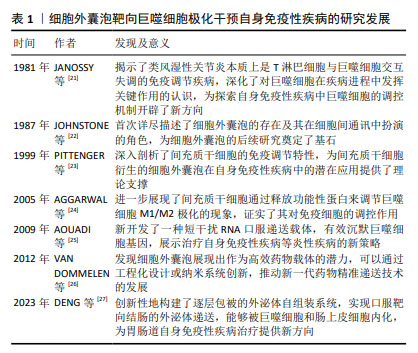
2.1 间充质干细胞衍生的细胞外囊泡靶向巨噬细胞极化干预自身免疫性疾病的研究进展 见表1。
 2.2 M1和M2型巨噬细胞的不同表型特征
2.2 M1和M2型巨噬细胞的不同表型特征 巨噬细胞是机体免疫的重要组成成分,几乎存在于成年动物体内所有组织中,在特定微环境中巨噬细胞有着不同的表型和名称[16,28],但其在不同组织中的功能较为相似,它们可以监测组织发育和炎症进程、抵御病原体并维持系统稳态[29-30]。
巨噬细胞可以接受各种生物信号。当巨噬细胞受到Toll样受体相关配体和干扰素γ刺激时,可以向M1型巨噬细胞极化;受到白细胞介素4及白细胞介素13刺激时向M2表型极化。在不同病理情况下,巨噬细胞极化具有高度的可塑性与灵活性[31-32]。巨噬细胞极化是一个动态的、受多因素影响的过程,其表型可以根据组织微环境的更新而改变。巨噬细胞形成一种表型后,若环境中出现新的影响,它仍可以继续发生改变从而产生不同的功能[33-34]。
M1或M2型巨噬细胞可以影响Th1免疫反应/Th2免疫反应或其他类型的炎症反应的发生[35]。其中M1巨噬细胞为促炎表型,可以产生肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、一氧化氮、环氧化酶2和活性氧等促炎因子,有病原体杀伤能力及清除肿瘤细胞的能力。而M2巨噬细胞可产生白细胞介素10、白细胞介素4受体和精氨酸酶1等,表达清道夫受体和相关分子,促进细胞增殖和组织修复[28,31,36-37]。根据激活场景与激活标准,巨噬细胞亚型可分为以下几种:M(IL-4)、M(Ig)、M(IL-10)、M(GC)、M(IFN-γ)、M(LPS)等[38-39],M2巨噬细胞也可分为M2a、M2b、M2c和M2d亚类[39-40]。巨噬细胞不同类别的极化表型和功能如图3所示。
 2.3 间充质干细胞靶向巨噬细胞精准调控自身免疫性疾病的途径
2.3.1 间充质干细胞可以通过释放或间接作用于功能性蛋白来调节M1/M2极化
(1)肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白6:
2.3 间充质干细胞靶向巨噬细胞精准调控自身免疫性疾病的途径
2.3.1 间充质干细胞可以通过释放或间接作用于功能性蛋白来调节M1/M2极化
(1)肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白6:在炎症调控与组织修复的复杂网络中,肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白6作为间充质干细胞分泌的关键蛋白,扮演着至关重要的角色。当间充质干细胞在体内环境中受到炎性因子的刺激时,它们响应性地分泌肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白6,其不仅抑制肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6和白细胞介素1β等促炎细胞因子的活性,还促进转生长因子β1的分泌,从而有效地减轻了机体的炎症反应[41]。这一发现揭示了间充质干细胞在自身免疫性疾病治疗中的作用机制,即通过靶向多种细胞因子,间接达到治疗自身免疫性疾病的效果。
肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白6在促进组织修复与M2巨噬细胞极化方面的作用也得到了广泛研究。例如,DI等[42]研究发现,局部移植骨髓间充质干细胞可显著促进糖尿病角膜上皮创面的愈合,其中肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白6的表达水平升高,角膜上皮细胞增殖情况得到改善,炎症反应显著减轻。此外,在糖尿病小鼠角膜和体外巨噬细胞培养中,肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白6减轻了炎性细胞浸润,促进募集的巨噬细胞极化为M2表型,吞噬能力增加。当骨髓间充质干细胞中的肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白6使用短发夹RNA敲除后,其促进上皮干细胞活化和巨噬细胞M2极化的能力在很大程度上被削弱。
犬脂肪间充质干细胞分泌的肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白6在处理小鼠结肠炎时也展现了治疗潜力,其不仅降低了炎症范围和肠壁厚度,减少了组织损伤和炎症细胞的浸润,还下调了肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6的表达,上调了白细胞介素10的表达;使用肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白6的小干扰RNA转染后犬脂肪间充质干细胞调节结肠炎症的能力被显著削弱,进一步证实了肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白6在炎症控制中的关键作用[43]。
SHIN等[44]研究则揭示了肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白6在胶原诱导型关节炎小鼠模型中的治疗效果。人脐带间充质干细胞通过与巨噬细胞共培养,不仅能抑制巨噬细胞经典的M1极化,还通过旁分泌机制诱导M2极化。在使用肿瘤坏死因子α预处理后,人脐带间充质干细胞释放的环氧化酶2和肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白6等关键免疫调节因子显著增加,这表明在类风湿性关节炎的特异性炎症环境下,间充质干细胞可以通过环氧化酶2和肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白6信号传导的协同作用来调节巨噬细胞的极化表型。当环氧化酶2和肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白6都被抑制时,人脐带间充质干细胞促进巨噬细胞M2极化的能力几乎完全消失,这一发现强调了环氧化酶2和肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白6在巨噬细胞极化过程中的协同作用,以及它们在调节免疫反应中的重要性。
综上所述,肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白6作为间充质干细胞分泌的关键蛋白,在炎症调控与组织修复中发挥着核心作用。它不仅能够抑制炎症反应,还能够促进M2巨噬细胞的极化,从而加速组织修复进程。未来的研究可以进一步探索肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白6与其他炎症递质的相互作用,以及它在不同疾病模型中的作用机制,以期开发出更加精准和有效的治疗策略,为自身免疫性疾病患者带来新的希望。
(2)前列腺素E2:前列腺素E2作为一种关键的炎症递质,在调节免疫反应、促进组织修复中扮演着核心角色。近年来的研究中发现,前列腺素E2通过激活不同的前列腺素受体,影响巨噬细胞的极化状态,从而在多种炎症性疾病,包括自身免疫性疾病、伤口愈合、心血管等疾病中发挥炎症调节作用[45]。
