炎因子如白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β的产生,并下调巨噬细胞和树突状细胞中炎症因子和细胞因子的分泌,包括白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素12,这些调节作用对于炎症消退及组织再生修复至关重要[59]。MORRISON等[60]研究发现,骨髓间充质干细胞通过上调M2表型标志物CD206的表达,诱导巨噬细胞由促炎性的M1表型向抗炎性的M2表型转化,从而减少促炎因子的释放并增加抗炎因子的分泌。此外,间充质干细胞来源外泌体还能够将线粒体转移至巨噬细胞内,增强其吞噬活性,并通过促进氧化磷酸化抑制促炎细胞因子的产生。由于强大的抗炎和免疫抑制作用,间充质干细胞在减轻炎症和促进肺组织损伤后的再生修复方面具有显著的临床意义。ZHANG等[61]发现,骨髓间充质干细胞改善了小鼠肺部炎症反应,同时逆转了白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素10等炎症因子的有害变化;细胞实验结果还表明,骨髓间充质干细胞在体外共培养中能够恢复脂多糖诱导的肺泡上皮细胞和巨噬细胞的线粒体呼吸功能障碍,进一步支持了间充质干细胞在炎症相关肺损伤修复中的潜在应用价值。CD8+ T细胞浸润增加可加剧肺部炎症反应及组织损伤,而抑制CD8+ T细胞活性有助于改善疾病进程。研究表明,骨髓间充质干细胞可通过分泌亚锡钙素2来减少CD8+ T细胞,从而缓解小鼠的炎症反应[62]。CXC趋化因子受体3是CD8+ T细胞迁移到多种组织的重要趋化因子受体,尤其是在炎症和感染状态下[63],其表达显著增强CD8+ T细胞的细胞毒作用,并促进γ-干扰素的产生[64]。ZHU等[65]发现,经骨髓间充质干细胞治疗后,小鼠肺部CD8+ T细胞CXC趋化因子受体3的表达水平显著降低,表明骨髓间充质干细胞能够通过抑制CD8+ T细胞中CXC趋化因子受体3的表达来减轻肺部损伤及炎症反应。调节性T细胞在炎症消退和肺组织修复中同样发挥关键作用,并促进肺泡上皮细胞的增殖。研究发现,骨髓间充质干细胞通过促进调节性T细胞向肺部聚集,减少肺泡腔内炎性细胞的浸润,同时逆转了肺纤维化进程,进而发挥抗炎、免疫调节、抗纤维化作用[66]。
间充质干细胞及其外泌体的潜在治疗作用,见表2。

2.3 基于水凝胶递送系统的间充质干细胞疗法 在传统给药方式下,间充质干细胞及其外泌体容易被降解且活性迅速丧失,严重限制了其治疗效果。多项临床前研究表明,间充质干细胞在肺组织中的实际植入率较低,仅为0%-20%[67]。相关实验数据显示,在新生大鼠支气管肺发育不良模型中给予人骨髓来源间充质干细胞后第18天,仅在部分肺组织细胞中检测到人源β2-微球蛋白,提示其在体内的存留时间及功能发挥极为有限[68]。水凝胶凭借优异的生物相容性和可调控的物理化学特性,已成为间充质干细胞及其外泌体递送的理想载体。WANG等[69]对比了直接局部应用外泌体与水凝胶负载外泌体在体内的清除率,结果发现,在相同剂量下,前者于4 d内几乎完全被清除,而后者仍在肺部均匀保留,表现出良好的缓释效果。HAN等[70]构建了一个细胞-纳米颗粒共递送系统(MSCs-Lip@NCAF),该系统表现出快速的肺靶向和肺内的持续积累效应,从而显著提升了间充质干细胞修复肺损伤的能力。HUANG等[71]设计并合成了一种新的生物活性水凝胶Nap-GFFYK-Thiol,使用二硫键作为可切割接头来控制分子自组装,Nap-GFFYK-Thiol水凝胶通过旁分泌作用提高细胞活力,增强了人胎盘来源间充质干细胞的促血管生成和抗凋亡作用。此外,水凝胶具有良好的生物相容性。YUAN等[72]通过研究不同支架对免疫学特性的影响,发现负载间充质干细胞的水凝胶支架极低程度引起同种异体淋巴细胞的增殖,提示其具有较低的免疫原性。ALVARADO-VELEZ等[73]设计了一种可释放Fas配体的琼脂糖基水凝胶。Fas配体是一种可诱导细胞毒性CD8+ T细胞凋亡的蛋白,该水凝胶系统在局部显著减少了宿主CD8+ T细胞的数量,并提高了损伤区域移植的同种异体间充质干细胞的存活率,同时水凝胶还作为外源性间充质干细胞抵御宿主免疫系统攻击的保护屏障,将间充质干细胞包埋在藻酸盐水凝胶中可以通过充当物理屏障来延缓促炎T细胞和细胞因子的浸润,从而缓冲植入的间充质干细胞免受宿主免疫系统的攻击[74]。另一方面,向水凝胶中添加一些化学物质或生物活性因子也提高了 间充质干细胞的活力,负载血小板衍生生长因子BB的纤维蛋白水凝胶使间充质干细胞球体的存活率增加了1倍[75]。荧光素酶成像证实壳聚糖水凝胶显著增加了间充质干细胞来源外泌体中蛋白质和miRNA的稳定性,并进一步增强了间充质干细胞衍生外泌体的内皮保护和促血管生成能力[76]。甘氨酸-组氨酸-赖氨酸修饰的藻酸盐水凝胶可以上调间充质干细胞分泌促血管生成因子的能力[77]。综上所述,与传统递送方式相比,水凝胶不仅为间充质干细胞及其外泌体提供了稳定的三维支架,实现在肺组织中的缓释释放并延长滞留时间,还能够有效保护细胞活性和生物功能,从而显著提升治疗效果。
2.4 间充质干细胞及其外泌体在支气管肺发育不良治疗中的挑战与未来展望
2.4.1 干细胞治疗的安全性问题 ①自体干细胞取自患者自身,具有不产生同种反应性抗体和免疫排斥的显著优势,因而在临床中应用广泛,尤其在血液系统疾病的治疗领域表现出良好疗效[78]。由于支气管肺发育不良主要发生于早产患儿,其自体干细胞储备有限,难以满足治疗需求,因此临床上往往考虑使用异体干细胞进行治疗。然而,异体干细胞移植可能引发免疫排斥反应,影响细胞的存活和治疗效果,这一问题不容忽视。在多种干细胞类型中,间充质干细胞因其低免疫原性和免疫调节能力而备受关注。研究表明,间充质干细胞可通过抑制T细胞增殖、调节炎症微环境等机制降低宿主免疫反应[79]。然而,即便如此,异体间充质干细胞仍可能激活宿主免疫系统,导致存活率下降、分泌功能受损,进而影响治疗效果[79]。因此,在支气管肺发育不良的干细胞治疗中,如何克服免疫排斥,提高细胞存活率和治疗持久性,仍然是临床应用亟待解决的挑战。②干细胞具备自我更新和多向分化的能力,在再生医学领域展现出巨大的应用潜力。然而,其不受控的增殖可能带来严重的安全隐患,其中肿瘤形成风险尤为值得关注。特别是诱导多能干细胞,由于其通过基因重编程获得多能性,可能携带基因突变或表观遗传异常,从而增加致瘤性[80]。因此,在间充质干细胞治疗研究中,如何降低肿瘤发生风险是关键挑战之一。
2.4.2 外泌体治疗的生物利用度与递送问题 传统的静脉输注或腹腔内注射给药方式容易导致外泌体在肺部以外的组织滞留,并被肝脏、脾脏或肾脏等器官迅速清除,从而降低在肺部的有效浓度,影响治疗效果[81]。为改善外泌体的肺部靶向性,HAN
等[82]采用雾化气道吸入的方式递送外泌体,该方法显著提高了外泌体在肺部的沉积率,在7 d内外泌体几乎仅富集于肺组织,提升了靶向作用。这一策略不仅增强了外泌体的局部有效浓度,减少系统性清除,还能降低全身性不良反应,为外泌体靶向治疗支气管肺发育不良提供了新的思路。尽管雾化吸入在一定程度上提高了肺部递送效率,但仍然无法完全解决外泌体在体内的短半衰期和精准递送问题。未来,仍需进一步优化递送载体、开发靶向修饰技术,以及探索联合治疗策略,以实现更加高效、安全、精准的支气管肺发育不良靶向治疗。
