中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 2823-2833.doi: 10.12307/2026.101
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
溶酶体酶在代谢性疾病中的关键角色
邹瑜茜1,陈燕燕2,蒋 鹏1,陈 婷1,丁伶伶1
- 江苏大学医学院,1生理教研室,2药理学教研室,江苏省镇江市 212013
-
收稿日期:2025-04-03接受日期:2025-06-04出版日期:2026-04-18发布日期:2025-09-06 -
通讯作者:丁伶伶,博士,讲师,硕士生导师,江苏省双创博士,江苏大学医学院生理教研室,江苏省镇江市 212013 -
作者简介:邹瑜茜,女,2001 年生,江苏省苏州市人,汉族,江苏大学在读硕士,主要从事代谢性疾病相关研究。 -
基金资助:中国博士后面上项目(2023M741425),项目负责人:丁伶伶;江苏省高校自然科学基金项目(24KJB320001),项目负
责人:陈燕燕;江苏省研究生科研与实践创新计划项目(KYCX25_4289),项目负责人:邹瑜茜
Critical role of lysosomal enzymes in metabolic diseases
Zou Yuxi1, Chen Yanyan2, Jiang Peng1, Chen Ting1, Ding Lingling1
- 1Department of Physiology, 2Department of Pharmacology, Medical School of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2025-04-03Accepted:2025-06-04Online:2026-04-18Published:2025-09-06 -
Contact:Ding Lingling, PhD, Lecturer, Master’s supervisor, Jiangsu Province Entrepreneurship and Innovation Ph.D. Talent Program, Department of Physiology, Medical School of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Zou Yuxi, MS candidate, Department of Physiology, Medical School of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:China Postdoctoral Science Foundation General Program, No. 2023M741425 (to DLL); Natural Science Foundation of Universities in Jiangsu Province, No. 24KJB320001 (to CYY); Jiangsu Province Graduate Student Research and Practice Innovation Program, No. KYCX25_4289 (to ZYX)
摘要:
文题释义:
溶酶体:是真核细胞中的一种膜封闭细胞器,其内部环境呈酸性(pH值为4.5-5.0),为溶酶体酶提供了最佳活性条件。
代谢综合征:是一组与代谢异常相关的临床症状和体征的集合,这些异常显著增加了个体患心血管疾病和2型糖尿病的风险。代谢综合征并不是单一的疾病,而是一组相互关联的风险因素群。
背景:患有代谢综合征的个体发生慢性疾病的风险增加,尤其是2型糖尿病、非酒精性脂肪肝病及心血管疾病。而溶酶体与多种代谢性疾病存在联系,但具体的作用尚未完全阐明。
目的:通过文献检索探究溶酶体在代谢综合征的研究进展,为阐明溶酶体及溶酶体酶在代谢综合征中的作用机制提供思路。
方法:第一作者于2024年10月应用计算机检索PubMed、Web of Science数据库建库至2024年10月发表的相关文献,以“metabolic syndrome,glucose metabolism,lipid metabolism,type 2 diabetes mellitus,non-alcoholic fatty liver disease,lysosomes,lysosomal enzymes”为英文检索词,最终纳入90篇文献进行汇总分析。
结果与结论:①代谢紊乱与代谢综合征及其他与代谢相关的疾病有关,代谢紊乱包括葡萄糖代谢紊乱和脂质代谢紊乱,葡萄糖代谢受到干扰后易引发糖尿病的发生,可能导致严重并发症和促成代谢综合征的发生;脂质代谢异常可能会造成血脂异常和脂肪肝疾病;②溶酶体酶在代谢中发挥了重要作用,其功能障碍导致多种代谢紊乱;③溶酶体酶中几种组织蛋白酶的异常与胰岛素抵抗有关并进一步引发2型糖尿病;④溶酶体酸性脂肪酶活性缺陷是导致非酒精性脂肪肝病发展的触发因素之一。
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-6317-8183(邹瑜茜)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
邹瑜茜, 陈燕燕, 蒋 鹏, 陈 婷, 丁伶伶. 溶酶体酶在代谢性疾病中的关键角色[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(11): 2823-2833.
Zou Yuxi, Chen Yanyan, Jiang Peng, Chen Ting, Ding Lingling. Critical role of lysosomal enzymes in metabolic diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2823-2833.
2.1.1 葡萄糖代谢紊乱 葡萄糖是人体最重要的能量来源,以血糖的形式在人体血液中循环,其来源为饮食中碳水化合物的降解和肝脏和肌肉中储存糖原的糖原分解。值得注意的是,胰岛素和胰高血糖素是调节葡萄糖代谢的强大激素[31],以维持血糖浓度在正常范围内。胰岛素是由胰腺β细胞分泌的激素,通过3种方式控制血糖浓度:①胰岛素通过一种机制刺激胰岛素敏感的外周组织(主要是骨骼肌)的细胞增加葡萄糖摄取,该机制是通过胰岛素刺激将细胞内池中的葡萄糖转运蛋白动员到质膜上,这一过程也称为胰岛素介导的葡萄糖摄取[32-33];②胰岛素作用于肝脏以促进糖原生成从而降低血糖[34];③胰岛素同时抑制胰高血糖素(由胰腺α细胞分泌,在禁食或血糖浓度低于正常范围时通过促进肝脏中的糖原分解来维持血糖浓度)的分泌,从而阻止肝脏产生葡萄糖[31]。然而,在代谢综合征条件下,由于血糖清除(即骨骼肌细胞葡萄糖摄取和糖原生成)和葡萄糖生成(即糖原分解)的不平衡,葡萄糖代谢受到干扰。这些受干扰的过程是由胰腺β细胞分泌胰岛素的异常作用、缺乏胰岛素刺激下的葡萄糖消失、肝葡萄糖生成调控不良以及涉及葡萄糖代谢的几种酶功能障碍引起的结果[31,35],受干扰的葡萄糖代谢导致空腹和餐后血糖浓度升高,即高血糖。此外,高血糖还可能导致糖尿病酮症酸中毒[36],这是一种代谢性酸中毒,临床表现为血浆酸度增加(血浆pH值降低)[37]。糖尿病酮症酸中毒是糖尿病的一种严重并发症,往往当身体因相对胰岛素缺乏而以脂肪为能量来源而不是葡萄糖时发生,导致血液循环中产生过多的酸性酮体,从而扰乱血液中的酸碱平衡。因此,这些不断积累的证据表明,葡萄糖代谢的紊乱促成了代谢综合征。
2.1.2 脂质代谢紊乱 除了葡萄糖代谢紊乱外,脂质代谢异常也对代谢综合征有重大影响。比如中心性肥胖和血脂异常是与代谢综合征密切相关的风险因素[38]。脂质不仅是身体的主要能量来源还是细胞膜的重要结构成分。三酰甘油和胆固醇是最重要的脂质[39],三酰甘油是一种关键人体能量来源,由与甘油骨架酯键连接的游离脂肪酸组成;而胆固醇具有多种功能包括作为细胞膜的成分、类固醇激素和维生素D的前体,以及氧化胆固醇和胆汁酸的前体[39-40]。总之维持正常的脂质代谢至关重要。脂质代谢是一个复杂的过程,涉及从体内合成脂质或摄入膳食脂质到降解或转化为体内多种含脂结构的多个步骤[41-43]。生理上,脂质代谢由多种酶(参与脂质生成、脂解和脂质转化)以及通过脂蛋白在体内分布脂质来调节,脂蛋白是由脂质和特定蛋白质组成的复合
物[44]。脂蛋白包括乳糜微粒、极低密度脂蛋白、低密度脂蛋白和高密度脂蛋白,构成了脂质运输系统,使得不溶性的三酰甘油和胆固醇能够在血液中运输。因此,这些过程中的任何缺陷或脂质分解代谢和/或合成代谢之间的任何不平衡都会导致严重的脂质代谢紊乱,从而产生临床问题。代谢综合征经常是由于营养物质摄入过多,导致血浆三酰甘油水平升高、血浆胆固醇水平高和高密度脂蛋白水平降低,这被称为血脂异常[45]。此外,异位脂肪堆积,也称为非脂肪储存器官中三酰甘油的过度积累[46],也会发生。例如,过量的脂肪在肝脏中积累,导致脂肪肝疾病。与肝脏类似,肌肉内部也会出现异位脂质堆积,这种情况被称为肌脂变性。在这种情况下,脂肪渗透到肌细胞内(肌细胞内脂肪),以及筋膜内的脂肪包围骨骼肌(肌间脂肪)[47],引起骨骼肌代谢紊乱。此外,代谢综合征期间人体内过量的脂质也是诱发脂肪组织、骨骼肌和肝脏胰岛素抵抗的因素之一[48]。实际上,有研究表明,增加血浆游离脂肪酸浓度的脂质输注会减少人类的胰岛素刺激葡萄糖消耗[49-50],这意味着游离脂肪酸的积累会导致胰岛素抵抗的病理。综上所述,考虑到脂质代谢紊乱对代谢综合征的影响,维持脂质分解代谢和合成代谢之间的平衡至关重要。
