[1] LORENTZON M. Treating osteoporosis to prevent fractures: current concepts and future developments. J Intern Med. 2019;285(4): 381-394.
[2] RAISZ LG. Pathogenesis of osteoporosis: concepts, conflicts, and prospects. J Clin Invest. 2005;115(12):3318-3325.
[3] REGINSTER JY, BURLET N. Osteoporosis: A still increasing prevalence. Bone. 2006;38(2, Supplement 1):4-9.
[4] 杨成,吴斗,刘强.骨质疏松症流行病学、影响因素及其相关机制研究进展[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2023,12(4):306-310.
[5] 邱晓萍,刘铠婕,林宇慧,等.骨质疏松症的流行病学、管理与防治研究进展[J].山东医药,2023,63(21):107-111.
[6] CUMMINGS SR, MELTON LJ. Epidemiology and outcomes of osteoporotic fractures. Lancet. 2002;359(9319):1761-1767.
[7] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会,章振林.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)[J].中国全科医学,2023,26(14):1671-1691.
[8] YANG N, ZHANG X, LI L, et al. Ginsenoside Rc Promotes Bone Formation in Ovariectomy-Induced Osteoporosis In Vivo and Osteogenic Differentiation In Vitro. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(11): 6187.
[9] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977.
[10] 高文静,侯敏,王攀,等.外泌体作为中药新活性成分的研究进展[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2019,21(9):1869-1876.
[11] ZHUANG X, DENG ZB, MU J, et al. Ginger-derived nanoparticles protect against alcohol-induced liver damage. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:28713.
[12] LI Z, WANG H, YIN H, et al. Arrowtail RNA for Ligand Display on Ginger Exosome-like Nanovesicles to Systemic Deliver siRNA for Cancer Suppression . Sci Rep-Uk. 2018;8(1):14644.
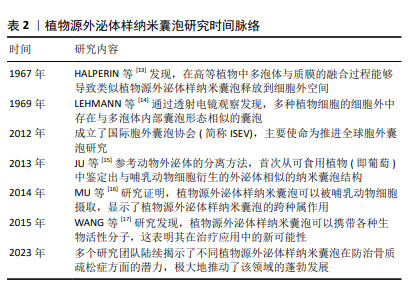
[13] HALPERIN W, JENSEN WA. Ultrastructural changes during growth and embryogenesis in carrot cell cultures. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967;18(3): 428-443.
[14] LEHMANN H, SCHULZ D. [Electron microscopical studies of differentiating processes in mosses : II. Formation of cell plate and cell wall]. Planta. 1969;85(4):313-325.
[15] JU S, MU J, DOKLAND T, et al. Grape exosome-like nanoparticles induce intestinal stem cells and protect mice from DSS-induced colitis. Mol Ther. 2013;21(7):1345-1357.
[16] MU J, ZHUANG X, WANG Q, et al. Interspecies communication between plant and mouse gut host cells through edible plant derived exosome-like nanoparticles. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2014;58(7):1561-1573.
[17] WANG Q, REN Y, MU J, et al. Grapefruit-Derived Nanovectors Use an Activated Leukocyte Trafficking Pathway to Deliver Therapeutic Agents to Inflammatory Tumor Sites. Cancer Res. 2015;75(12):2520-2529.
[18] MURPHY DE, DE JONG OG, BROUWER M, et al. Extracellular vesicle-based therapeutics: natural versus engineered targeting and trafficking. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51(3):1-12.
[19] VAN NIEL G, D’ANGELO G, RAPOSO G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(4):213-228.
[20] REN L, ZENG F, DENG J, et al. Inflammatory osteoclasts-derived exosomes promote bone formation by selectively transferring lncRNA LIOCE into osteoblasts to interact with and stabilize Osterix. Faseb J. 2022;36(2):e22115.
[21] COSENZA S, TOUPET K, MAUMUS M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes are more immunosuppressive than microparticles in inflammatory arthritis. Theranostics. 2018;8(5):1399-1410.
[22] DENG L, WANG Y, PENG Y, et al. Osteoblast-derived microvesicles: A novel mechanism for communication between osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Bone. 2015;79:37-42.
[23] KIM J, LI S, ZHANG S, et al. Plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles and their therapeutic activities. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2022;17(1):53-69.
[24] TENG Y, REN Y, SAYED M, et al. Plant-Derived Exosomal MicroRNAs Shape the Gut Microbiota. Cell Host Microbe. 2018;24(5):637-652.e8.
[25] XU XH, YUAN TJ, DAD HA, et al. Plant Exosomes As Novel Nanoplatforms for MicroRNA Transfer Stimulate Neural Differentiation of Stem Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. Nano Lett. 2021;21(19):8151-8159.
[26] 刘伟,刘永博,王梓,等.人参的化学成分与转化机理研究进展[J].吉林农业大学学报,2023,45(6):664-673.
[27] KIM HJ, JUNG SW, KIM SY, et al. Panax ginseng as an adjuvant treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. J Ginseng Res. 2018;42(4):401-411.
[28] KANG S, MIN H. Ginseng, the ‘Immunity Boost’: The Effects of Panax ginseng on Immune System. J Ginseng Res. 2012;36(4):354-368.