2.4.3 标准化制备与质量控制的挑战 如何稳定供应大量具有一致疗效的细胞是基于间充质干细胞的疗法在临床应用中面临的关键挑战之一,由于临床需求通常远超单次培养的产能,因此在不同时间和不同供者获取的细胞,如何确保其生物学特性和治疗效果的一致性成为重要问题。建立标准化的培养技术,以保证每批次细胞均具备相同的功能和疗效,是推进干细胞疗法发展的关键。针对基于间充质干细胞的疗法,另一大挑战在于细胞扩增过程中治疗效力的稳定性。尽管已有充分证据表明间充质干细胞具备良好的增殖能力,并可通过传代扩增其数量,但在连续传代过程中,间充质干细胞的治疗效力是否能够保持始终如一,仍未得到明确界定。为实现间充质干细胞的规模化应用,需要进一步优化培养和传代策略,明确其传代上限,以在不影响生物学特性和治疗效果的前提下,最大程度地扩大细胞数量。
2.4.4 未来研究方向 水凝胶作为细胞外基质的潜在替代品,是维持体内间充质干细胞及其衍生物功能的理想支架或递送载体[83]。由于循环系统的快速清除作用,外泌体在靶组织的持续作用时间极为有限,难以在特定部位长期滞留并有效修复受损组织,如何提高外泌体在局部组织的滞留时间和稳定性成为研究的关键;水凝胶因其优异的生物相容性以及疏松多孔的结构特性,成为外泌体递送的理想载体。通过与水凝胶结合,外泌体可在特定区域延长保留时间,并实现缓慢释放,从而提升治疗效果。此外,水凝胶还能有效保护外泌体,使其免受体内恶劣环境的影响[84],尤其是在支气管肺发育不良相关肺损伤的炎症微环境下,水凝胶能够减少外泌体的降解,提高外泌体在损伤部位的稳定性。因此,负载外泌体的水凝胶已成为再生医学和支气管肺发育不良治疗领域的研究热点。未来,优化水凝胶的理化特性,以进一步提高其对外泌体的保护能力和靶向递送效率,将成为推动临床应用的重要方向。此外,研究发现褪黑激素与间充质干细胞联合给药可以有效地保持肺部间充质干细胞在长期传代后的自我更新和分化特性,褪黑激素通过改善肺部周围的炎症微环境使间充质干细胞具有更好的再生功能[85]。因此,干细胞与相关抗炎、抗氧化物质的联合治疗策略同样受到更多的关注。
| [1] ZHUO Y, LI WS, LU W, et al. TGF-β1 mediates hypoxia-preconditioned olfactory mucosa mesenchymal stem cells improved neural functional recovery in Parkinson’s disease models and patients. Mil Med Res. 2024; 11(1):48. [2] HUANG R, CHEN T, WANG S, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Prophylaxis of Chronic Graft-vs-Host Disease After Haploidentical Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant: An Open-Label Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2024;10(2):220-226. [3] NORTHWAY WH JR, ROSAN RC, PORTER DY. Pulmonary disease following respirator therapy of hyaline-membrane disease. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. N Engl J Med. 1967;276(7):357-368. [4] YU H, LI D, ZHAO X, et al. Fetal origin of bronchopulmonary dysplasia: contribution of intrauterine inflammation. Mol Med. 2024;30(1):135. [5] 张珂,饶兴愉.新生儿呼吸窘迫综合征患儿发生支气管肺发育不良的Nomogram预测模型的建立与评估[J].重庆医科大学学报,2024,49(10):1110-1118. [6] FAWKE J, LUM S, KIRKBY J, et al. Lung function and respiratory symptoms at 11 years in children born extremely preterm: the EPICure study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;182(2):237-245. [7] YOUNGE N, GOLDSTEIN RF, BANN CM, et al. Survival and Neurodevelopmental Outcomes among Periviable Infants. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(7):617-628. [8] 周应祯,王婷,付星梦,等.支气管肺发育不良的预后[J].中国当代儿科杂志, 2025,27(1):115-120. [9] ENZER KG, BAKER CD, WISNIEWSKI BL. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Clin Chest Med. 2024;45(3):639-650. [10] ZAKRZEWSKI W, DOBRZYŃSKI M, SZYMONOWICZ M, et al. Stem cells: past, present, and future. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):68. [11] KIMBLE A, ROBBINS ME, PEREZ M. Pathogenesis of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: Role of Oxidative Stress from ‘Omics’ Studies. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(12):2380. [12] XUEFEI Y, XINYI Z, QING C, et al. Effects of Hyperoxia on Mitochondrial Homeostasis: Are Mitochondria the Hub for Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia? Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:642717. [13] WU D, LIANG M, DANG H, et al. Hydrogen protects against hyperoxia-induced apoptosis in type II alveolar epithelial cells via activation of PI3K/Akt/Foxo3a signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;495(2):1620-1627. [14] MÖBIUS MA, FREUND D, VADIVEL A, et al. Oxygen Disrupts Human Fetal Lung Mesenchymal Cells. Implications for Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019;60(5):592-600. [15] POPOVA AP, BENTLEY JK, CUI TX, et al. Reduced platelet-derived growth factor receptor expression is a primary feature of human bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014; 307(3):L231-L239. [16] POPOVA AP. Mesenchymal Cells and Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: New Insights about the Dark Side of Oxygen. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019;60(5): 501-502. [17] LEIJTEN J, GEORGI N, MOREIRA TEIXEIRA L, et al. Metabolic programming of mesenchymal stromal cells by oxygen tension directs chondrogenic cell fate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014; 111(38):13954-13959. [18] KRINNER A, ZSCHARNACK M, BADER A, et al. Impact of oxygen environment on mesenchymal stem cell expansion and chondrogenic differentiation. Cell Prolif. 2009;42(4):471-484. [19] NARALA VR, FUKUMOTO J, HERNÁNDEZ-CUERVO H, et al. Akap1 genetic deletion increases the severity of hyperoxia-induced acute lung injury in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018; 314(5):L860-L870. [20] RATNER V, SOSUNOV SA, NIATSETSKAYA ZV, et al. Mechanical ventilation causes pulmonary mitochondrial dysfunction and delayed alveolarization in neonatal mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013; 49(6):943-950. [21] 李梦曌,孙文强,朱雪萍.线粒体功能障碍在早产儿支气管肺发育不良发病机制中的研究进展[J].临床肺科杂志,2024, 29(7):1089-1092. [22] KANDASAMY J, OLAVE N, BALLINGER SW, et al. Vascular Endothelial Mitochondrial Function Predicts Death or Pulmonary Outcomes in Preterm Infants. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017; 196(8):1040-1049. [23] WILLIS GR, FERNANDEZ-GONZALEZ A, ANASTAS J, et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Exosomes Ameliorate Experimental Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Restore Lung Function through Macrophage Immunomodulation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;197(1):104-116. [24] PHINNEY DG, DI GIUSEPPE M, NJAH J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells use extracellular vesicles to outsource mitophagy and shuttle microRNAs. Nat Commun. 2015;6:8472. [25] DUTRA SILVA J, SU Y, CALFEE CS, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell extracellular vesicles rescue mitochondrial dysfunction and improve barrier integrity in clinically relevant models of ARDS. Eur Respir J. 2021;58(1):2002978. [26] ISLAM MN, DAS SR, EMIN MT, et al. Mitochondrial transfer from bone-marrow-derived stromal cells to pulmonary alveoli protects against acute lung injury. Nat Med. 2012;18(5):759-765. [27] YUN EJ, LORIZIO W, SEEDORF G, et al. VEGF and endothelium-derived retinoic acid regulate lung vascular and alveolar development. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016;310(4):L287-L298. [28] ZHANG Y, HAO Z, WANG P, et al. Exosomes from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance fracture healing through HIF-1α-mediated promotion of angiogenesis in a rat model of stabilized fracture. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(2):e12570. [29] WANG J, ZHANG A, HUANG F, et al. MSC-EXO and tempol ameliorate bronchopulmonary dysplasia in newborn rats by activating HIF-1α. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2023;58(5):1367-1379. [30] CHOU HC, CHANG CH, CHEN CH, et al. Consecutive daily administration of intratracheal surfactant and human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuates hyperoxia-induced lung injury in neonatal rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):258. [31] ZHAO H, WANG X, FANG B. HIF1A promotes miR-210/miR-424 transcription to modulate the angiogenesis in HUVECs and HDMECs via sFLT1 under hypoxic stress. Mol Cell Biochem. 2022;477(8):2107-2119. [32] ZOU XY, YU Y, LIN S, et al. Comprehensive miRNA Analysis of Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Extracellular Vesicles. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2018;43(1):152-161. [33] QU Q, LIU L, CUI Y, et al. miR-126-3p containing exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells promote angiogenesis and attenuate ovarian granulosa cell apoptosis in a preclinical rat model of premature ovarian failure. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):352. [34] MOREIRA A, WINTER C, JOY J, et al. Intranasal delivery of human umbilical cord Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stromal cells restores lung alveolarization and vascularization in experimental bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020;9(2):221-234. [35] LIU J, YAN Z, YANG F, et al. Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Accelerate Cutaneous Wound Healing by Enhancing Angiogenesis through Delivering Angiopoietin-2. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021;17(2):305-317. [36] ANTAR SA, ASHOUR NA, MARAWAN ME, et al. Fibrosis: Types, Effects, Markers, Mechanisms for Disease Progression, and Its Relation with Oxidative Stress, Immunity, and Inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(4):4004. [37] MASSAGUÉ J, SHEPPARD D. TGF-β signaling in health and disease. Cell. 2023; 186(19):4007-4037. [38] REN LL, LI XJ, DUAN TT, et al. Transforming growth factor-β signaling: From tissue fibrosis to therapeutic opportunities. Chem Biol Interact. 2023;369:110289. [39] ONG CH, THAM CL, HARITH HH, et al. TGF-β-induced fibrosis: A review on the underlying mechanism and potential therapeutic strategies. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021;911:174510. [40] USUNIER B, BROSSARD C, L’HOMME B, et al. HGF and TSG-6 Released by Mesenchymal Stem Cells Attenuate Colon Radiation-Induced Fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1790. [41] GONG SC, YOON Y, JUNG PY, et al. Antifibrotic TSG-6 Expression Is Synergistically Increased in Both Cells during Coculture of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Macrophages via the JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(21):13122. [42] PARK SA, KIM MJ, PARK SY, et al. EW-7197 inhibits hepatic, renal, and pulmonary fibrosis by blocking TGF-β/Smad and ROS signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015;72(10):2023-2039. [43] SUN L, HE X, KONG J, et al. Menstrual blood-derived stem cells exosomal miR-let-7 to ameliorate pulmonary fibrosis through inhibiting ferroptosis by Sp3/HDAC2/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024;126:111316. [44] SUN L, ZHU M, FENG W, et al. Exosomal miRNA Let-7 from Menstrual Blood-Derived Endometrial Stem Cells Alleviates Pulmonary Fibrosis through Regulating Mitochondrial DNA Damage. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:4506303. [45] ZHAO Y, DU L, SUN J, et al. Exosomal miR-218 derived from mesenchymal stem cells inhibits endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition by epigenetically modulating of BMP2 in pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023;39(6):2919-2936. [46] SU LJ, ZHANG JH, GOMEZ H, et al. Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced Lipid Peroxidation in Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Ferroptosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:5080843. [47] CHEN Q, LIN J, DENG Z, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells protect against papain-induced emphysema by preventing apoptosis through activating VEGF-VEGFR2-mediated AKT and MEK/ERK pathways in rats. Regen Ther. 2022;21:216-224. [48] YANG W, HUANG C, WANG W, et al. Bone mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes prevent hyperoxia-induced apoptosis of primary type II alveolar epithelial cells in vitro. PeerJ. 2022;10:e13692. [49] TAN BWQ, SIM WL, CHEONG JK, et al. MicroRNAs in chronic airway diseases: Clinical correlation and translational applications. Pharmacol Res. 2020;160:105045. [50] SUI X, LIU W, LIU Z. Exosomal lncRNA-p21 derived from mesenchymal stem cells protects epithelial cells during LPS-induced acute lung injury by sponging miR-181. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021; 53(6):748-757. [51] CHEN T, ZHENG L, LUO P, et al. Crosstalk between m6A modification and autophagy in cancer. Cell Biosci. 2024;14(1):44. [52] ZHANG Y, ZHANG J, FU Z. Role of autophagy in lung diseases and ageing. Eur Respir Rev. 2022;31(166):220134. [53] LI M, PAN B, SHI Y, et al. Increased expression of CHOP and LC3B in newborn rats with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Int J Mol Med. 2018;42(3):1653-1665. [54] SURESHBABU A, SYED M, DAS P, et al. Inhibition of Regulatory-Associated Protein of Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin Prevents Hyperoxia-Induced Lung Injury by Enhancing Autophagy and Reducing Apoptosis in Neonatal Mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016;55(5):722-735. [55] WEI X, YI X, LV H, et al. Correction: MicroRNA-377-3p released by mesenchymal stem cell exosomes ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by targeting RPTOR to induce autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(9):746. [56] SHRESTHA D, YE GX, STABLEY D, et al. Pulmonary immune cell transcriptome changes in double-hit model of BPD induced by chorioamnionitis and postnatal hyperoxia. Pediatr Res. 2021;90(3):565-575. [57] WANG Y, HUANG R, LU Y, et al. Immuno-protective vesicle-crosslinked hydrogel for allogenic transplantation. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):5176. [58] HUANG Y, WU Q, TAM PKH. Immunomodulatory Mechanisms of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Potential Clinical Applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(17):10023. [59] YUAN D, BAO Y, EL-HASHASH A. Mesenchymal stromal cell-based therapy in lung diseases; from research to clinic. Am J Stem Cells. 