在炎性环境中,间充质干细胞通过直接分泌前列腺素E2或诱导其他细胞产生前列腺素E2,对巨噬细胞的极化状态产生深远影响,进而干预小鼠结肠炎的进程。研究显示,在结肠炎小鼠模型中,脂肪间充质干细胞能够通过抑制琥珀酸积累和增加脯氨酰羟化酶2含量,抑制M1巨噬细胞过表达缺氧诱导因子1α,从而重编程M1巨噬细胞的糖酵解途径,最终促使巨噬细胞从M1表型向M2型转变[46]。M1巨噬细胞分泌的琥珀酸可以反馈促进脂肪间充质干细胞分泌前列腺素E2,这一反馈机制进一步促进了巨噬细胞的M2极化,为炎症的缓解和组织修复创造了有利条件。这一机制揭示了间充质干细胞在调控巨噬细胞极化中的精细作用,为理解炎症与组织修复的动态平衡提供了新视角。
此外,在肿瘤坏死因子α刺激下,犬脂肪组织来源间充质干细胞可以分泌更高浓度的肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白6和前列腺素E2,这两种分子在诱导巨噬细胞向M2型极化过程中起着关键作用,能够有效调节结肠炎性细胞因子,改善葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠结肠炎[47]。这一发现进一步强调了前列腺素E2在调节免疫反应和促进组织修复中的核心作用。
在人单核细胞与小鼠脂肪组织来源间充质干细胞共培养条件下,前列腺素E2增多显著抑制了人单核细胞分泌白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18,同时抑制了NOD样受体热蛋白结构域相关蛋白3(NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain associated protein 3,NLRP3)炎症小体复合物的形成和白细胞介素18的分泌,减少了巨噬细胞总数和M1巨噬细胞群[48]。这一结果不仅揭示了前列腺素E2在抑制炎症反应中的机制,还为其在调节免疫细胞功能中的作用提供了实证。
水凝胶作为新型生物材料,为间充质干细胞治疗自身免疫性疾病提供了新的可能性。CAO等[49]研究显示,固定化IGF-1C结构域肽的壳聚糖可注射水凝胶与人胎盘衍生的间充质干细胞共移植,能够通过生成前列腺素E2进一步介导M2巨噬细胞的极化,并促进结肠炎小鼠的功能和结构恢复。这一创新性治疗方法不仅提高了间充质干细胞的治疗效果,还为未来基于生物材料的治疗策略提供了重要启示。
(3)趋化因子及其特异性受体:趋化因子与其特异性受体在自身免疫性糖尿病胰岛移植中扮演关键角色。基质细胞衍生因子1与趋化因子受体4的互动,成为改善移植效果的新策略[50]。基质细胞衍生因子1通过调节趋化因子受体4促进免疫细胞迁移,对胰岛移植物产生保护作用,胰腺中的炎症因子水平下降,调节性T细胞、M2型巨噬细胞和树突状细胞功能增强,证实了基质细胞衍生因子1在免疫调节中的作用。将通过此方法预处理的胰岛移植至小鼠体内,非肥胖糖尿病小鼠血糖得到有效控制。然而,细胞因子信号转导抑制物SOCS3能够抑制基质细胞衍生因子1的保护作用,可抵消其对胰岛功能的改善。未来研究需深入探索基质细胞衍生因子1与SOCS3的相互作用,以期开发更精准的糖尿病治疗策略,推动医学进步,改善患者预后。
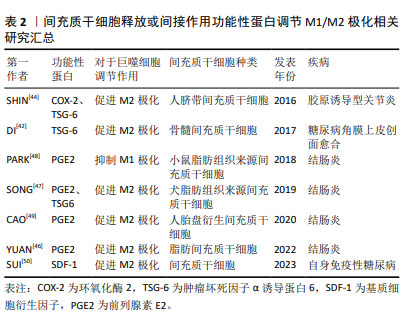
上述实验中所涉及到的间充质干细胞来源、功能性蛋白种类以及对于巨噬细胞表型的调节作用如表2所示。
 2.3.2 间充质干细胞可以影响炎症小体调控巨噬细胞极化