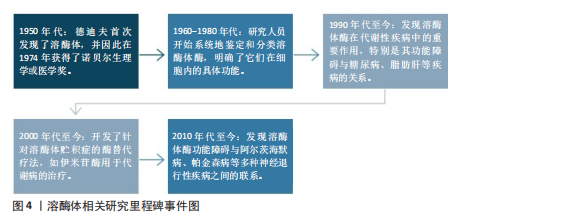
2.2 溶酶体在代谢中的作用 溶酶体是膜封闭的细胞器,广泛分布于几乎所有类型的真核细胞的细胞质中[51-52]。溶酶体膜内部的各种水解酶则称为溶酶体酶,具有降解蛋白质、核酸、多糖和脂类等大分子物质的作用。在细胞中,溶酶体发挥降解大分子、维持生理稳态、外排等作用。如图4所示,为溶酶体相关研究里程碑事件。研究表明溶酶体在代谢性疾病中发挥重要作用,这与溶酶体酶及溶酶体的功能密不可分。
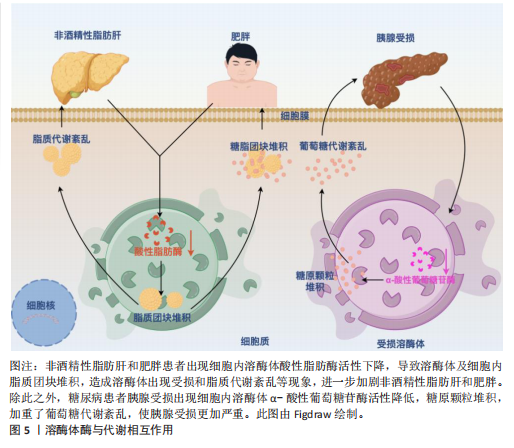
2.2.1 溶酶体酶与代谢功能之间的相互作用 溶酶体中含有大约60种降解溶酶体酶,这些酶能够降解蛋白质、脂质、碳水化合物和核酸从而在代谢中发挥重要作用[53-54]。根据不同的底物,溶酶体酶可以分为5类:①磷酸酶:包括酸性磷酸酶和酸性磷酸二酯酶,其底物分别是磷酸单酯和磷酸二酯;②核酸酶:它们的底物是DNA和RNA,包括酸性脱氧核糖核酸酶和酸性核糖核酸酶;③多糖/黏多糖水解酶:共有7个亚类,例如葡萄糖苷酶和甘露糖苷酶,其底物分别是糖原和甘露糖苷;④蛋白酶:包括组织蛋白酶、胶原酶和肽酶,其底物分别是蛋白质、胶原和肽;⑤脂质降解酶:包括酯酶和磷脂酶,其底物分别是脂肪酰基酯和磷脂[55]。所有的溶酶体酶都是酸性水解酶,在酸性pH值(4.5-5.0)下活性最佳[56]。然而,研究表明,几种溶酶体酶在中性pH值下也保持较低的活性[57-58]。研究表明溶酶体酶与代谢功能之间存在相互作用,一方面溶酶体酶发生缺陷会影响细胞内代谢废物的清除、脂质堆积等,导致脂质和糖类代谢紊乱,进而与代谢综合征的发生发展密切相关。另一方面,代谢综合征也会进一步导致溶酶体酶的活性异常,形成一种恶性循环,见图5。例如,在糖尿病肾病中,肾细胞的溶酶体结构和功能受损,引起患者血清组织蛋白酶L活性增加[59]。BRINGS等[60]在141例2型糖尿病肾病患者中发现血清组织蛋白酶L水平与患者蛋白尿的严重程度呈正相关,而高尿组织蛋白酶L水平可以预测2型糖尿病患者白蛋白尿的改善情况。与之相关的,GARSEN等[61]研究发现组织蛋白酶L缺乏的糖尿病小鼠没有出现白蛋白尿,这也意味着组织蛋白酶L在糖尿病肾病的发病机制中起着关键作用。除此之外,研究发现血浆组织蛋白酶D活性在2型糖尿病患者中受到影响,由于糖尿病患者血糖升高代谢紊乱,可引起血浆pH值降低,进而升高血浆组织蛋白酶D的活性[62]。
此外,溶酶体功能的损害也可能影响非酒精性脂肪肝病的进展。例如,S-亚硝基谷胱甘肽还原酶活性的降低与肥胖和糖尿病相关,这可能导致溶酶体硝基应激增加和自噬受损,从而导致肝脏胰岛素抵抗[63]。由此可见,溶酶体酶与代谢功能之间存在相互作用,二者相互影响,形成恶性循环。
2.2.2 溶酶体功能在代谢中的作用 溶酶体通过降解、回收和清除等功能,在细胞代谢中起到核心作用,维持细胞稳态并支持多种生理过程,从而在机体的生理功能活动中发挥重要作用。溶酶体功能及其在代谢中的作用如下所述:
(1)降解大分子:溶酶体的一个基本特征是其酸性的腔(pH值为 4.5–5.0),这有助于溶酶体酶的最佳功能。溶酶体腔的酸性pH值是由位于溶酶体膜上的囊泡型H+-ATPase(v-ATPase)的作用产生的,该酶从细胞质中导入H+离子,其中ATP被水解[53]。从功能上讲,溶酶体过去主要被认为是细胞的关键消化系统,在这里不仅降解来自细胞外的物质,还消化细胞成分,例如衰老的细胞器或未使用的细胞质物质[53]。因此,溶酶体通过3条途径消化物质:①内吞作用:通过内吞小泡从细胞外摄取的分子;②吞噬作用:大颗粒(如细菌)被摄入到吞噬泡或吞噬体中;③自噬:降解和回收细胞自身成分。例如,近些年,在脂质代谢中,脂肪吞噬被确定为一种独特的自噬形式,包括巨噬脂、微噬脂和伴侣介导的自噬,这3种脂噬途径有助于三酰甘油等脂质的降解[64]。在葡萄糖代谢中,溶酶体还参与糖原自噬,利用α-酸性葡萄糖苷酶,降解糖原为葡萄糖,补充血糖水平[65]。在溶酶体降解后,许多产物,如氨基酸和核苷酸,会被回收回细胞以合成新的细胞成分或通过胞吐作用排出[52]。
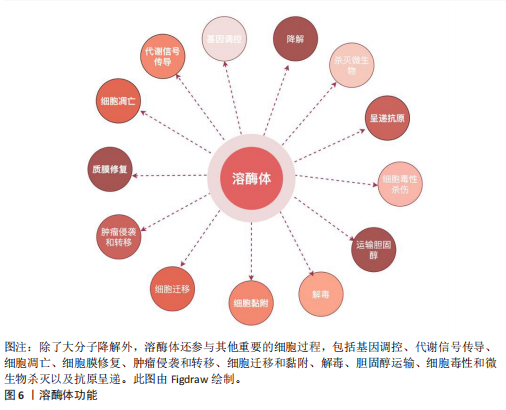
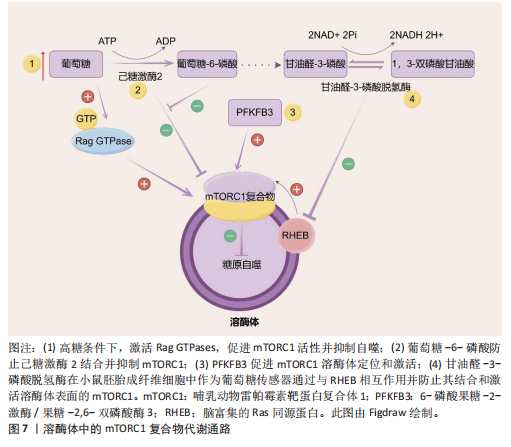
(2)调节细胞过程以维持生理稳态:除了作为细胞的消化系统外,溶酶体还被认为是细胞稳态的重要调节者[66]。最近的研究表明,溶酶体还参与了其他细胞过程,包括杀死细胞内病原体、抗原呈递、质膜修复、外泌体释放、细胞黏附和迁移、肿瘤侵袭和转移、凋亡、代谢信号传导和基因调控(图6)。其中有两个关键的营养感应网络将代谢信息传递给溶酶体:第一个为哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR)复合体1(mTORC1)营养感应信号网络,该网络在激活前被招募到溶酶体表面,参与细胞生长并抑制自噬,例如,在小鼠胚胎成纤维细胞中,葡萄糖可以通过Rag GTPase将信号传递给溶酶体表面的mTORC1[67];第二个为腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶(AMP-activated protein kinase,AMPK)信号网络,该网络感知细胞能量状态并在能量不足条件下激活自噬。当葡萄糖供应充足时,甘油醛-1,6-二磷酸结合醛缩酶,阻止醛缩酶与钙转运瞬时受体电位通道亚家族V(Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid,TRPV)和v-ATPase相互作用,抑制自噬[68]。这些证据表明溶酶体在细胞功能和生理稳态中起着关键作用。
(3)溶酶体外排:虽然溶酶体位于细胞质中,但其位置会因溶酶体在细胞中心与边缘之间的运动而改变,这一过程可能受到细胞扰动的影响。正如前文提到的溶酶体降解后的产物也可以通过胞吐作用释放。新兴研究表明,溶酶体通过溶酶体胞吐作用参与细胞外空间中的细胞间通讯,这一过程是指溶酶体通过与质膜融合在不同刺激下将其内容物释放到细胞外。溶酶体胞吐作用是任何细胞类型都有的重要功能。一旦释放,溶酶体的内容物会在细胞外液体中以不同的时间和距离移动,并随后与识别的目标细胞相互作用以实现细胞间通讯[69]。相关地,溶酶体胞吐作用在多种生理过程中发挥关键作用,例如细胞毒性T淋巴细胞的脱颗粒作用[70],破骨细胞介导的骨吸收[71],色素沉着期间的黑素细胞功能[72],对寄生虫攻击的免疫反应,精子在受精过程中释放水解酶以及血小板在凝血中的功能[73]。在糖脂代谢过程中,溶酶体通过其内的酶类,如酸性水解酶、分解糖脂等物质,释放出可以被细胞再次利用的基本组成单位,如糖分子和脂肪酸。脂肪酸是重要的能量代谢来源,同时也参与到细胞信号(如过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ信号通路传导中[74],影响细胞的生长和分化[75]。因此,溶酶体胞吐作用发挥着重要的生理功能。
总的来说,溶酶体不仅是细胞内的“垃圾处理站”,还是代谢网络中的关键节点。理解溶酶体在代谢中的具体作用及其功能障碍的影响,对于揭示疾病机制和开发新的治疗策略具有重要意义。
2.3 溶酶体酶与代谢性疾病的关系 溶酶体已成为代谢信号传导的中心枢纽,在此过程中,信号通路将溶酶体与控制细胞代谢许多方面的关键合成和分解代谢过程联系起来[76]。此外,如前所述,溶酶体酶也参与了代谢功能,包括降解脂质(即溶酶体酸性脂肪酶)、碳水化合物(即β-半乳糖苷酶)、 蛋白质(即组织蛋白酶)和核
酸(即核酸酶)。一方面,新兴研究表明,溶酶体酶的功能障碍导致多种代谢紊乱,表明溶酶体酶在代谢中的重要性。事实上,研究观察到糖尿病大鼠胰岛溶酶体功能障碍和涉及葡萄糖代谢的几种溶酶体酶催化活性降低(即酸性葡聚糖-1,4-α-葡萄糖苷酶和酸性α-葡萄糖苷酶),这是糖尿病大鼠模型的一个重要缺陷。因此,这种缺陷损害了胰岛中营养刺激的胰岛素释放机制,从而导致糖尿病大鼠葡萄糖代谢紊乱。另一方面,代谢紊乱,如在代谢综合征中观察到的情况,也会导致溶酶体酶功能障碍。例如,肥胖通过氧化应激和溶酶体pH值异常导致组织蛋白酶L成熟下降,进而导致组织蛋白酶L活性下调,引发另一种酶(即组织蛋白酶B)的异常激活,从而导致溶酶体功能障碍。同样,肥胖引起的肝脏内异位脂质积累(脂质代谢紊乱)已被证明与溶酶体蛋白酶及其他溶酶体酶的异常有关。以下就溶酶体酶在2型糖尿病、脂肪肝和肥胖中的病理作用机制进行重点阐述。