2024;13(2):37-58. [60] MORRISON TJ, JACKSON MV, CUNNINGHAM EK, et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Modulate Macrophages in Clinically Relevant Lung Injury Models by Extracellular Vesicle Mitochondrial Transfer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;196(10):1275-1286. [61] ZHANG K, GAO Y, DENG Y, et al. Studies on the effects of bone marrow stem cells on mitochondrial function and the alleviation of ARDS. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476(1):93-107. [62] CHEN X, LIU Q, HUANG W, et al. Stanniocalcin-2 contributes to mesenchymal stromal cells attenuating murine contact hypersensitivity mainly via reducing CD8+ Tc1 cells. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(5):548. [63] CALDEIRA-DANTAS S, FURMANAK T, SMITH C, et al. The Chemokine Receptor CXCR3 Promotes CD8+ T Cell Accumulation in Uninfected Salivary Glands but Is Not Necessary after Murine Cytomegalovirus Infection. J Immunol. 2018;200(3):1133-1145. [64] GUO K, YOMBO DJK, WANG Z, et al. The chemokine receptor CXCR3 promotes CD8+ T cell-dependent lung pathology during influenza pathogenesis. Sci Adv. 2024;10(1):eadj1120. [65] ZHU J, FENG B, XU Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate LPS-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting the proinflammatory function of Ly6C+ CD8+ T cells. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(10):829. [66] TAKAO S, NAKASHIMA T, MASUDA T, et al. Human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells cultured in serum-free media demonstrate enhanced antifibrotic abilities via prolonged survival and robust regulatory T cell induction in murine bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):506. [67] EE MT, THÉBAUD B. The Therapeutic Potential of Stem Cells for Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: “It’s About Time” or “Not so Fast” ? Curr Pediatr Rev. 2018;14(4):227-238. [68] PIERRO M, IONESCU L, MONTEMURRO T, et al. Short-term, long-term and paracrine effect of human umbilical cord-derived stem cells in lung injury prevention and repair in experimental bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Thorax. 2013;68(5):475-484. [69] WANG Y, CAO Z, WEI Q, et al. VH298-loaded extracellular vesicles released from gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel facilitate diabetic wound healing by HIF-1α-mediated enhancement of angiogenesis. Acta Biomater. 2022;147:342-355. [70] HAN MM, HE XY, TANG L, et al. Nanoengineered mesenchymal stem cell therapy for pulmonary fibrosis in young and aged mice. Sci Adv. 2023;9(29):eadg5358. [71] HUANG A, LIU D, QI X, et al. Self-assembled GFFYK peptide hydrogel enhances the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in a mouse hindlimb ischemia model. Acta Biomater. 2019;85:94-105. [72] YUAN T, LI K, GUO L, et al. Modulation of immunological properties of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells by collagen scaffolds in cartilage tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2011;98(3):332-341. [73] ALVARADO-VELEZ M, ENAM SF, MEHTA N, et al. Immuno-suppressive hydrogels enhance allogeneic MSC survival after transplantation in the injured brain. Biomaterials. 2021;266:120419. [74] ANSARI S, CHEN C, HASANI-SADRABADI MM, et al. Hydrogel elasticity and microarchitecture regulate dental-derived mesenchymal stem cell-host immune system cross-talk. Acta Biomater. 