2.3.2 间充质干细胞可以影响炎症小体调控巨噬细胞极化 深入探究间充质干细胞调控巨噬细胞的作用机制,能发现其表达NLRP3炎症小体的关键成分,然而,与常规理解不同,人脐带间充质干细胞中NLRP3炎症小体激活后并不触发焦亡,也不影响干细胞表面标志物的表达。在溃疡性结肠炎模型中,当脐带间充质干细胞表达的NLRP3炎症小体激活后,能显著抑制T细胞反应和巨噬细胞的M1极化,并发挥免疫调节功能[50]。
间充质干细胞不仅自身表达NLRP3炎症小体,还能够调控其他细胞中NLRP3炎症小体的激活。例如,脂肪间充质干细胞能通过抑制人单核细胞细胞中NLRP3炎症小体的形成,增加前列腺素E2的释放,从而调节M1巨噬细胞群,有效改善结肠炎。SHIN等[44]研究进一步揭示,人脐带间充质干细胞衍生的细胞外囊泡可以通过白细胞介素1β反馈回路,抑制巨噬细胞中NLRP3炎症小体的激活,进而抑制M1型巨噬细胞的活化,为缓解类风湿性关节炎提供新策略。人脐带间充质干细胞在自身免疫性疾病中的治疗潜力,可能源于其能同时靶向多种细胞因子,调节巨噬细胞的表型,展现出在疾病治疗中的多维性与精准性。
2.3.3 间充质干细胞可以与常用药物组合以增强药物疗效 间充质干细胞与传统药物的协同作用,有提高药物疗效和安全性的潜力。以治疗类风湿性关节炎的主流药物——甲氨蝶呤为例,尽管疗效确切,但伴随的不良反应,如胃肠道不适、肾功能损伤、骨髓抑制、肺部毒性和心理影响,限制了其广泛应用。ZHAI等[51]将甲氨蝶呤与人脐带间充质干细胞联合应用,不仅显著提升了药物的安全性,更增强了治疗效果,体现在关节炎小鼠生存期延长、炎症浸润减少、关节骨表面完整性改善。人脐带间充质干细胞可以通过增加调节性T细胞的数量,与甲氨蝶呤共同促进巨噬细胞向M2型极化,有效减轻了小鼠的肠道、肺、肝、肾损伤,展现了协同治疗的抗炎效果和安全性。
骨髓间充质干细胞与法舒地尔的联合干预,为自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的治疗提供了新视角。YU等[52]发现骨髓间充质干细胞与法舒地尔联合应用在自身免疫性脑脊髓膜炎模型中展现了显著的治疗效果,不仅降低了疾病严重程度,还通过协同促进神经营养因子表达,增强了神经保护作用。法舒地尔的加入可以通过抑制Toll样受体4/髓样分化因子88炎症信号转导和炎症因子释放,有效降低了疾病的严重程度,尽管其对M1小胶质细胞向M2表型转化的影响有限,但仍展现了协同治疗的潜力。
在结肠炎治疗领域,脂肪间充质干细胞与柳氮磺吡啶的协同应用可以通过降低M1巨噬细胞水平,促进巨噬细胞向M2表型转变,以及抑制核因子κB(nuclear factor kappa-B,NF-κB)通路激活,有效改善了结肠炎进程。脂肪间充质干细胞通过调节鞘氨醇-1-磷酸信号通路,抑制鞘氨醇激酶活性并增加鞘氨醇磷酸酶表达,减轻结肠组织炎症和细胞凋亡,展现了显著减缓疾病进展的潜力[53]。
间充质干细胞与传统药物的协同应用,不仅提升了治疗效果,还显著提高了药物安全性,为多种疾病的治疗提供了创新思路和策略。然而,要将这些治疗策略完全转化为临床实践,需深入研究其背后的复杂机制。
2.4 间充质干细胞衍生的细胞外囊泡靶向巨噬细胞极化调节自身免疫性疾病的机制探索 间充质干细胞可以通过释放细胞外囊泡靶向巨噬细胞极化,调控多种信号通路,从而在自身免疫性疾病的治疗中发挥作用。以下将详细阐述间充质干细胞来源细胞外囊泡在不同疾病模型中调控巨噬细胞极化的机制。
2.4.1 磷酸酶及张力蛋白同源物(phosphatase and tensin homolog,PTEN)通路 在探索系统性红斑狼疮的治疗策略过程中,间充质干细胞及其外泌体展现出巨大潜力。ZHANG等[54]的研究在此背景下展开,他们发现来自骨髓间充质干细胞的外泌体可以促进系统性红斑狼疮模型小鼠肾脏中的巨噬细胞向M2表型极化,这些M2型巨噬细胞可以通过分泌抗炎细胞因子、吞噬凋亡细胞、募集调节性T细胞来缓解小鼠的狼疮性肾炎,进一步研究发现外泌体中的miR-16和miR-21分别通过靶向调节PDCD4和PTEN通路来促进巨噬细胞M2极化,这些巨噬细胞高效地清除凋亡碎片并诱导生成更多调节性T细胞来缓解狼疮性肾炎。
