[1] MICHELLE WV, CARMEN S, SEUNGWOO Y, et al. Exercise and Hippocampal Memory Systems. Trends Cogn Sci. 2019;23(4):318-333.
[2] KIRK IE, DESTINY LM, KATHRYN AR. The aging hippocampus: interactions between exercise, depression, and BDNF. Neuroscientist. 2012; 18(1):82-97.
[3] FATEMEH P, RAHIM M, MASOUD R. Exercise and Syzygium aromaticum reverse memory deficits, apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction of the hippocampus in Alzheimer’s disease. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;286(25):114871.
[4] C’IANA C, HYO YOUL M, HENRIETTE VP. On the Run for Hippocampal Plasticity. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2017;8(4):a029736.
[5] EMRAH D, HENRIETTE VP, MICHAEL S. Can physical exercise in old age improve memory and hippocampal function? Brain. 2016;139(3):662-673.
[6] ROBERT RK, BRADLEY RK. The effects of peripheral hormone responses to exercise on adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14(24):1202349.
[7] KAIYIN C, CHAOYANG L, GUOLIANG F. Aerobic Exercise Delays Alzheimer’s Disease by Regulating Mitochondrial Proteostasis in the Cerebral Cortex and Hippocampus. Life (Basel). 2023;13(5):1204.
[8] DOMINGOS C, PÊGO JM, SANTOS NC. Effects of physical activity on brain function and structure in older adults: A systematic review. Behav Brain Res. 2020;402:113061.
[9] DE SNOO ML, MILLER AMP, RAMSARAN AI, et al. Exercise accelerates place cell representational drift. Curr Biol. 2023;33(3):R96-R97.
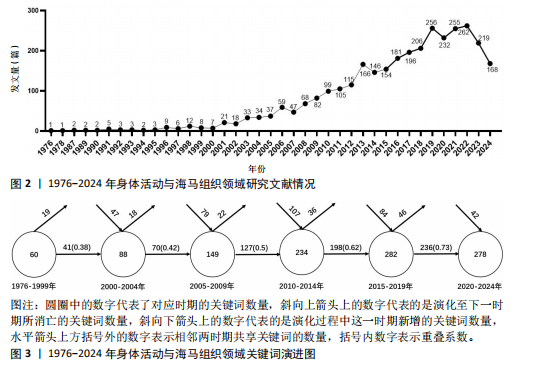
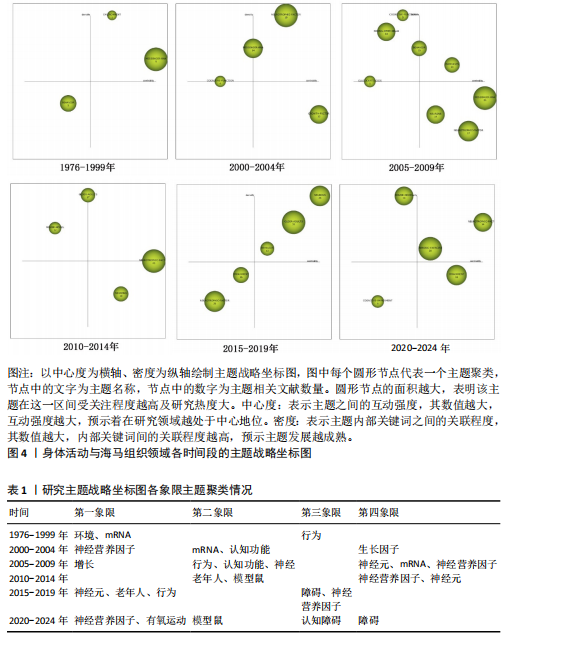
[10] YE L, JIAN Z, XIYAO G, et al. Mapping the current trends and hotspots of adult hippocampal neurogenesis from 2004-2023: a bibliometric analysis. Front Neurosci. 2024;18:1416738.
[11] RAMPASSO IS, SANTANA M, SERAFIM MP, et al. Anholon R. Trends in remote work: A science mapping study. Work. 2022;71(2):441-450.
[12] 陈晓鹏, 严晓燕, 孙洋, 等. 基于SciMAT的防护服装研究动态演进分析[J]. 服装学报,2023, 8(6):521-528.
