[1] ZHANG H, ZHOU J, GUAN J, et al. How to restore rotation center in total hip arthroplasty for developmental dysplasia of the hip by recognizing the pathomorphology of acetabulum and Harris fossa? J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):339.
[2] WANG Z, LI H, ZHOU Y, et al. Three-dimensional femoral morphology in Hartofilakidis type C developmental dysplastic hips and the implications for total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2020;44(10):1935-1942.
[3] DU Y, LI T, SUN J, et al. The Effect of the False Acetabulum on Femoral Proximal Medullary Canal in Unilateral Crowe Type IV Developmental Dislocation of the Hip. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2020; 16:631-637.
[4] NICHOLSON A, DUNNE K, TAAFFE S, et al. Developmental dysplasia of the hip in infants and children. BMJ. 2023;383:e074507.
[5] BREKELMANS WA, POORT HW, SLOOFF TJ. A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts. Acta Orthop Scand. 1972; 43(5):301-317.
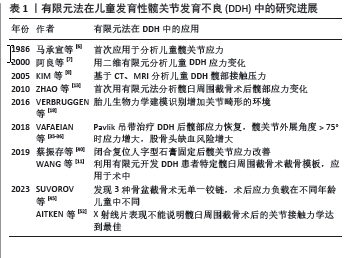
[6] 马承宣,刘贵林,房论光,等.儿童髋关节表面应力分布状态及与髋臼指数的关系[J]. 中华小儿外科杂志,1986,7(1):31-32.
[7] 阿良,吉士俊,范慈方.有限元分析先天性髋关节半脱位及髋臼发育不良的应力变化[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2000(6):7-10.
[8] KIM YH, PARK WM, CHOI IH. Planning of Shelf Operation in Dysplastic Hip by CT and MRI Based Finite Element Contact Analysis. JSME International Journal Series C. 2005; 48(4):586-591.
[9] 陈诺,邱丽华,常晓丹. 基于CT图像马拉松运动员步态周期中髋关节应力分布的有限元分析[J]. 中华放射学杂志,2023,57(12): 1305-1311.
[10] 田丰德, 赵德伟, 李东怡, 等. 髋臼缺损程度对成人髋关节应力影响的三维有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(3):380-384.
[11] WANG X, LIU S, PENG J, et al. Development of a novel customized cutting and rotating template for Bernese periacetabular osteotomy. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):217.
[12] CHEN S, ZHANG L, MEI Y, et al. Role of the Anterior Center-Edge Angle on Acetabular Stress Distribution in Borderline Development Dysplastic of Hip Determined by Finite Element Analysis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:823557.
[13] ZHAO X, CHOSA E, TOTORIBE K, et al. Effect of periacetabular osteotomy for acetabular dysplasia clarified by three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Orthop Sci. 2010;15(5):632-640.
[14] 张景贺, 窦永峰, 许世东, 等. 有限元模拟单通道分体内镜下双侧腰椎管减压对腰椎生物力学的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024, 28(12):1849-1854.
[15] FEYZI M, FALLAHNEZHAD K, TAYLOR M, et al. A review on the finite element simulation of fretting wear and corrosion in the taper junction of hip replacement implants. Comput Biol Med. 2021;130:104196.
[16] CHETHAN KN, SHYAMASUNDER BN, ZUBER M, et al. Finite element analysis of hip implant with varying in taper neck lengths under static loading conditions. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021; 208:106273.
[17] 张静, 萨日娜, 嘎拉台. 基于瞬态分析的桡骨远端骨折外固定支具结构优化设计[J]. 医用生物力学,2022,37(5):952-959.
[18] VERBRUGGEN SW, LOO JH, HAYAT TT, et al. Modeling the biomechanics of fetal movements. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2016;15(4):995-1004.
[19] POLKOWSKI GG, CLOHISY JC. Hip biomechanics. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2010;18(2):56-62.
[20] DE PIERI E, FRIESENBICHLER B, LIST R, et al. Subject-Specific Modeling of Femoral Torsion Influences the Prediction of Hip Loading During Gait in Asymptomatic Adults. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9: 679360.
[21] HARRIS MD, SHEPHERD MC, SONG K, et al. The biomechanical disadvantage of dysplastic hips. J Orthop Res. 2022;40(6):1387-1396.