2.4.2 NOTCH通路 弥漫性肺泡出血是系统性红斑狼疮的常见并发症,CHEN等[55]研究发现,人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以抑制小鼠肺组织中NOTCH1的表达,减轻炎症出血,同时促进巨噬细胞M2极化。外泌体中的miR-146a-5p表达升高,是促进巨噬细胞转化为M2表型的关键因素,但当NOTCH1过表达时,外泌体的促进功能会被抵消,这提示在开发相关治疗策略时需要考虑NOTCH1的调控。这项研究为系统性红斑狼疮相关弥漫性肺泡出血的治疗提供了新思路。
2.4.3 NF-κB通路 关于缺氧这一特殊条件,QIAN等[56]探讨了它对脂肪来源间充质干细胞衍生外泌体炎症调节的影响,研究结果显示,在缺氧条件下外泌体显示出更强的炎症调节能力,它可以通过递送miR-216a-5p到巨噬细胞内,靶向高迁移率族蛋白B1的3’非翻译区,调节HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB信号通路,进而诱导巨噬细胞M2极化来缓解结肠炎。刘子瑜[57]研究发现,齿龈间充质干细胞衍生外泌体可以通过递送miR-1246,下调TERF2IP的表达,进而精准抑制NF-κB信号通路,并促进STAT3相关信号的表达,从而达到抑制炎症反应、促进巨噬细胞M2极化的效果,以此来治疗实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎症状。
2.4.4 Toll样受体(Toll-like receptors,TLR)相关通路 Toll样受体相关通路在促进髓鞘再生中发挥着作用,ZHANG等[58]研究发现,使用源自恒河猴间充质干细胞的外泌体治疗脱髓鞘小鼠模型,可以显著改善小鼠的认知功能、促进髓鞘再生和巨噬细胞M2极化,这一过程的关键在于外泌体能够阻断TLR2信号传导,进而抑制TLR2/IRAK1/NF-κB通路,减少对髓鞘再生的限制作用。外泌体不仅直接作用于少突胶质细胞的前体细胞,还间接作用于脱髓鞘中枢神经系统中的小胶质细胞,共同促进髓鞘再生。
2.4.5 磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B(phosphoinositide 3 kinase/protein kinase B,PI3K/AKT)通路 LU等[59]则聚焦于PI3K/AKT通路在外泌体诱导巨噬细胞极化中的作用。人脐带间充质干细胞治疗能够有效抑制兔自身免疫性泪腺炎的炎症并恢复泪腺功能,显著抑制了M1巨噬细胞标记物表达,促进M2巨噬细胞标记物的表达;进一步的研究显示,人脐带间充质干细胞通过激活PI3K/AKT通路诱导巨噬细胞向M2表型极化以减轻自身免疫性泪腺炎症状。这一发现不仅揭示了外泌体在自身免疫性疾病中的新机制,也为自身免疫性疾病的治疗提供了新的策略。
2.4.6 未探索具体信号通路的RNA递送 除了上述已经清晰阐述的机制通路,近期的研究还揭示了细胞外囊泡中的一些关键RNA对巨噬细胞极化的重要作用,为外泌体在免疫调节和疾病治疗中的应用提供了新的视角,但具体的信号通路尚不清楚。
DOU等[60]的研究是一个重要突破,发现tsRNA-21109的表达与系统性红斑狼疮患者的临床数据密切相关,tsRNA-21109缺陷外泌体可以促进M1巨噬细胞标志物的表达,同时减少M2巨噬细胞标志物表达。间充质干细胞衍生外泌体可能通过转移tsRNA-21109抑制巨噬细胞的M1型极化。在体外实验中,此种间充质干细胞衍生的tsRNA-21109缺陷外泌体通过抑制巨噬细胞M1极化减轻了系统性红斑狼疮的症状。