[13] 夏洋, 李文梅. 近20年国际学业情绪研究主题动态演化路径分析[J]. 当代外语研究,2023, 23(5):94-102+132.
[14] 李丽霞, 任卓明, 张子柯. 基于关键词的知识图谱挖掘信息技术学科演化趋势[J]. 电子科技大学学报,2020,49(5):780-787.
[15] 陶文兵, 金海. 一种新的基于图谱理论的图像阈值分割方法[J]. 计算机学报,2007,30(1):110-119.
[16] 董雪季, 王晓慧. 国际科学计量学研究主题动态演化路径分析[J]. 数字图书馆论坛,2018(10): 9-17.
[17] CARRASCO-GARRIDO C, DE-PABLOS-HEREDERO C, RODRíGUEZ-SÁNCHEZ J. Exploring hybrid telework: A bibliometric analysis. Heliyon. 2023;9(12): e22472.
[18] EVA S, BENJAMIN R, OLIVER G, et al. Effects of exergaming on hippocampal volume and brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Neurol. 2021;29(2):441-449.
[19] YUKI T, KAZUYA S, SONG-GYU R, et al. Short-term running exercise alters DNA methylation patterns in neuronal nitric oxide synthase and brain-derived neurotrophic factor genes in the mouse hippocampus and reduces anxiety-like behaviors. FASEB J. 2021;35(8):e21767.
[20] AGUIAR AS JR, STRAGIER E, DA LUZ SCHEFFER D, et al. Effects of exercise on mitochondrial function, neuroplasticity and anxio-depressive behavior of mice. Neuroscience. 2014;271:56-63.
[21] AGHJAYAN SL, LESNOVSKAYA A, ESTEBAN-CORNEJO I, et al. Aerobic exercise, cardiorespiratory fitness, and the human hippocampus. Hippocampus. 2021;31(8):817-844.
[22] HENDRIKSE J, CHYE Y, THOMPSON S, et al. Regular aerobic exercise is positively associated with hippocampal structure and function in young and middle-aged adults. Hippocampus. 2022;32(3): 137-152.
[23] CHOI SH, BYLYKBASHI E, CHATILA ZK, et al. Combined adult neurogenesis and BDNF mimic exercise effects on cognition in an Alzheimer’s mouse model. Science. 2018;361(6406): eaan8821.
[24] HANNA C, HAMILTON J, ARNAVUT E, et al. Brain Mapping the Effects of Chronic Aerobic Exercise in the Rat Brain Using FDG PET. J Pers Med. 2022; 12(6):860.
[25] HAN P, GU BY, MU LW, et al. Moderate-Intensity Treadmill Exercise Regulates GSK3α/β Activity in the Cortex and Hippocampus of APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice. J Integr Neurosci. 2024;23(7):136.
[26] LI Y, LUO YM, ZHU PL, et al. Running exercise improves astrocyte loss, morphological complexity and astrocyte-contacted synapses in the hippocampus of CUS-induced depression model mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2024; 239:173750.
[27] JIANG HL, KIMURA Y, INOUE S, et al. Effects of different exercise modes and intensities on cognitive performance, adult hippocampal neurogenesis, and synaptic plasticity in mice. Exp Brain Res. 2024;242(7):1709-1719.
[28] KHAN MB, ALAM H, SIDDIQUI S, et al. Exercise Improves Cerebral Blood Flow and Functional Outcomes in an Experimental Mouse Model of Vascular Cognitive Impairment and Dementia (VCID). Transl Stroke Res. 2024;15(2):446-461.
[29] TAO X, SUN RF, HAN CL, et al. Cognitive-motor dual task: An effective rehabilitation method in aging-related cognitive impairment. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:1051056.
[30] WANG R, ZHANG HY, LI HJ, et al. The influence of exercise interventions on cognitive functions in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Public Health. 2022;10:1046841.
[31] JIN Y, LI X, WEI CL, et al. Effects of exercise-targeted hippocampal PDE-4 methylation on synaptic plasticity and spatial learning/memory impairments in D-galactose-induced aging rats. Exp Brain Res. 2024;242(2):309-320.
[32] SUN GC, LEE YJ, LEE YC, et al. Exercise prevents the impairment of learning and memory in prenatally phthalate-exposed male rats by improving the expression of plasticity-related proteins. Behav Brain Res. 2021;413:113444.