2.3.1 2型糖尿病中的溶酶体酶 溶酶体酶在糖原生成、糖原分解和糖基化中发挥作用,因此与整体葡萄糖代谢相关。事实上,研究表明几种异常的组织蛋白酶与胰岛素抵抗有关,凸显了溶酶体酶在2型糖尿病中的重要性。此外,另一种溶酶体酶,己糖胺酶A也参与调节胰岛素敏感性,因为它通过去除N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖残基将GM2神经节苷脂转化为GM3神经节苷脂,而GM3神经节苷脂参与胰岛素抵抗。因此,溶酶体酶功能障碍是导致葡萄糖代谢紊乱并进而引发2型糖尿病的一个触发因素。此外,2型糖尿病也会导致溶酶体酶的异常。例如,链脲佐菌素诱导的糖尿病会导致大鼠肝脏中半胱氨酸蛋白酶(特别是组织蛋白酶B)的特异性活性降低,其中基因表达降低可能是导致酶活性降低的机制之一。近年来的研究表明,溶酶体不仅是细胞内的“消化器官”,还参与了多种信号传导通路,如mTOR通路。代谢综合征患者的mTOR通路可能过度激活,导致细胞对胰岛素的敏感性下降。另一项研究表明,溶酶体通过mTOR通路感知细胞内外的营养状态。其具体机制除了2.2.2中简要阐述的Rag GTPases途径,还包括:①在心肌细胞和非心肌细胞中,糖酵解中间产物葡萄糖-6-磷酸阻止糖酵解酶己糖激酶2与mTORC1结合并抑制mTORC1[77]。②一种糖酵解调节剂,6-磷酸果糖-2-激酶/果糖-2,6-双磷酸酶3(6-phosphofructo-2- kinase/fructose-2,6-biphospatase 3,PFKFB3)在癌细胞中促进mTORC1溶酶体定位和激活[78]。③甘油醛-3-磷酸脱氢酶(Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase,GAPDH)被证明在小鼠胚胎成纤维细胞中作为葡萄糖传感器通过与脑富集的Ras同源蛋白(Ras homolog enriched in brain,RHEB)相互作用并防止其结合和激活溶酶体表面的mTORC1[79](图7)。除此之外,一项研究发现作为最常用的抗糖尿病药物,二甲双胍通过早老素增强蛋白2靶向溶酶体AMPK通路,其机制为早老素增强蛋白2通过与ATP6AP1结合抑制v-ATPase的活性,激活溶酶体AMPK,从而实现二甲双胍的有益效应[80](图8)。此外,胰岛β细胞溶酶体功能障碍是2型糖尿病的重要机制。例如,Niemann-Pick病C1型蛋白通过保障溶酶体正常功能,调控线粒体自噬过程,进而促进线粒体氧化磷酸化介导的代谢重编程,这确保了胰岛β细胞分化成熟及功能正常[81]。总的来说,这些不断积累的证据突显了溶酶体酶在2型糖尿病中的重要作用,从而为2型糖尿病的发病机制提供了新的视角。
2.3.2 非酒精性脂肪肝病中的溶酶体酶 除了在2型糖尿病中的作用外,溶酶体酶还因在调节脂质代谢中的作用而在非酒精性脂肪肝病中显得重要。一项临床研究发现,患有代谢综合征的患者中血清芳基硫酸酯酶活性增加以及酸性磷酸酶活性较低,可能是因为溶酶体功能下降,并且与脂肪组织数量有关[82]。事实上,最近的研究揭示了溶酶体酸性脂肪酶介导的脂解在调节脂质介质(如花生四烯酸类和血栓素B2,这类生物活性脂质通过特定的生物合成途径在细胞外刺激下局部产生)的生成[83]、极低密度脂蛋白分泌、细胞外聚集低密度脂蛋白的降解以及脂肪组织脂解中的作用,表明了溶酶体酶在脂质代谢中的重要性。然而,溶酶体酶在脂质代谢中的功能障碍是导致非酒精性脂肪肝病发展的病理触发因素之一。例如,新兴研究表明,非酒精性脂肪肝病的特
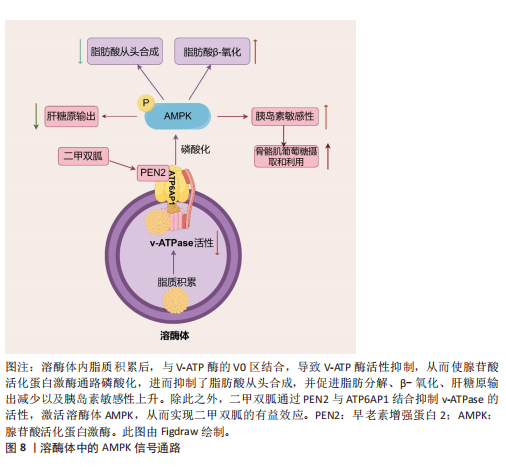
点是溶酶体酸性脂肪酶活性的具体缺陷,提示溶酶体酸性脂肪酶在非酒精性脂肪肝病中的致病作用。另一项研究发现,溶酶体酸性脂酶缺乏使得小鼠肝脏脂质代谢异常、炎症反应增强、纤维化及癌症相关蛋白的失调以及能量代谢紊乱。CAROTTI等[84]研究发现溶酶体酸性脂肪酶在体内体外实验模型和非酒精性脂肪肝患者中经历了泛素化修饰,导致其N端区域被遮蔽,影响了酶的活性,并且这些修饰后的溶酶体酸性脂肪酶倾向于聚集在溶酶体外;证明了泛素化、功能失调的溶酶体酸性脂肪酶积累与疾病的严重程度有关联,特别是与微泡性脂肪变性和脂质溶酶体等非酒精性脂肪肝患者的病理特征有关。mTOR通路的异常还会影响能量代谢,导致脂肪堆积和葡萄糖代谢紊乱。FUKUO等[85]发现叶酸代谢紊乱通过抑制mTOR信号通路下调组织蛋白酶L的表达,进而阻碍自噬体-溶酶体的成熟,最终导致脂质在肝细胞中的堆积。此外,其他研究也观察到非酒精性脂肪肝病患者肝内组织蛋白酶(如组织蛋白酶B、组织蛋白酶D和组织蛋白酶L)的表达降低,这与自噬蛋白水解的抑制有关。ZHAO等[86]研究发现聚胍纳米抑制剂进入溶酶体后,与V-ATP酶的V0区相互作用并靶向结合,导致V-ATP酶活性抑制,从而激活了AMPK通路,进而抑制了脂肪酸从头合成,并促进脂肪分解和β-氧化,最终改善了肝脏中的脂质积累(图8)。因此,大量证据表明溶酶体酶与非酒精性脂肪肝病发病机制之间存在联系,使溶酶体酶也成为理解非酒精性脂肪肝病进展机制的核心。
2.3.3 肥胖中的溶酶体酶 肥胖是世界上最常见的代谢疾病之一,其特征在于脂肪细胞内三酰甘油的异常积累。最近的研究表明,自噬调节脂质动员以维持能量平衡,而自噬与溶酶体密不可分,自噬小体形成后,会与溶酶体融合形成自噬溶酶体。在自噬溶酶体中,自噬小体内的货物被溶酶体中的水解酶逐步降解为氨基酸、核苷酸、脂肪酸等基本单元。一项研究发现,在Trp53诱导的糖酵解调节磷酸酶(TP53-Induced Glycolysis and Apoptosis Regulator,TIGAR)转基因小鼠中,脂肪量增加且倾向于肥胖表型,定量转录组测序确定了TIGAR小鼠脂肪组织中富含亮氨酸重复序列的激酶2(leucine-rich repeat kinase 2,LRRK2)和Rab7B小分子GTP酶(Ras-related protein Rab-7B,RAB7B)水平的增加[87]。且该团队临床试验证实TIGAR过表达通过抑制聚泛素化降解而增加LRRK2的水平,从而抑制巨自噬和伴侣介导的自噬,同时增加脂质积累[87]。以肥胖为基础,容易引起其他疾病的发生,如肥胖相关肾小球病等。研究表明,在足细胞中的酸性鞘磷脂酶通过调控NOD样受体家族吡啉结构域包含蛋白3(NOD-like receptor pyrin domain containing 3,NLRP3)炎性小体激活和外泌体释放,在肥胖引起的肾小球炎症和损伤中起着关键作用[88]。在肥胖状态下,脂肪组织中的巨噬细胞通过吞噬和清除死亡或凋亡的脂肪细胞,维持组织稳态的功能受到干扰,跨膜4 L六家族成员19(Transmembrane 4 L Six Family Member 19,TM4SF19)被证明是一种表达在巨噬细胞中的溶酶体蛋白。CHOI等[89]团队研究发现高脂饮食导致的肥胖增加了脂肪组织中巨噬细胞TM4SF19的表达,通过与溶酶体的V-ATPase相互作用,TM4SF19抑制了溶酶体酸化,影响了巨噬细胞清除凋亡脂肪细胞的能力。TM4SF19的缺失增加了溶酶体酸化,加速了凋亡脂肪细胞的清除。2021年,ZHAO等[90]为了探索新的调控脂肪生成的关键因子,对小鼠和人的前脂肪细胞分化组学数据进行大规模系统生物学筛选,发现溶酶体蛋白含Bax抑制基序的跨膜蛋白1(Transmembrane Bax Inhibitor Motif Containing 1,TMBIM1)在小鼠脂肪前体细胞3T3-L1中进行敲减后会促进前脂肪细胞分化过程并且显著提高脂肪合成通路关键基因PPARγ和CEBPα的表达量;而在3T3-L1细胞中过表达TMBIM1后脂肪积累减少,研究证明其机制为TMBIM1通过降低E3泛素连接酶神经前体细胞表达发育调控样蛋白4(NEDD4)介导的PPARγ稳定性而显著抑制脂肪生成。溶酶体酶在肥胖的发生和发展过程中扮演了重要角色,如TIGAR、酸性鞘磷脂酶、TM4SF19及TMBIM1不仅影响脂肪组织的功能,还与多种代谢紊乱密切相关。深入理解溶酶体酶的作用机制,有助于开发新的治疗策略,应对肥胖及其并发症。
这些证据表明溶酶体酶在代谢综合征的发生发展中扮演着重要角色。但在另一方面,目前大多数研究溶酶体酶仅停留在是否与疾病相关,缺乏足够的证据证明溶酶体酶功能障碍是导致代谢综合征的原因还是结果。不同个体因为遗传背景、生活方式和环境等因素影响,其溶酶体酶活性有所不同,这使得难以解释为何并非所有具有相同风险因素的人都会患上代谢综合征。而大多数研究使用的是动物模型,这并不能完全模拟人类复杂的生理环境,所以某些结论可能无法直接外推到人体。建议在未来开展引入大数据分析方法,例如整合多组学数据(如基因组、转录组、蛋白质组等)来探究个体特异性因素对溶酶体酶活性及代谢状态的影响。虽然现有研究表明溶酶体酶可能在代谢综合征中扮演着重要角色,但仍需进一步深入研究来克服上述问题与挑战,以便为该领域提供更加准确可靠的科学依据。