LI等[61]研究发现,人间充质干细胞衍生细胞外囊泡对兔自身免疫性泪腺炎具有预防和治疗作用,能够诱导巨噬细胞M2极化,并提高调节性T细胞的比例,从而改善组织损伤。他们发现人脐带间充质干细胞衍生细胞外囊泡中高表达miR-100-5p,敲低miR-100-5p可以减弱人脐带间充质干细胞衍生细胞外囊泡对于M2巨噬细胞极化的促进作用。人脐带间充质干细胞可能通过递送miR-100-5p来促进M2巨噬细胞极化和调节性T细胞生成,从而缓解自身免疫性泪腺炎。
XU等[62]研究揭示了人经血间充质干细胞衍生细胞外囊泡在肠道炎症调节中的新机制,他们发现这些囊泡受到肿瘤坏死因子α刺激后,通过增加miR-24-3p的表达,靶向下调小鼠结肠中干扰素调节因子1的表达,进而促进M2巨噬细胞的极化,减少了小鼠结肠炎损伤。
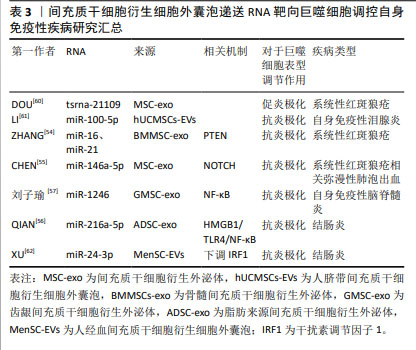
间充质干细胞衍生细胞外囊泡通过调节多条信号通路参与巨噬细胞的极化过程,展现其在免疫调节和疾病治疗中的多元化潜力。这些研究不仅提供了新的治疗策略和方法,也为深入理解外泌体的生物学功能和疾病机制提供了有力支持。关于间充质干细胞衍生细胞外囊泡递送RNA靶向巨噬细胞调控自身免疫性疾病汇总情况如表3所示。
 2.5 基于工程化细胞外囊泡构建纳米载药平台靶向巨噬细胞治疗自身免疫性疾病
2.5.1 通过改造间充质干细胞衍生细胞外囊泡实现非侵入式靶向给药
2.5 基于工程化细胞外囊泡构建纳米载药平台靶向巨噬细胞治疗自身免疫性疾病
2.5.1 通过改造间充质干细胞衍生细胞外囊泡实现非侵入式靶向给药 在非侵入性靶向给药领域的研究中,细胞外囊泡作为一种新型的药物载体展现出巨大潜力。面对1型糖尿病的治疗,WANG等[63]开发了一种高表达程序性死亡受体-配体1分子的纳米系统H@TI-EVs,通过电穿孔将具有抗炎及成像作用的5-氨基乙酰丙酸己基酯包埋至间充质干细胞衍生的细胞外囊泡中。在1型糖尿病动物模型中,H@TI-EVs能通过PD-L1/PD-1轴调节免疫微环境,促进巨噬细胞向M2表型转化,抑制CD4+ T细胞激活,进而保护胰岛细胞,展现出治疗潜力。
类风湿性关节炎患者通常采用关节内注射糖皮质激素的方法进行治疗,在关节内反复注射糖皮质激素会引起高血糖、感染、骨密度降低和软骨损伤等不良反应。针对类风湿性关节炎治疗过程中的弊端,BUI等[64]制备了一种基于硫酸软骨素C的溶解微针,以非侵入性方式将人脂肪间充质干细胞来源细胞外囊泡输送到炎症关节,这种溶解微针携带的细胞外囊泡有效抑制了成纤维细胞样滑膜细胞和M1巨噬细胞的活化,同时促进骨髓源性干细胞的软骨分化,改善了类风湿性关节炎模型小鼠的临床症状,没有观察到明显的不良反应。YOU等[65]通过代谢糖工程对脂肪源性干细胞的外泌体进行精细的表面编辑,并由此开发出硫酸葡聚糖-外泌体,这种表面编辑方法保持了外泌体的结构和功能。硫酸葡聚糖-外泌体可以通过促进M1型巨噬细胞转变为M2型巨噬细胞来改善类风湿关节炎小鼠的滑膜微环境。该技术也可用于多种与巨噬细胞相关疾病的治疗,如炎症性肠病、阿尔茨海默病等。
通过改造间充质干细胞来源的细胞外囊泡,研究人员成功开发了一系列非侵入性靶向药物。这些研究展示了细胞外囊泡在非侵入性靶向给药中的巨大潜力,不仅为糖尿病、类风湿性关节炎、炎症性疾病和中枢神经系统疾病提供了创新的治疗策略,还为未来的药物开发和临床应用开辟了广阔前景。
