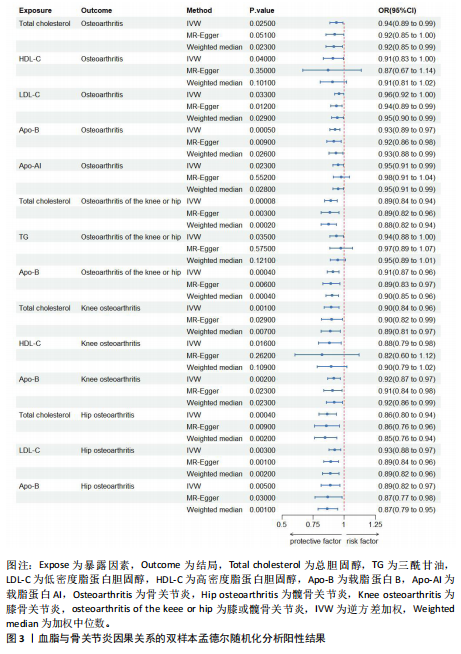
[1] MOTTA F, BARONE E, SICA A, et al. Inflammaging and Osteoarthritis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2023;64(2):222-238.
[2] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2): 293-311.
[3] MOLNAR V, MATIŠIĆ V, KODVANJ I, et al. Cytokines and Chemokines Involved in Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(17):9208.
[4] HINES MR, GOMEZ-CONTRERAS PC, LIMAN S, et al. A reciprocal relationship between mitochondria and lipid peroxidation determines the chondrocyte intracellular redox environment. Redox Biol. 2024;75:103306.
[5] NEDUNCHEZHIYAN U, VARUGHESE I, SUN AR, et al. Obesity, Inflammation, and Immune System in Osteoarthritis. Front Immunol. 2022;4(13):907750.
[6] ZHENG L, ZHANG Z, SHENG P, et al. The role of metabolism in chondrocyte dysfunction and the progression of osteoarthritis. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;3(66):101249.
[7] DE ROOVER A, ESCRIBANO-NÚÑEZ A, MONTEAGUDO S, et al. Fundamentals of osteoarthritis: Inflammatory mediators in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2023;31(10):1303-1311.
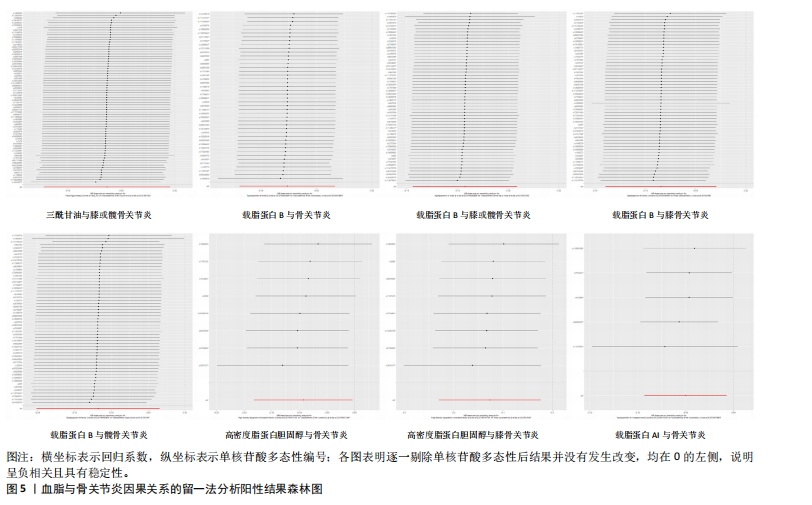
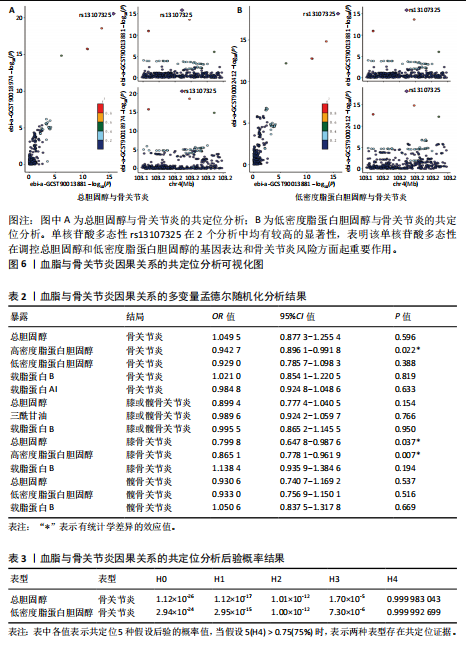
[8] GU Y, JIN Q, HU J, et al. Causality of genetically determined metabolites and metabolic pathways on osteoarthritis: a two-sample mendelian randomization study. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):357.
[9] CAO C, SHI Y, ZHANG X, et al. Cholesterol-induced LRP3 downregulation promotes cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis by targeting Syndecan-4 . Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):7139.
[10] ANSARI MY, AHMAD N, HAQQI TM. Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: Role of polyphenols. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;9(129):110452.