2017;60:181-189. [75] ZHAO N, COYNE J, ABUNE L, et al. Exogenous Signaling Molecules Released from Aptamer-Functionalized Hydrogels Promote the Survival of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Spheroids. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(22):24599-24610. [76] ZHANG K, ZHAO X, CHEN X, et al. Enhanced Therapeutic Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes with an Injectable Hydrogel for Hindlimb Ischemia Treatment. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(36):30081-30091. [77] HO SS, MURPHY KC, BINDER BY, et al. Increased Survival and Function of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Spheroids Entrapped in Instructive Alginate Hydrogels. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016; 5(6):773-781. [78] DURAND N, ZUBAIR AC. Autologous versus allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell therapy: The pros and cons. Surgery. 2022;171(5):1440-1442. [79] GOPALARETHINAM J, NAIR AP, IYER M, et al. Advantages of mesenchymal stem cell over the other stem cells. Acta Histochem. 2023;125(4):152041. [80] DERKS LLM, VAN BOXTEL R. Stem cell mutations, associated cancer risk, and consequences for regenerative medicine. Cell Stem Cell. 2023;30(11):1421-1433. [81] TAN F, LI X, WANG Z, et al. Clinical applications of stem cell-derived exosomes. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024;9(1):17. [82] HAN Y, ZHU Y, YOUNGBLOOD HA, et al. Nebulization of extracellular vesicles: A promising small RNA delivery approach for lung diseases. J Control Release. 2022; 352:556-569. [83] GARCIA-APONTE OF, KAHLENBERG S, KOUROUPIS D, et al. Effects of Hydrogels on Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells Paracrine Activity and Extracellular Vesicles Production. J Extracell Vesicles. 2025;14(3):e70057. [84] JU Y, HU Y, YANG P, et al. Extracellular vesicle-loaded hydrogels for tissue repair and regeneration. Mater Today Bio. 2022; 18:100522. [85] HANNA M, ELNASSAG SS, MOHAMED DH, et al. Melatonin and mesenchymal stem cells co-administration alleviates chronic obstructive pulmonary disease via modulation of angiogenesis at the vascular-alveolar unit. Pflugers Arch. 2024; 476(7):1155-1168. |
| [1] | 吴妍廷, 李 宇, 廖金凤. 氧化镁纳米粒调控成骨与血管生成相关基因表达促进骨缺损愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1885-1895. |
| [2] | 蒋星海, 宋玉林, 李德津, 邵建敏, 徐军志, 刘华凯, 吴应国, 沈岳辉, 冯思诚. 血管内皮生长因子165基因转染骨髓间充质干细胞构建血管化两亲性肽凝胶模块[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1903-1911. |
| [3] | 刘宏杰, 牟秋菊, 申玉雪, 梁 飞, 祝丽丽. 金属有机框架/羧甲基壳聚糖-氧化海藻酸钠/富血小板血浆水凝胶促糖尿病感染创面愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1929-1939. |
| [4] | 董春阳, 周天恩, 莫孟学, 吕文权, 高 明, 朱瑞凯, 高志伟. 二甲双胍联合血水草敷料治疗深Ⅱ度烧伤创面的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2001-2013. |
| [5] | 杨学涛, 朱梦菡, 张宸熙, 孙一民, 叶 玲. 抗氧化纳米材料在口腔中的应用和不足[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2044-2053. |
| [6] | 刘 洋, 刘东辉, 徐 磊, 展 旭, 孙昊博, 康 凯. 刺激响应型可注射水凝胶在心肌梗死精准化治疗中的作用与趋势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2072-2080. |
| [7] | 王 峥, 程 吉, 于金龙, 刘文红, 王召红, 周鲁星. 水凝胶材料在脑卒中治疗中的应用进展与未来展望[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2081-2090. |
| [8] | 郭宇超, 倪前伟, 尹 晨, 吉格尔·赛义力汗, 高 瞻. 季铵化壳聚糖紧急止血材料:合成、机制与应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2091-2100. |