2.5.2 通过间充质干细胞衍生的细胞外囊泡构建载药平台以延长药物半衰期 细胞外囊泡作为药物递送载体时,面临着血浆半衰期短、易被肝清除及无法靶向病变组织等难题,阻碍了外泌体的临床应用。用何种办法来延长药物半衰期、优化药物动力学是亟待解决的问题。张晶[66]发现细胞外泌体在体内的组织分布和半衰期受其表面的细胞黏附类分子和糖基化状态的影响,通过精确敲除整合素家族分子以及特异性去除N-糖基化分子,可显著降低细胞外泌体在体内的非特异性黏附,延长体内循环半衰期,增强其成药性。
2.5.3 通过工程化改造实现细胞外囊泡口服给药 在消化道相关自身免疫性疾病如溃疡性结肠炎等的治疗领域,静脉注射间充质干细胞的外泌体,虽然能在一定程度上改善胃肠炎症,但这种给药方法具有局限性及潜在的不良反应。相比之下,口服给药因便捷性和患者接受度高,是胃肠道疾病给药的首选方法。但外泌体中含有容易被胃肠环境降解的蛋白质和核酸,难以实现口服给药。为解决这一难题,DENG等[27]构建了一种高效的逐层包被外泌体自组装系统,使用具有生物相容性、可降解的水溶性壳聚糖衍生物和氧化魔芋葡甘露聚糖多糖作为外层包被材料,该药物在口服给药过程中能保护外泌体免受降解,并在炎性结肠中将外泌体有控制的释放,能够被巨噬细胞和肠上皮细胞内化,通过抑制MAPK/NF-κB信号通路来改善结肠炎症。与传统静脉给药相比,口服逐层包被的外泌体可以有效缓解溃疡性结肠炎。
2.5.4 通过工程化改造细胞外囊泡减轻移植物和植入材料的异体反应 在器官移植与生物材料植入领域,异体反应是影响移植成功率和患者长期生存质量的挑战。
MOHAMMADI等[67]研制了一种杂交海藻酸盐微胶囊,它可以通过释放来自人脐带间充质干细胞的外泌体,减弱胰岛移植后的异体反应。将包被杂交海藻酸盐微胶囊的大鼠胰岛移植到1型糖尿病小鼠体内,可以使小鼠血糖在170 d内保持在正常范围,外泌体可能通过干扰NF-κB通路来促进巨噬细胞向M2表型转化。此外杂交海藻酸盐微胶囊可以通过控制外泌体的释放,以减轻机体对植入式生物材料的局部免疫反应。
2.5.5 通过工程化改造细胞外囊泡提高中草药药物成分生物利用度 在现代医药学领域,西医药物在自身免疫性疾病的治疗中扮演着重要角色,而中草药凭借其独特的抗炎特性,也展现出了不可忽视的治疗潜力。但由于中草药不易溶解、渗透性差、生物利用度低的原因,显著限制了其临床应用。为解决这个问题,YAN等[68]开发了一种多功能药物递送系统——使用脂肪间充质干细胞衍生外泌体为载体运输淫羊藿苷。淫羊藿苷是提取自草本药物淫羊藿的活性化合物,具有强大的抗炎特性。这种载体运输系统可以靶向类风湿关节炎滑膜组织中的巨噬细胞,促进其转变为M2型巨噬细胞。在脂肪间充质干细胞衍生外泌体的运输下,淫羊藿苷得以有效地积累在关节中,通过抑制ERK/HIF-1α/GLUT1通路减少糖酵解并促进巨噬细胞表型从M1到M2转变。这种多功能药物递送系统显著提升了中草药有效成分的生物利用度。
2.5.6 通过工程化细胞外囊泡解决中枢神经系统药物跨越血脑屏障的难题 在中枢神经系统自身免疫性疾病的研究中,药物如何跨过血脑屏障实现脑靶向药物递送是一大挑战,鼻腔给药可能是其中一种解决办法。翟源心[69]通过工程化改造,将脑源性神经营养因子装载入经过靶向修饰的外泌体,有效克服了脑源性神经营养因子难以成药的难题。经鼻腔给药后,这些外泌体除少量遗留在鼻腔外,其余大部分穿透血脑屏障,广泛分布于脑组织,显著提升了的脑靶向药物递送效率。这一方法不仅促进了中枢神经系统脱髓鞘模型小鼠的运动能力恢复,还加速了髓鞘再生。肖赟 [70]构建了一种神经干细胞来源细胞外囊泡药物载体,能够靶向中枢神经系统患病部位,在保证药物原本结构的基础上,实现与靶细胞高效结合;在实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎和双环己酮草酰二腙诱导脱髓鞘动物模型上,实现了药物的高效递送,有较好的治疗效果。