| [1] HU LW, GONG YC, ZOU HX, et al. Outdoor light at night is a modifiable environmental factor for metabolic syndrome: The 33 Communities Chinese Health Study (33CCHS). Sci Total Environ. 2024;954:176203. [2] ALBERTI KG, ECKEL RH, GRUNDY SM, et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation. 2009;120(16):1640-1645. [3] ENGIN A. The Definition and Prevalence of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome: Correlative Clinical Evaluation Based on Phenotypes. Adv Exp Med Biol.2024;1460: 1-25. [4] EXPERT PANEL ON DETECTION E, TREATMENT OF HIGH BLOOD CHOLESTEROL IN A. Executive Summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, And Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA. 2001;285(19): 2486-2497. [5] ADJEI NK, SAMKANGE-ZEEB F, BOAKYE D, et al. Ethnic differences in metabolic syndrome in high-income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2024;25(4): 727-750. [6] FERRARI CKB. Chapter 6 - Epidemiology of metabolic syndrome: global scenario//MUKHOPADHYAY S, MONDAL S. Metabolic Syndrome. Academic Press, 2024:59-71. [7] DIEGO VP, MANUSOV EG, MAO X, et al. Metabolic syndrome traits exhibit genotype-by-environment interaction in relation to socioeconomic status in the Mexican American family heart study. Front Genet. 2024;15:1240462. [8] CAMERON AJ, SHAW JE, ZIMMET PZ. The metabolic syndrome: prevalence in worldwide populations. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2004;33(2):351-375. [9] PRONE-OLAZABAL D, DAVIES I, GONZÁLEZ-GALARZA FF. Metabolic Syndrome: An Overview on Its Genetic Associations and Gene–Diet Interactions. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2023;21(10):545-560. [10] ALBERTI KG, ZIMMET P, SHAW J, et al. The metabolic syndrome--a new worldwide definition. Lancet. 2005;366(9491):1059-1062. [11] ZHANG Y, GAO Y, LIU QS, et al. Chemical contaminants in blood and their implications in chronic diseases. J Hazard Mater. 2024;466:133511. [12] WANG G, SHEN X, WANG Y, et al. Analysis of risk factors related to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a retrospective study based on 31,718 adult Chinese individuals. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1168499. [13] SHEASHEA M, XIAO JB, FARAG MA. MUFA in metabolic syndrome and associated risk factors: is MUFA the opposite side of the PUFA coin? Food Funct. 2021;12(24): 12221-12234. [14] REGGIORI F, MOLINARI M. ER-phagy: mechanisms, regulation, and diseases connected to the lysosomal clearance of the endoplasmic reticulum. Physiol Rev. 2022;102(3):1393-1448. [15] ARDEN C, PARK SH, YASASILKA XR, et al. Autophagy and lysosomal dysfunction in diabetes and its complications. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2024;35(12):1078-1090. [16] HAMADOU AH, ZHANG JY, LI HT, et al. Modulating the glycemic response of starch-based foods using organic nanomaterials: strategies and opportunities. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(33):11942-11966. [17] HAO WJ, HE ZY, ZHU HY, et al. Sea buckthorn seed oil reduces blood cholesterol and modulates gut microbiota. Food Funct. 2019;10(9):5669-5681. [18] LI BY, XU XY, GAN RY, et al. Targeting Gut Microbiota for the Prevention and Management of Diabetes Mellitus by Dietary Natural Products. Foods. 2019; 8(10):440. [19] XU S, LU F, GAO J, et al. Inflammation-mediated metabolic regulation in adipose tissue. Obes Rev. 2024;25(6):e13724. [20] LI XL, HUANG J, YUN JH, et al. D-Arabitol Ameliorates Obesity and Metabolic Disorders via the Gut Microbiota-SCFAs-WAT Browning Axis. J Agric Food Chem. 2023;71(1):522-534. [21] PENG Y, GU T, ZHONG T, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in metabolic disorders: opposite roles of phytochemicals and food contaminants. Curr Opin Food Sci. 2022;48:100913. [22] GUO C, ZHANG L, ZHAO M, et al. Targeting lipid metabolism with natural products: A novel strategy for gastrointestinal cancer therapy. Phytother Res. 2023;37(5):2036-2050. [23] GROS F, MULLER S. The role of lysosomes in metabolic and autoimmune diseases. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2023;19(6):366-383. [24] SHAH IU, SAMEEN A, MANZOOR MF, et al. Association of dietary calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D with type 2 diabetes among US adults: National health and nutrition examination survey 2007–2014—A cross-sectional study. Food Sci Nutr. 2021;9(3): 1480-1490. [25] SACCHETTA L, CHIRIACÒ M, NESTI L, et al. Synergistic effect of chronic kidney disease, neuropathy, and retinopathy on all-cause mortality in type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a 21-year longitudinal study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022;21(1):233. [26] DZIEGIELEWSKA-GESIAK S. Metabolic Syndrome in an Aging Society – Role of Oxidant-Antioxidant Imbalance and Inflammation Markers in Disentangling Atherosclerosis. Clin Interv Aging. 