| [9] | 胡雄科, 刘少华, 谭 谦, 刘 昆, 朱光辉. 紫草素干预骨髓间充质干细胞改善老年小鼠股骨的微结构[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1609-1615. |
| [10] | 宋浦蓁, 马贺宾, 陈宏广, 章亚东. 骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体联合转化生长因子β1对巨噬细胞的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1616-1623. |
| [11] | 蔡子鸣, 于庆贺, 马鹏飞, 张 鑫, 周龙千, 张崇阳, 林文平. 血红素氧合酶1减轻脂多糖诱导髓核间充质干细胞的炎症反应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1624-1631. |
| [12] | 袁小霜, 杨 姁, 杨 波, 陈晓旭, 田 婷, 王飞清, 李艳菊, 刘 洋, 杨文秀. 弥漫性大B细胞淋巴瘤细胞条件培养液对人骨髓间充质干细胞增殖、凋亡的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1632-1640. |
| [13] | 李镇宇, 张思明, 柏家祥, 朱 晨. 蛇床子素改善高糖环境下骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化功能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1641-1648. |
| [14] | 韩念荣, 黄异飞, 艾克热木·吾斯曼, 刘岩路, 胡 炜. 高糖微环境中程序性细胞死亡受体1抑制大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1649-1657. |
| [15] | 金东升, 赵张红, 朱子银, 张 森, 孙祖延, 邓 江. 淫羊藿苷缓释微球三维支架对兔骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1658-1668. |
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者于2025年3月独立完成全部文献检索工作。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 各数据库建库至2025年3月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中国知网和PubMed数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 以“间充质干细胞,外泌体,支气管肺发育不良,纳米水凝胶,作用机制”为中文检索词;以“mesenchymal stem cells,exosomes,bronchopulmonary dysplasia,nanohydrogels,mechanism of action”为英文检索词。
1.1.5 检索类型 纳入文献包括原始研究、综述、述评、经验交流及荟萃分析等。
1.1.6 检索策略 采用主题词和自由词结合的方式进行检索,以PubMed数据库为例,具体检索策略见图1。
1.1.7 文献检索量 初步检索到500余篇文献。
1.2 入选标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①间充质干细胞与支气管肺发育不良相关研究文献;②间充质干细胞来源外泌体与支气管肺发育不良相关研究文献;③水凝胶等工程化材料与间充质干细胞相关研究文献;④水凝胶等工程化材料与外泌体相关研究文献;⑤支气管肺发育不良病理机制相关研究文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①与此研究领域相关性较弱的文献;②发表年代较久、参考价值有限的文献;③研究内容相对滞后、实验设备老化或存在重复性的研究文献。
1.3 文献质量评估及数据提取 通过计算机初步检索,共获得与研究目的相关的中英文文献500余篇。由资料整理人员根据既定的纳入与排除标准进行筛选,最终选取85篇文献纳入分析。文献筛选流程见图2。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
3.2 此综述区别于他人他篇的特点 此文章综述了间充质干细胞及其外泌体在支气管肺发育不良病理过程中所发挥的抗氧化应激、促进血管生成及血管修复、治疗肺纤维化、抗细胞凋亡和调节自噬、免疫调节、抗炎症反应等潜在治疗作用,着重关注了水凝胶递送系统的应用;同时简要介绍间充质干细胞及其外泌体治疗支气管肺发育不良所面临的挑战及未来的研究方向。
3.3 综述的局限性 ①此文章尽管综述了大量文献,但无法涵盖所有有关间充质干细胞及外泌体与支气管肺发育不良中的文章,导致部分最新的发现未被纳入综述;②此文章聚焦于水凝胶递送系统在间充质干细胞治疗中的应用研究,但未深入探讨水凝胶的具体制备方法及其所用材料在理化性质和功能表现上的差异;③目前已有少量研究提示,不同组织来源间充质干细胞及其外泌体在疾病治疗中的效果可能存在一定差异,然而,文章未对此方面内容进行探讨。
3.4 综述的重要意义 此文章综述了间充质干细胞及其外泌体在支气管肺发育不良中的研究现状,系统介绍了间充质干细胞及其外泌体在支气管肺发育不良中的潜在治疗作用,以及水凝胶递送系统提升治疗效果的应用研究。最后,还探讨了间充质干细胞及其外泌体治疗支气管肺发育不良所面临的挑战与未来研究的热点方向,旨在为支气管肺发育不良的临床治疗提供新的思路。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 间充质干细胞及其外泌体作为治疗支气管肺发育不良的一种新兴策略,其在肺组织损伤修复中的具体作用机制仍有待深入探讨。值得关注的是,工程化纳米水凝胶的应用显著增强了间充质干细胞及其外泌体的治疗效果;未来应加强对水凝胶制备工艺及材料性能的基础研究,以推动该治疗策略的临床转化。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
文题释义:
间充质干细胞:是一类具有多向分化潜能的成体干细胞,能在特定条件下分化为多种细胞类型,如成骨细胞、软骨细胞、肺泡上皮细胞、血管内皮细胞等,还能分泌多种生长因子、细胞因子和外泌体,在组织损伤修复中具有重要的调节作用。
支气管肺发育不良:是一种以肺泡发育受限、肺组织结构简化、肺血管发育不良以及肺功能异常为主要表现的新生儿肺部疾病。
#br#
支气管肺发育不良是一种新生儿常见肺部疾病,主要特征为肺泡发育受限、肺组织结构简化、肺血管发育障碍以及肺功能异常,目前的治疗手段仍难以有效阻止其进展。间充质干细胞及其外泌体通过旁分泌作用,在缓解氧化应激、促进血管生成与修复、抗纤维化、抑制细胞凋亡、调节自噬以及调控免疫和炎症反应等方面发挥多重治疗作用,显示出良好的应用前景。同时,水凝胶递送系统的引入,使间充质干细胞及其外泌体能够实现肺部的靶向输送与缓释释放,显著增强其治疗效果。未来的研究将聚焦于水凝胶材料的优化与制备工艺的改进,进一步推动间充质干细胞及外泌体在支气管肺发育不良治疗中的转化应用。
#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||