[22] CHU L, HE Z, QU X, et al. Different subchondral trabecular bone microstructure and biomechanical properties between developmental dysplasia of the hip and primary osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. 2019;22: 50-57.
[23] HENAK CR, ABRAHAM CL, ANDERSON AE, et al. Patient-specific analysis of cartilage and labrum mechanics in human hips with acetabular dysplasia. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(2):210-217.
[24] DANTAS P, GONCALVES S R, GRENHO A, et al. Hip joint contact pressure and force: a scoping review of in vivo and cadaver studies. Bone Joint Res. 2023;12(12):712-721.
[25] SONG K, ANDERSON AE, WEISS JA, et al. Musculoskeletal models with generic and subject-specific geometry estimate different joint biomechanics in dysplastic hips. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2019;22(3):259-270.
[26] KLISIC PJ. Congenital dislocation of the hip--a misleading term: brief report. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1989;71(1):136.
[27] LODER RT, SKOPELJA EN. The epidemiology and demographics of hip dysplasia. ISRN Orthop. 2011;2011:238607.
[28] KOTLARSKY P, HABER R, BIALIK V, et al. Developmental dysplasia of the hip: What has changed in the last 20 years? World J Orthop. 2015;6(11):886-901.
[29] INCZE-BARTHA Z, INCZE-BARTHA S, SIMON SZ, et al. Finite Element Analysis of Normal and Dysplastic Hip Joints in Children. J Pers Med. 2023;13(11):1593.
[30] SHIN CH, YOO WJ, PARK MS, et al. Acetabular Remodeling and Role of Osteotomy After Closed Reduction of Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016;98(11):952-957.
[31] TSUKAGOSHI Y, KAMADA H, TAKEUCHI R, et al. Three-dimensional MRI analyses of prereduced femoral head sphericity in patients with developmental dysplasia of the hip after Pavlik harness failure. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2018;27(5):394-398.
[32] SADEGHIAN SM, ARTHURS OJ, LI X, et al. Neonatal Hip Loading in Developmental Dysplasia: Finite Element Simulation of Proximal Femur Growth and Treatment. HSS J. 2023;19(4):418-427.
[33] MORALEDA L, ALBIÑANA J, SALCEDO M, et al. Displasia in the development of the hip. Rev Esp Cir Ortop Traumatol. 2013;57(1):67-77.
[34] VAQUERO-PICADO A, GONZALEZ-MORAN G, GARAY EG, et al. Developmental dysplasia of the hip: update of management. EFORT Open Rev. 2019;4(9):548-556.
[35] VAFAEIAN B, ADEEB S, EL-RICH M, et al. Hip Joint Contact Pressure Distribution During Pavlik Harness Treatment of an Infant Hip: A Patient-Specific Finite Element Model. J Biomech Eng. 2018;140(7). doi: 10.1115/1.4039827.
[36] VAFAEIAN B, ADEEB S, EL-RICH M, et al. Prediction of mechanical behavior of cartilaginous infant hips in pavlik harness: A subject-specific simulation study on normal and dysplastic hips. J Orthop Res. 2019;37(3):655-664.
[37] MÁRQUEZ-FLÓREZ KM, SILVA O, NARVAEZ-TOVAR CA, et al. A Comparison of the Contact Force Distributions on the Acetabular Surface Due to Orthopedic Treatments for Developmental Hip Dysplasia. J Biomech Eng. 2016;138(7). doi: 10.1115/1.4033547.
[38] BOROWSKI A, THAWRANI D, GRISSOM L, et al. Bilaterally dislocated hips treated with the Pavlik harness are not at a higher risk for failure. J Pediatr Orthop. 2009;29(7):661-665.
[39] HUAYAMAVE V, LOZINSKI B, ROSE C, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of femoral anteversion in developmental dysplasia of the hip and potential implications for closed reduction. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2020;72:179-185.
[40] 蔡振存,朴成哲,周宏宇,等.有限元法分析儿童发育不良髋关节“人”字型固定后的应力特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(36): 5841-5845.
[41] LIU J, GAO T, LI J, et al. Evaluation of the short-term curative effect of closed reduction in the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip based on three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):455.
[42] ZHANG Z, SUI D, QIN H, et al. Contact pressure distribution of the hip joint during closed reduction of developmental dysplasia of the hip: a patient-specific finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):600.