2021;16: 1057-1070. [27] BALLING M, AFZAL S, SMITH GD, et al. Elevated LDL Triglycerides and Atherosclerotic Risk. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2023;81(2):136-152. [28] LI M, CHI X, WANG Y, et al. Trends in insulin resistance: insights into mechanisms and therapeutic strategy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):216. [29] ZIOLKOWSKA S, BINIENDA A, JABŁKOWSKI M, et al. The Interplay between Insulin Resistance, Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, Base Excision Repair and Metabolic Syndrome in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(20):11128. [30] BARBER TM, KYROU I, RANDEVA HS, et al. Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance at the Crossroad of Obesity with Associated Metabolic Abnormalities and Cognitive Dysfunction. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(2):546. [31] ARONOFF SL, BERKOWITZ K, SHREINER B. Glucose metabolism and regulation: beyond insulin and glucagon. Diabetes Spectr. 2004;17(3):183-190. [32] GERICH JE, SCHNEIDER V, DIPPE SE, et al. Characterization of the glucagon response to hypoglycemia in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974;38(1):77-82. [33] DASNANDY A, VIRGE R, HEGDE HV, et al. A review of patent literature on the regulation of glucose metabolism by six phytocompounds in the management of diabetes mellitus and its complications. J Integr Med. 2023;21(3):226-235. [34] TU J, LIU G, CAO X, et al. Hypoglycemic effects of wheat bran alkyresorcinols in high-fat/high-sucrose diet and low-dose streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic male mice and protection of pancreatic β cells. Food Funct. 2019;10(6):3282-3290. [35] MIZUNOE Y, KOBAYASHI M, TAGAWA R, et al. Association between Lysosomal Dysfunction and Obesity-Related Pathology: A Key Knowledge to Prevent Metabolic Syndrome. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(15):3688. [36] ELENDU C, DAVID JA, UDOYEN AO, et al. Comprehensive review of diabetic ketoacidosis: an update. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023;85(6):2802-2807. [37] SANGHAVI SF, SWENSON ER. Arterial Blood Gases and Acid–Base Regulation. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2023;44(5): 612-626. [38] GUI J, LI Y, LIU H, et al. Obesity-and lipid-related indices as a predictor of obesity metabolic syndrome in a national cohort study. Front Public Health. 2023;11: 1073824. [39] HEGELE RA. Plasma lipoproteins: genetic influences and clinical implications. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10(2):109-121. [40] BROWN MS, GOLDSTEIN JL. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1986;232(4746):34-47. [41] ENGIN A. Lipid Storage, Lipolysis, and Lipotoxicity in Obesity. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1460:97-129. [42] JAFFAR HM, UL AIN HB, TUFAIL T, et al. Impact of silymarin-supplemented cookies on liver enzyme and inflammatory markers in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients. Food Sci Nutr. 2024;12(10):7273-7286. [43] WEI K, WEI Y, XU WD, et al. Corn peptides improved obesity-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through relieving lipid metabolism, insulin resistance and oxidative stress. Food Funct. 2022;13(10):5782-5793. [44] GUGLIUCCI A. Triglyceride-Rich Lipoprotein Metabolism: Key Regulators of Their Flux. J Clin Med. 2023;12(13): 4399. [45] DAS D, SHRUTHI NR, BANERJEE A, et al. Endothelial dysfunction, platelet hyperactivity, hypertension, and the metabolic syndrome: molecular insights and combating strategies. Front Nutr. 2023; 10:1221438. [46] DAHIK VD, KC P, MATERNE C, et al. ABCG1 orchestrates adipose tissue macrophage plasticity and insulin resistance in obesity by rewiring saturated fatty acid pools. Sci Transl Med. 2024;16(777):eadi6682. [47] FLORES-OPAZO M, KOPINKE D, HELMBACHER F, et al. Fibro-adipogenic progenitors in physiological adipogenesis and intermuscular adipose tissue remodeling. Mol Aspects Med. 2024;97: 101277. [48] LEMOS GDO, TORRINHAS RS, WAITZBERG DL. Nutrients, Physical Activity, and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Setting of Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients. 