[11] GOICOECHEA L, CONDE DE LA ROSA L, TORRES S, et al. Mitochondrial cholesterol: Metabolism and impact on redox biology and disease. Redox Biol. 2023;3(61):102643.
[12] SAMPATH SJP, VENKATESAN V, GHOSH S, et al. Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Osteoarthritis-An Updated Review. Curr Obes Rep. 2023;12(3):308-331.
[13] ANDERSSON M, HAGLUND E, AILI K, et al. Associations between metabolic factors and radiographic knee osteoarthritis in early disease - a cross-sectional study of individuals with knee pain. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):938.
[14] RICHMOND RC, DAVEY SMITH G. Mendelian Randomization: Concepts and Scope. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2022;12(1):a040501.
[15] FABO T, KHAVARI P. Functional characterization of human genomic variation linked to polygenic diseases. Trends Genet. 2023;39(6):462-490.
[16] PIERCE BL, BURGESS S. Efficient design for Mendelian randomization studies: subsample and 2-sample instrumental variable estimators. Am J Epidemiol. 2013; 178(7):1177-1184.
[17] ZUBER V, GRINBERG NF, GILL D, et al. Combining evidence from Mendelian randomization and colocalization: Review and comparison of approaches. Am J Hum Genet. 2022;109(5):767-782.
[18] ARVANITIS M, TAYEB K, STROBER BJ, et al.
Redefining tissue specificity of genetic regulation of gene expression in the presence of allelic heterogeneity. Am J Hum Genet. 2022;109(2):223-239.
[19] SAKAUE S, KANAI M, TANIGAWA Y, et al. A cross-population atlas of genetic associations for 220 human phenotypes. Nat Genet. 2021;53(10):1415-1424.
[20] CHOUDHURY A, BRANDENBURG JT, CHIKOWORE T, et al. Meta-analysis of sub-Saharan African studies provides insights into genetic architecture of lipid traits. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):2578.
[21] KLIMENTIDIS YC, ARORA A, NEWELL M, et al. Phenotypic and Genetic Characterization of Lower LDL Cholesterol and Increased Type 2 Diabetes Risk in the UK Biobank. Diabetes. 2020;69(10):2194-2205.
[22] KETTUNEN J, DEMIRKAN A, WÜRTZ P, et al. Genome-wide study for circulating metabolites identifies 62 loci and reveals novel systemic effects of LPA. Nat Commun, 2016;23(7):11122.
[23] RICHARDSON TG, LEYDEN GM, WANG Q, et al. Characterising metabolomic signatures of lipid-modifying therapies through drug target mendelian randomisation. PLoS Biol. 2022;20(2):e3001547.
[24] PIETZNER M, WHEELER E, CARRASCO-ZANINI J, et al. Genetic architecture of host proteins involved in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):6397.
[25] MBATCHOU J, BARNARD L, BACKMAN J, et al. Computationally efficient whole-genome regression for quantitative and binary traits. Nat Genet. 2021;53(7):1097-1103.
[26] TACHMAZIDOU I, HATZIKOTOULAS K, SOUTHAM L, et al. Identification of new therapeutic targets for osteoarthritis through genome-wide analyses of UK Biobank data. Nat Genet. 2019;51(2): 230-236.
[27] BOWDEN J, HOLMES MV. Meta-analysis and Mendelian randomization: A review. Res Synth Methods. 2019;10(4):486-496.
[28] LONG Y, TANG L, ZHOU Y, et al. Causal relationship between gut microbiota and cancers: a two-sample Mendelian randomisation study. BMC Med. 2023; 21(1):66.
[29] BURGESS S, BOWDEN J, FALL T. Sensitivity Analyses for Robust Causal Inference from Mendelian Randomization Analyses with Multiple Genetic Variants. Epidemiology. 2017;28(1):30-42.
[30] MOUNIER N, KUTALIK Z. Bias correction for inverse variance weighting Mendelian randomization. Genet Epidemiol. 2023; 47(4):314-331.
[31] BURGESS S, BUTTERWORTH A, THOMPSON SG. Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data. Genet Epidemiol. 2013;37(7):658-665.
[32] LI J, TANG M, GAO X, et al. Mendelian randomization analyses explore the relationship between cathepsins and lung cancer. Commun Biol. 2023;6(1):1019.
[33] RASOOLY D, PELOSO GM. Two-Sample Multivariable Mendelian Randomization Analysis Using R. Curr Protoc. 2021;1(12): e335.
[34] YAVORSKA OO, BURGESS S. MendelianRandomization: an R package for performing Mendelian randomization analyses using summarized data. Int J Epidemiol. 2017;46(6):1734-1739.
[35] ZHENG J, BAIRD D, BORGES MC, et al. Recent developments in Mendelian randomization studies. Curr Epidemiol Rep. 2017;4(4):330-345.
[36] BURGESS S, THOMPSON SG. Multivariable Mendelian randomization: the use of pleiotropic genetic variants to estimate causal effects. Am J Epidemiol. 2015;181(4): 251-260.