[33] KIM TW, PARK SS, KIM SH, et al. Exercise before pregnancy exerts protective effect on prenatal stress-induced impairment of memory, neurogenesis, and mitochondrial function in offspring. J Exerc Rehabil. 2024;20(1):2-10.
[34] CUSTODIO RJP, KIM HJ, KIM J, et al. Hippocampal dentate gyri proteomics reveals Wnt signaling involvement in the behavioral impairment in the THRSP-overexpressing ADHD mouse model. Commun Biol. 2023;6(1):55.
[35] MO FF, ZHANG HW, TANG YX, et al. Pyruvate accumulation may contribute to acceleration-induced impairment of physical and cognitive abilities: an experimental study. Biosci Rep. 2021; 41(4):BSR20204284.
[36] PARNPIANSIL P, JUTAPAKDEEGUL N, CHENTANEZ T, et al. Exercise during pregnancy increases hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA expression and spatial learning in neonatal rat pup. Neurosci Lett. 2003;352(1):45-48.
[37] TAKAMATSU Y, INOUE T, NISHIO T, et al. Potential effect of physical exercise on the downregulation of BDNF mRNA expression in rat hippocampus following intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurosci Lett. 2024;824:137670.
[38] SOLVSTEN CAE, DAUGAARD TF, LUO Y, et al. The Effects of Voluntary Physical Exercise-Activated Neurotrophic Signaling in Rat Hippocampus on mRNA Levels of Downstream Signaling Molecules. J Mol Neurosci. 2017;62(2):142-153.
[39] TRAN PV, CARLSON ES, FRETHAM SJB, et al. Early-Life Iron Deficiency Anemia Alters Neurotrophic Factor Expression and Hippocampal Neuron Differentiation in Male Rats. J Nutr. 2008;138(12): 2495-2501.
[40] BOSCH BM, BRINGARD A, LOGRIECO MG, et al. A single session of moderate intensity exercise influences memory, endocannabinoids and brain derived neurotrophic factor levels in men. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):14371.
[41] LIANG ZQ, ZHANG Z, QI S, et al. Effects of a Single Bout of Endurance Exercise on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Humans: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Biology (Basel). 2023;12(1):126.
[42] SPARTANO NL, HIMALI JJ, TRINQUART L, et al. Accelerometer-Measured, Habitual Physical Activity and Circulating Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor: A Cross-Sectional Study. J Alzheimers Dis. 2022;85(2):805-814.
[43] VASUDEVAN K, HASSELL JE JR, MAREN S. Hippocampal Engrams and Contextual Memory. Adv Neurobiol. 2024;38:45-66.
[44] LEITER O, BRICI D, FLETCHER SJ, et al. Platelet-derived exerkine CXCL4/platelet factor 4 rejuvenates hippocampal neurogenesis and restores cognitive function in aged mice. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):4375.
[45] NIU XJ, ZHAO YH, YANG N, et al. Proteasome activation by insulin-like growth factor-1/nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 signaling promotes exercise-induced neurogenesis. Stem Cells. 2020;38(2):246-260.
[46] HALL JM, GOMEZ-PINILLA F, SAVAGE LM. Nerve Growth Factor Is Responsible for Exercise-Induced Recovery of Septohippocampal Cholinergic Structure and Function. Front Neurosci. 2018;12:773.
[47] VARMA VR, TANG X, CARLSON MC. Hippocampal Sub-Regional Shape and Physical Activity in Older Adults. Hippocampus. 2016;26(8):1051-1060.
[48] CALLOW DD, WON J, ALFINI AJ, et al. Microstructural Plasticity in the Hippocampus of Healthy Older Adults after Acute Exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2021;53(9):1928-1936.
[49] MCEWEN SC, SIDDARTH P, ABEDELSATER B, et al.
Simultaneous Aerobic Exercise and Memory Training Program in Older Adults with Subjective Memory Impairments. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018; 62(2):795-806.
[50] CUI XY, GUI WJ, MIAO JW, et al. A Combined Intervention of Aerobic Exercise and Video Game in Older Adults: The Efficacy and Neural Basis on Improving Mnemonic Discrimination. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2023;78(8):1436-1444. |