2023;15(5): 1217. [49] BODEN G. Role of fatty acids in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance and NIDDM. Diabetes. 1997;46(1):3-10. [50] RODEN M, PRICE TB, PERSEGHIN G, et al. Mechanism of free fatty acid-induced insulin resistance in humans. J Clin Invest. 1996;97(12):2859-2865. [51] PU J, GUARDIA CM, KEREN-KAPLAN T, et al. Mechanisms and functions of lysosome positioning. J Cell Sci. 2016;129(23): 4329-4339. [52] The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. Lysosome. Encyclopedia Britannica. 2025. [53] GM C. Lysosome. The Cell: A Molecular Approach. Sinauer Associates Inc. 2000. [54] FERRARI V, TEDESCO B, COZZI M, et al. Lysosome quality control in health and neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024;29(1):116. [55] MURAKAMI M. The phospholipase A2 superfamily as a central hub of bioactive lipids and beyond. Pharmacol Ther. 2023; 244:108382. [56] NIXON RA. Autophagy–lysosomal-associated neuronal death in neurodegenerative disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2024;148(1): 42. [57] FREEMAN SA, GRINSTEIN S, ORLOWSKI J. Determinants, maintenance, and function of organellar pH. Physiol Rev. 2023;103(1): 515-606. [58] MÄCHTEL R, BOROS FA, DOBERT JP, et al. From Lysosomal Storage Disorders to Parkinson’s Disease–Challenges and Opportunities. J Mol Biol. 2023;435(12): 167932. [59] WU M, ZHANG M, ZHANG Y, et al. Relationship between lysosomal dyshomeostasis and progression of diabetic kidney disease. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(11):958. [60] BRINGS S, FLEMING T, HERZIG S, et al. Urinary cathepsin L is predictive of changes in albuminuria and correlates with glucosepane in patients with type 2 diabetes in a closed-cohort study. J Diabetes Complications. 2020;34(9):107648. [61] GARSEN M, ROPS AL, DIJKMAN H, et al. Cathepsin L is crucial for the development of early experimental diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2016;90(5):1012-1022. [62] DING L, HOUBEN T, OLIGSCHLAEGER Y, et al. Plasma Cathepsin D Activity Rather Than Levels Correlates With Metabolic Parameters of Type 2 Diabetes in Male Individuals. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11:575070. [63] QIAN Q, ZHANG Z, ORWIG A, et al. S-Nitrosoglutathione Reductase Dysfunction Contributes to Obesity-Associated Hepatic Insulin Resistance via Regulating Autophagy. Diabetes. 2017; 67(2):193-207. [64] GRABNER GF, XIE H, SCHWEIGER M, et al. Lipolysis: cellular mechanisms for lipid mobilization from fat stores. Nat Metab. 2021;3(11):1445-1465. [65] MANCINI MC, NOLAND RC, COLLIER JJ, et al. Lysosomal glucose sensing and glycophagy in metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2023;34(11):764-777. [66] BOYA P. Lysosomal function and dysfunction: mechanism and disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012;17(5):766-774. [67] DE LA CALLE ARREGUI C, PLATA-GÓMEZ AB, DELEYTO-SELDAS N, et al. Limited survival and impaired hepatic fasting metabolism in mice with constitutive Rag GTPase signaling. Nat Commun. 2021; 12(1):3660. [68] EATON AF, MERKULOVA M, BROWN D. The H+-ATPase (V-ATPase): from proton pump to signaling complex in health and disease. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021;320(3): C392-C414. [69] MELDOLESI J. Exosomes and Ectosomes in Intercellular Communication. Curr Biol. 2018;28(8):R435-R444. [70] CHANG HF, SCHIRRA C, PATTU V, et al. Lytic granule exocytosis at immune synapses: lessons from neuronal synapses. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1177670. [71] MOSTOV K, WERB Z. Journey across the osteoclast. Science. 