[37] SANDERSON E. Multivariable Mendelian Randomization and Mediation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2021;11(2):a038984.
[38] BAKKER MK, VAN STRATEN T, CHONG M, et al. Anti-Epileptic Drug Target Perturbation and Intracranial Aneurysm Risk: Mendelian Randomization and Colocalization Study. Stroke. 2023;54(1):208-216.
[39] GIAMBARTOLOMEI C, VUKCEVIC D, SCHADT EE, et al. Bayesian test for colocalisation between pairs of genetic association studies using summary statistics. PLoS Genet. 2014;10(5):e1004.383.
[40] DRIVAS TG, LUCAS A, RITCHIE MD. eQTpLot: a user-friendly R package for the visualization of colocalization between eQTL and GWAS signals. BioData Min. 2021; 14(1):32.
[41] KATZ JN, ARANT KR, LOESER RF. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review. JAMA. 2021; 325(6):568-578.
[42] Bliddal H. Definition pathology and pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Ugeskr Laeger. 2020;182(42):V06200477.
[43] HEINEMEIER KM, SCHJERLING P, HEINEMEIER J, et al. Radiocarbon dating reveals minimal collagen turnover in both healthy and osteoarthritic human cartilage. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8(346):346ra90.
[44] ALLEN KD, THOMA LM, GOLIGHTLY YM. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(2): 184-195.
[45] SEKULA P, DEL GRECO MF, PATTARO C, et al. Mendelian Randomization as an Approach to Assess Causality Using Observational Data. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;27(11): 3253-3265.
[46] SCHADE DS, SHEY L, EATON RP. Cholesterol Review: A Metabolically Important Molecule. Endocr Pract. 2020;26(12):1514-1523.
[47] SONG Y, LIU J, ZHAO K, et al. Cholesterol-induced toxicity: An integrated view of the role of cholesterol in multiple diseases. Cell Metab. 2021;33(10):1911-1925.
[48] SCHWAGER JL, NEVITT MC, TORNER J, et al. Association of Serum Low-Density Lipoprotein, High-Density Lipoprotein, and Total Cholesterol With Development of Knee Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2022;74(2):274-280.
[49] FUNCK-BRENTANO T, NETHANDER M, MOVÉRARE-SKRTIC S, et al. Causal Factors for Knee, Hip, and Hand Osteoarthritis: A Mendelian Randomization Study in the UK Biobank. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71(10):1634-1641.
[50] CHEN J, TANG Z, SLOMINSKI AT, et al. Vitamin D and its analogs as anticancer and anti-inflammatory agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2020;1(207):112738.
[51] ZHANG K, JI Y, DAI H, et al. High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and Apolipoprotein A1 in Synovial Fluid: Potential Predictors of Disease Severity of Primary Knee Osteoarthritis. Cartilage. 2021;13(1_suppl): 1465S-1473S.
[52] RYE KA, BARTER PJ. Regulation of high-density lipoprotein metabolism. Circ Res. 2014;114(1_suppl):143-156.
[53] KOSTOPOULOU F, MALIZOS KN, PAPATHANASIOU I, et al. MicroRNA-33a regulates cholesterol synthesis and cholesterol efflux-related genes in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17(1):42.
[54] 陈江水,杨华瑞,方志,等.脂质代谢异常与骨关节炎关系研究进展[J].海南医学,2018,29(5):682-684.
[55] HINDY G, ÅKESSON KE, MELANDER O, et al. Cardiometabolic polygenic risk scores and osteoarthritis outcomes: a Mendelian randomization study using data from the Malmö diet and cancer study and the UK biobank. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71(6):925-934.
[56] DIFFENDERFER MR, SCHAEFER EJ. The composition and metabolism of large and small LDL. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2014;25(3): 221-226.
[57] 石银朋,奚阳,张志毅,等.血脂对骨关节炎影响研究进展[J].中国实用内科杂志,2020,40(1):67-69.
[58] FELSON DT, MISRA D, LAVALLEY M, et al. Essential Fatty Acids and Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2024;76(6): 796-801.
[59] HANSEN SB, WANG H. The shared role of cholesterol in neuronal and peripheral inflammation. Pharmacol Ther. 2023;9(249): 108486.
[60] PHILLIPS MC. Molecular mechanisms of cellular cholesterol efflux. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(35):24020-24029.
[61] LUO J, YANG H, SONG BL. Mechanisms and regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Nature reviews. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020; 21(4):225-245.
[62] LI S, MA C, LI Y, et al. The schizophrenia-associated missense variant rs13107325 regulates dendritic spine density. Transl Psychiatry. 2022;12(1):361.
[63] FRANGOS T, MARET W. Zinc and Cadmium in the Aetiology and Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nutrients. 2020;13(1):53.
[64] WANG Z, LIU M, ZHOU Y, et al. Effect of blood lipids and lipid-lowering therapies on osteoarthritis risk: A Mendelian randomization study. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;11(9):990569.
[65] MENG H, JIANG L, SONG Z, et al. Causal Associations of Circulating Lipids with Osteoarthritis: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients. 2022; 14(7):1327. |