[29] CAO M, YAN H, HAN X, et al. Ginseng-derived nanoparticles alter macrophage polarization to inhibit melanoma growth. J Immunother Cancer. 2019;7(1):326.
[30] HAN X, WEI Q, LV Y, et al. Ginseng-derived nanoparticles potentiate immune checkpoint antibody efficacy by reprogramming the cold tumor microenvironment. Mol Ther. 2022;30(1):327-340.
[31] SEO K, YOO JH, KIM J, et al. Ginseng-derived exosome-like nanovesicles extracted by sucrose gradient ultracentrifugation to inhibit osteoclast differentiation. Nanoscale. 2023;15(12):5798-5808.
[32] ZHANG D, DU J, YU M, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 prevents osteoporosis via the AHR/PRELP/NF-κB signaling axis. Phytomedicine. 2022;104:154205.
[33] 毕嘉谣,田湾湾,张翼,等.经典名方中山药的本草考证[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2021,23(8):159-162.
[34] ZHANG L, NG TB, LAM J KW, et al. Research and Development of Proteins and Peptides with Therapeutic Potential from Yam Tubers. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2019;20(3):277-284.
[35] WONG KL, LAI YM, LI KW, et al. A Novel, Stable, Estradiol-Stimulating, Osteogenic Yam Protein with Potential for the Treatment of Menopausal Syndrome. Sci Rep. 2015;5:10179.
[36] HWANG JH, PARK YS, KIM HS, et al. Yam-derived exosome-like nanovesicles stimulate osteoblast formation and prevent osteoporosis in mice. J Control Release. 2023;355:184-198.
[37] ZHANG C, PENG J, WU S, et al. Dioscin promotes osteoblastic proliferation and differentiation via Lrp5 and ER pathway in mouse and human osteoblast-like cell lines. J Biomed Sci. 2014;21(1):30.
[38] ALCANTARA EH, SHIN MY, SOHN HY, et al. Diosgenin stimulates osteogenic activity by increasing bone matrix protein synthesis and bone-specific transcription factor Runx2 in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. J Nutr Biochem. 2011;22(11):1055-1063.
[39] MENG X, WANG X, HAN Y, et al. Protective effects of apple polyphenols on bone loss in mice with high fat diet-induced obesity. Food Funct. 2022;13(15):8047-8055.
[40] SIM Y, SEO HJ, KIM DH, et al. The Effect of Apple-Derived Nanovesicles on the Osteoblastogenesis of Osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 Cells. J Med Food. 2023;26(1):49-58.
[41] WU J, MA X, LU Y, et al. Edible Pueraria lobata-Derived Exosomes Promote M2 Macrophage Polarization. Molecules. 2022;27(23): 8184.
[42] LI L, CHEN B, ZHU R, et al. Fructus Ligustri Lucidi preserves bone quality through the regulation of gut microbiota diversity, oxidative stress, TMAO and Sirt6 levels in aging mice. Aging (Albany NY). 2019; 11(21):9348-9368.
[43] ZHAN W, DENG M, HUANG X, et al. Pueraria lobata-derived exosome-like nanovesicles alleviate osteoporosis by enhacning autophagy. J Control Release. 2023;364:644-653.
[44] SMITH BJ, HATTER B, WASHBURN K, et al. Dried Plum’s Polyphenolic Compounds and Carbohydrates Contribute to Its Osteoprotective Effects and Exhibit Prebiotic Activity in Estrogen Deficient C57BL/6 Mice. Nutrients. 2022;14(9):1685.
[45] RENDINA E, HEMBREE KD, DAVIS MR, et al. Dried plum’s unique capacity to reverse bone loss and alter bone metabolism in postmenopausal osteoporosis model. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e60569.
[46] PARK YS, KIM HW, HWANG JH, et al. Plum-Derived Exosome-like Nanovesicles Induce Differentiation of Osteoblasts and Reduction of Osteoclast Activation. Nutrients. 2023;15(9):2107.
[47] 尹子丽,谭文红,冯德强,等.骨碎补的本草考证及炮制、药用历史沿革[J].中国药房,2019,30(12):1725-1728.
[48] SHI XL, LIU K, WU LG. Interventional value of total flavonoids from Rhizoma Drynariae on Cathepsin K, a potential target of osteoporosis. Chin J Integr Med. 2011;17(7):556-560.
[49] 邓强,乔小万,李中锋,等.骨碎补活性成分治疗骨骼系统疾病研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2022,24(7):1-5.
[50] 张莉丽,张布衣,余阳.骨碎补总黄酮上调骨质疏松症模型大鼠Wnt/LRP-5/β-catenin通路表达的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2023, 29(6):807-811.
[51] 梁倩欣.骨碎补源性细胞外囊泡基本特征、生物活性及靶向性研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2023.
[52] KARAMANIDOU T, TSOUKNIDAS A. Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Therapeutic Nanocarriers. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;23(1):191.
[53] MU N, LI J, ZENG L, et al. Plant-Derived Exosome-Like Nanovesicles: Current Progress and Prospects. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18: 4987-5009. |