1997;276(5310):219-20. [72] NETO MV, HALL MJ, CHARNECA J, et al. Photoprotective melanin is maintained within keratinocytes in a storage lysosome. J Invest Dermatol. 2024; 2024.02.05.578910. [73] FERNÁNDEZ-INFANTE C, HERNÁNDEZ-CANO L, HERRANZ Ó, et al. Platelet C3G: a key player in vesicle exocytosis, spreading and clot retraction. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024; 81(1):84. [74] FENG W, LIANG J, XU B, et al. Fatty acid metabolism affects hepatocellular carcinoma progression via the PPAR-γ signaling pathway and fatty acid β-oxidation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024; 141:112917. [75] CORBO JH, CHUNG J. Mechanisms of lipid droplet degradation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2024;90:102402. [76] LAMMING DW, BAR-PELED L. Lysosome: The metabolic signaling hub. Traffic. 2019; 20(1):27-38. [77] CHEN S, ZOU Y, SONG C, et al. The role of glycolytic metabolic pathways in cardiovascular disease and potential therapeutic approaches. Basic Res Cardiol. 2023;118(1):48. [78] CHU Y, CHANG Y, LU W, et al. Regulation of Autophagy by Glycolysis in Cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2020;12:13259-13271. [79] WALTON ZE, BROOKS RC, DANG CV. mTOR Senses Intracellular pH through Lysosome Dispersion from RHEB. BioEssays. 2019;41(7):1800265. [80] MA T, TIAN X, ZHANG B, et al. Low-dose metformin targets the lysosomal AMPK pathway through PEN2. Nature. 2022; 603(7899):159-165. [81] LIU B, HUA D, SHEN L, et al. NPC1 is required for postnatal islet β cell differentiation by maintaining mitochondria turnover. Theranostics. 2024;14(5):2058-2074. [82] OLSZEWSKA-SŁONINA DM. Serum Arylsulfatase and Acid Phosphatase Activity in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome as a Result of Oxidative Damage to Lysosomes. Protein Pept Lett. 2021;28(11):1246-1258. [83] LUBRANO V, NDREU R, BALZAN S. Classes of lipid mediators and their effects on vascular inflammation in atherosclerosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(2):1637. [84] CAROTTI S, LETTIERI-BARBATO D, PIEMONTE F, et al. Molecular and histological traits of reduced lysosomal acid lipase activity in the fatty liver. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(12): 1092. [85] FUKUO Y, YAMASHINA S, SONOUE H, et al. Abnormality of autophagic function and cathepsin expression in the liver from patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol Res. 2014;44(9):1026-1036. [86] ZHAO Y, HU K, WANG F, et al. Guanidine-Derived Polymeric Nanoinhibitors Target the Lysosomal V-ATPase and Activate AMPK Pathway to Ameliorate Liver Lipid Accumulation. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025;12(1): e2408906. [87] ZHANG T, LINGHU KG, TAN J, et al. TIGAR exacerbates obesity by triggering LRRK2-mediated defects in macroautophagy and chaperone-mediated autophagy in adipocytes. Autophagy. 2024;20(8):1741-1761. [88] HUANG D, KIDD JM, ZOU Y, et al. Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Inflammatory Exosome Release in Podocytes by Acid Sphingomyelinase During Obesity. Inflammation. 2023;46(5):2037-2054. [89] CHOI C, JEONG YL, PARK KM, et al. TM4SF19-mediated control of lysosomal activity in macrophages contributes to obesity-induced inflammation and metabolic dysfunction. Nat Commun. 2024; 15(1):2779. [90] ZHAO GN, TIAN ZW, TIAN T, et al. TMBIM1 is an inhibitor of adipogenesis and its depletion promotes adipocyte hyperplasia and improves obesity-related metabolic disease. Cell Metab. 2021;33(8):1640-1654.e8. |
| [1] | 文 凡, 向 阳, 朱 欢, 庹艳芳, 李 锋. 运动干预改善2型糖尿病患者的微血管功能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1225-1235. |
| [2] | 温小龙, 翁锡全, 冯 瑶, 曹文燕, 刘玉倩, 王海涛, . 炎症对2型糖尿病患者血清抗菌多肽及铁代谢相关参数影响的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1294-1301. |
| [3] | 鄢成波, 罗秋池, 樊佳兵, 顾叶婷, 邓 倩, 张军梅. 2型糖尿病对大鼠正畸牙移动与张力侧骨微结构参数的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(4): 824-831. |
| [4] | 曹文琪, 冯秀芝, 赵 奕, 王智民, 陈怡然, 杨 潇, 任艳玲. 巨噬细胞极化对2型糖尿病性骨质疏松症成骨-成血管偶联的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(4): 917-925. |