[43] YANG S, ZUSMAN N, LIEBERMAN E, et al. Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. Pediatrics. 2019;143(1): e20181147.
[44] NAKAMURA T, WADA A, NATORI T, et al. A Novel Method for Assessing the 3-dimensional Morphology of Cartilaginous Acetabulum Via Childhood Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J Pediatr Orthop. 2023;43(10): 640-648.
[45] SUVOROV V, FILIPCHUK V, MELNYK M. The biomechanical analysis of pelvic osteotomies applied for DDH treatment in pediatric patients. Wiad Lek. 2023;76(8):1804-1812.
[46] TOYOHARA R, KANEUJI A, TAKANO N, et al. A patient-cohort study of numerical analysis on sacroiliac joint stress distribution in pre- and post-operative hip dysplasia. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):14500.
[47] LEE KJ, PARK SJ, KWO SY, et al. Biomechanical study on the efficacy of the periacetabular osteotomy using Patient-specific finite element analysis. Int J Precis Eng Man. 2015;16(4):823-829.
[48] PARK SJ, LEE SJ, CHEN WM, et al. Computer-Assisted Optimization of the Acetabular Rotation in Periacetabular Osteotomy Using Patient’s Anatomy-Specific Finite Element Analysis. Appl Bionics Biomech. 2018;2018:9730525.
[49] KITAMURA K, FUJII M, IWAMOTO M, et al. Effect of coronal plane acetabular correction on joint contact pressure in Periacetabular osteotomy: a finite-element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):48.
[50] KITAMURA K, FUJII M, IWAMOTO M, et al. Is Anterior Rotation of the Acetabulum Necessary to Normalize Joint Contact Pressure in Periacetabular Osteotomy? A Finite-element Analysis Study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2022; 480(1):67-78.
[51] KITAMURA K, FUJII M, IKEMURA S, et al. Factors Associated With Abnormal Joint Contact Pressure After Periacetabular Osteotomy: A Finite-Element Analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2022;37(10):2097-2105.
[52] AITKEN HD, MILLER A, RIVAS DJL, et al. Radiographically successful periacetabular osteotomy does not achieve optimal contact mechanics in dysplastic hips. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2023;104: 105928.
[53] MENG Y, LU Z, ZHANG XL, et al. A short-term magnetic resonance imaging analysis of acetabular adaptation in developmental dysplasia of the hip by open reduction or open reduction combined with Dega osteotomy. Chin Med J (Engl). 2021;134(13):1619-1621.
[54] FU Z, ZHANG Z, DENG S, et al. MRI assessment of femoral head docking following closed reduction of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Bone Joint J. 2023;105-B(2):140-147.
[55] HASEGAWA K, KABATA T, KAJINO Y, et al. The influence of pelvic tilt on stress distribution in the acetabulum: finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):764.
[56] LI J. Development and validation of a finite-element musculoskeletal model incorporating a deformable contact model of the hip joint during gait. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021;113:104136.
[57] GAO Y, CHAI W, AN Z, et al. Effect of Hip Joint Center on Multi-body Dynamics and Contact Mechanics of Hip Arthroplasty for Crowe IV Dysplasia. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(11):3061-3069.
[58] MOSHFEGHIFAR F, GHOLAMALIZADEH T, FERGUSON Z, et al. LibHip: An open-access hip joint model repository suitable for finite element method simulation. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022;226:107140.
[59] DU Y, FU J, SUN J, et al. Acetabular Bone Defect in Total Hip Arthroplasty for Crowe II or III Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip: A Finite Element Study. Biomed Res Int. 2020 Aug 25;2020:4809013.
[60] INCZE-BARTHA Z, INCZE-BARTHA S, SIMON-SZABÓ Z, et al. Finite Element Analysis of Various Osteotomies Used in the Treatment of Developmental Hip Dysplasia in Children. J Pers Med. 2024; 14(2):189.
[61] VAFAEIAN B, ZONOOBI D, MABEE M, et al. Finite element analysis of mechanical behavior of human dysplastic hip joints: a systematic review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(4):438-447.
[62] IKE H, INABA Y, KOBAYASHI N, et al. Effects of rotational acetabular osteotomy on the mechanical stress within the hip joint in patients with developmental dysplasia of the hip: a subject-specific finite element analysis. Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B(4):492-497. |