| [5] | 李怡文, 刘飞祥, 张运克. 干细胞调控溶酶体功能治疗溶酶体贮积症[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(1): 145-152. |
| [6] | 陈启衡, 翁土军, 彭 江. 二甲基氧化甘氨酸对人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨、成脂分化及线粒体自噬的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(1): 50-57. |
| [7] | 苏晓杨, 陈文婷, 付怡丹, 赵 燕, 兰丹凤, 杨秋萍. Mer受体酪氨酸激酶与SD大鼠糖尿病周围神经病变的相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1593-1599. |
| [8] | 蔡之幸, 夏秋芳, 陈莉莉, 朱丹阳, 朱慧雯, 孙亚男, 梁文玉, 赵鹤倩. 柔肌顺膵饮改善2型糖尿病小鼠骨骼肌胰岛素抵抗的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(35): 7537-7543. |
| [9] | 王 通, 郑 宇, 贾承明, 杨 虎, 张广飞, 纪垚垚. 基于TCMSP数据库分析葛根麻芪方治疗肩周炎并2型糖尿病的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(35): 7669-7678. |
| [10] | 孙雅蕙, 王宇峰, 郭 超, 姚俊杰, 纪媛媛, 李中旭, 娄惠娟, 江晶蕾, 孙一萍, 徐 婧, 丛德毓. 推拿对2型糖尿病大鼠骨骼肌细胞外基质胶原沉积的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(26): 5549-5555. |
| [11] | 陈春兰, 叶美仪, 潘雨薇, 袁 佳, 周朋君. 脐带间充质干细胞对 2 型糖尿病的免疫调节作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(23): 5031-5040. |
| [12] | 余杭林, 田浩冬, 文世媛, 黄 丽, 刘昊为, 李汉森, 王培松, 彭 莉. 高强度间歇性运动干预2型糖尿病患者糖代谢及肠道菌群的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(2): 286-293. |
| [13] | 胡淑娟, 程 平, 张 啸, 丁一庭, 刘 璇, 蒲 锐, 汪献旺. 不同强度运动干预2型糖尿病大鼠骨骼肌羧酸酯酶1及炎症因子的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(2): 269-278. |
| [14] | 罗云彩, 孟茂花, 李 英, 王 欢, 陆 婧, 舒佳玉, 李文杰, 孙金熠, 董 强, . 铜元素影响糖尿病并发症的发生与发展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(17): 3641-3649. |
| [15] | 江 强, 于 洁, 耿子翔, 王 宁, 郭 嘉, 杨光月, 王培歌, 赵咏芳. 两种肌少症小鼠模型的功能表型、肌肉质量及力量特点比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(14): 2922-2929. |
虽然其他异常(如慢性炎症)也与代谢综合征相关,但上述诊断标准被认为是代谢综合征的诊断金标准[2]。目前估计,亚洲人口中有12%-37%、欧洲人口中有12%-26%以及北美人口中有超过30%的人患有代谢综合征[5-6],这使得代谢综合征成为一个流行病。代谢综合征的流行是遗传因素和环境因素及其相互作用的结果(图1)[7-9]。此外,除了增加患心血管疾病和 2型糖尿病的风险外,患有代谢综合征的个体还面临发展为其他慢性疾病(如癌症和脂肪肝)的风险[2,10-13],这表明公共卫生面临着巨大挑战。
溶酶体是细胞内的一个重要细胞器,主要职能是负责分解和回收细胞内的废物物质,它们含有多种酸性水解酶,能够降解蛋白质、脂质、核酸等大分子。溶酶体通过自噬(autophagy)和内吞作用(endocytosis)摄取细胞内外的大分子,并利用其内部的酸性水解酶将其分解为小分子[14]。近些年研究表明溶酶体功能障碍与多种代谢性疾病密切相关,可能导致胰岛素抵抗及β细胞功能受损,从而影响糖尿病的发生和发展[15-16],也可能会影响脂
肪组织中脂滴的分解导致脂肪堆积从而增加体质量[17-18]。肥胖相关的慢性炎症也会由于溶酶体无法及时清除衰老或损伤的细胞成分导致炎症因子释放而进一步加重[19-20]。因此,溶酶体在代谢性疾病的发生和发展中起着至关重要的作用。 溶酶体酶在代谢性疾病中的研究虽然取得了显著进展,但仍面临诸多挑战。尽管某些溶酶体酶(如溶酶体酸性脂肪酶、组织蛋白酶)的功能障碍与代谢性疾病相关已经被实验证实,但其具体的分子靶点和作用机制尚未完全阐明。溶酶体功能障碍可能涉及多种因素的相互作用,如氧化应激、炎症反应、信号通路失调等,目前这些因素之间的关系尚不完全清楚。此文的目的是通过总结现有的研究成果,更好地理解溶酶体酶在代谢性疾病中的关键角色,并为进一步的临床应用和药物开发提供重要参考。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1 资料来源
1.1.1 检索时间 由第一作者在2024年10月进行检索。
1.1.2 文献检索时限 各数据库建库时间至2024年10月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed、Web of Science等数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 英文检索词为“metabolic syndrome,glucose metabolism,lipid metabolism,type 2 diabetes mellitus,non-alcoholic fatty liver disease,lysosomes,lysosomal enzymes”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 有关溶酶体和代谢综合征的基础研究及综述。
1.1.6 检索策略 PubMed数据库检索策略,见图2。
1.2 纳入和排除标准
纳入标准:有关溶酶体和代谢综合征的研究文献,以及在此领域有重要研究意义的文献。排除标准:非溶酶体研究;非代谢综合征研究;内容重复的研究;内容、数据不完整的研究。
1.3 数据提取 共检索到440篇文献,排除与研究目的相关性差及内容陈旧、重复的文献350篇,纳入90篇符合标准的文献进行综述,见图3。
3.1 既往他人在该领域研究的贡献和存在的问题 目前研究发现,溶酶体与细胞代谢在许多方面有所联系。在溶酶体中酶发挥了降解脂质、糖类物质、蛋白质和核酸的功能,溶酶体酶的重要性也体现在其功能障碍会导致多种代谢紊乱。有研究发现涉及葡萄糖代谢的几种溶酶体酶催化活性降低,是导致糖尿病发生的重要因素。另一方面,肥胖、糖尿病等代谢紊乱疾病也会导致溶酶体酶的功能缺陷,更进一步造成代谢综合征的发生发展。最近的研究中发现,导致非酒精性脂肪肝病发展的病理因素之一是溶酶体酶如酸性脂肪酶在脂质代谢中的功能障碍。此外,组织蛋白酶也与非酒精性脂肪肝病的发病机制存在联系。但是溶酶体酶在代谢综合征中的具体机制仍然需要深入探索。溶酶体酶不仅参与细胞内物质降解,还在信号传导、自噬等过程中发挥作用,它的多功能性和复杂性使研究代谢综合征的发生机制变得具有挑战性。且溶酶体与细胞内其他细胞器(如线粒体、内质网)之间的复杂相互作用在代谢综合征中尚未完全阐明。代谢综合征中溶酶体酶活性的影响因素包括转录后修饰、饮食、运动、药物及个体之间的差异等,仍需进一步研究。由于个体间溶酶体酶的差异,实现个性化的精准治疗仍需更多基础研究的支持。
3.2 该综述区别于他人他篇的特点 此文详细叙述了溶酶体酶(如组织蛋白酶D)在代谢综合征中的作用,包括它在葡萄糖代谢、脂质代谢以及非酒精性脂肪肝病中的具体机制。大多数综述可能仅提及溶酶体的一般功能,而此文深入到溶酶体酶的具体类型及在代谢紊乱中的作用。文章特别提到血浆溶酶体酶可能作为潜在的生物标志物,例如组织蛋白酶D是肝炎发展的敏感且特异的标志物,这为临床诊断提供了新的思路。
3.3 该综述的局限性 此文主要集中在溶酶体酶与代谢综合征的关系上,虽然这一领域非常重要但可能忽略了其他重要的代谢调控机制,如激素调节、神经内分泌系统的作用等。且大部分实验数据来自动物模型(如糖尿病大鼠),这些结果在人类中的适用性需要进一步验证,尤其是在临床试验阶段的数据支持不足。
3.4 综述的重要意义 代谢综合征作为全球性的公共卫生问题,其相关疾病如2型糖尿病和非酒精性脂肪肝病均严重影响人体健康。目前多项研究表明溶酶体酶的功能障碍与多种代谢紊乱有关,包括葡萄糖和脂质代谢紊乱,但有关溶酶体酶与代谢综合征发生发展的关系及作用机制尚不清楚。该综述概述了溶酶体在代谢综合征中的研究进展,为探究溶酶体酶在代谢综合征发病机制中的作用提供理论基础,并为寻找代谢性疾病的治疗靶点拓展了思路。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||