[1] ANG CJ, SKOKAN TD, MCKINLEY KL. Mechanisms of Regeneration and Fibrosis in the Endometrium. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2023;39:197-221.
[2] 中华医学会妇产科学分会.宫腔粘连临床诊疗中国专家共识[J].中华妇产科杂志,2015,50(12):881-887.
[3] YU H, HUANG Y, YANG L. Research progress in the use of mesenchymal stem cells and their derived exosomes in the treatment of osteoarthritis. Ageing Res Rev. 2022;80:101684.
[4] CHENG L, HILL AF. Therapeutically harnessing extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2022;21(5):379-399.
[5] LEE WL, LIU CH, CHENG M, et al. Focus on the Primary Prevention of Intrauterine Adhesions: Current Concept and Vision. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(10):5175.
[6] SEVINÇ F, OSKOVI-KAPLAN ZA, ÇELEN Ş, et al. Identifying the risk factors and incidence of Asherman Syndrome in women with post-abortion uterine curettage. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2021;47(4):1549-1555.
[7] LIU L, CHEN G, CHEN T, et al. si-SNHG5-FOXF2 inhibits TGF-β1-induced fibrosis in human primary endometrial stromal cells by the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):479.
[8] ABUDUKEYOUMU A, LI MQ, XIE F. Transforming growth factor-β1 in intrauterine adhesion. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2020;84(2):e13262.
[9] XUE X, LI X, YAO J, et al. Transient and Prolonged Activation of Wnt Signaling Contribute Oppositely to the Pathogenesis of Asherman’s Syndrome. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(15):8808.
[10] ESPINDOLA MS, HABIEL DM, COELHO AL, et al. Differential Responses to Targeting Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021;203(4):458-470.
[11] LI C, WANG W, SUN S, et al. Expression and Potential Role of MMP-9 in Intrauterine Adhesion. Mediators Inflamm. 2021;2021:6676510.
[12] WU F, LEI N, YANG S, et al. Treatment strategies for intrauterine adhesion: focus on the exosomes and hydrogels. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1264006.
[13] CHEN K, ZHENG S, FANG F. Endometrial Stem Cells and Their Applications in Intrauterine Adhesion. Cell Transplant. 2023;32: 9636897231159561.
[14] SONG YT, LIU PC, TAN J, et al. Stem cell-based therapy for ameliorating intrauterine adhesion and endometrium injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):556.
[15] ZHU X, PÉAULT B, YAN G, et al. Stem Cells and Endometrial Regeneration: From Basic Research to Clinical Trial. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;14(4):293-304.
[16] 赵淑芬,柳怡,郑雪湘.宫腔粘连患者子宫内膜组织中雌激素受体及孕激素受体的表达情况和临床意义分析[J].中国计划生育和妇产科,2018,10(7):33-36,41.
[17] 陈庆,赵金燕,张雪,等.雌、孕激素通过TGF-β影响宫腔粘连的形成[J].山西医科大学学报,2021,52(7):883-888.
[18] GE J, CHEN Y, YANG H, et al. Expression and significance of estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor in endometrial tissue of patients with intrauterine adhesions. Gland Surg. 2021;10(4):1478-1486.
[19] 杜娟,康卉娴.ER和TGF-β1在宫腔粘连患者中的表达及其相关性的研究[J].宁夏医学杂志,2020,42(7):628-630.
[20] ZHANG J, JIANG P, TU Y, et al. Identification and validation of long non-coding RNA associated ceRNAs in intrauterine adhesion. Bioengineered. 2022;13(1):1039-1048.
[21] ZHOU Z, WANG H, ZHANG X, et al. Defective autophagy contributes to endometrial epithelial-mesenchymal transition in intrauterine adhesions. Autophagy. 2022;18(10):2427-2442.
[22] CHEN G, LIU L, SUN J, et al. Foxf2 and Smad6 co-regulation of collagen 5A2 transcription is involved in the pathogenesis of intrauterine adhesion. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(5):2802-2818.
[23] WANG Z, XIA L, CHENG J, et al. Combination Therapy of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation and Electroacupuncture for the Repair of Intrauterine Adhesions in Rats: Mechanisms and Functional Recovery. Reprod Sci. 2024;31(8):2318-2330.
[24] YUAN L, CAO J, HU M, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with estrogen synergistically promote endometrial regeneration and reverse EMT via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2022;20(1):121.
[25] YU J, ZHANG W, HUANG J, et al. Management of intrauterine adhesions using human amniotic mesenchymal stromal cells to promote endometrial regeneration and repair through Notch signalling. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(23):11002-11015.
[26] SUN D, JIANG Z, CHEN Y, et al. MiR-455-5p upregulation in umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells attenuates endometrial injury and promotes repair of damaged endometrium via Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling. Bioengineered. 2021;12(2):12891-12904.
[27] ZHANG D, DU Q, LI C, et al. Functionalized human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells and injectable HA/Gel hydrogel synergy in endometrial repair and fertility recovery. Acta Biomater. 2023;167: 205-218.
[28] LI J, HUANG B, DONG L, et al. WJ‑MSCs intervention may relieve intrauterine adhesions in female rats via TGF‑β1‑mediated Rho/ROCK signaling inhibition. Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(1):8.
[29] HUA Q, ZHANG Y, LI H, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived MSCs trans-differentiate into endometrial cells and regulate Th17/Treg balance through NF-κB signaling in rabbit intrauterine adhesions endometrium. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):301.
[30] 勾亚婷,张文文,李长江,等.NF-κB信号通路在人羊膜间充质干细胞治疗宫腔粘连中的作用[J].第三军医大学学报,2020,42(11): 1101-1108.
[31] ZHOU L, WANG H, SHEN D, et al. Stem cells implanted with nanofibrous mats for injured endometrial regeneration and immune-microenvironment remodeling. Mater Today Bio. 2023;23:100855.
[32] PARK M, HONG SH, PARK SH, et al. Perivascular Stem Cell-Derived Cyclophilin A Improves Uterine Environment with Asherman’s Syndrome via HIF1α-Dependent Angiogenesis. Mol Ther. 2020;28(8):1818-1832.
[33] HU S, DAI Y, XIN L, et al. Minimally invasive delivery of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells by an injectable hydrogel via Diels-Alder click reaction for the treatment of intrauterine adhesions. Acta Biomater. 2024;177:77-90.
[34] JIANG Q, LI J, PAN Y, et al. Melatonin-Primed MSCs Alleviate Intrauterine Adhesions by Affecting MSC-Expressed Galectin-3 on Macrophage Polarization. Stem Cells. 2022;40(10):919-931.
[35] WANG J, LI J, YIN L, et al. MSCs promote the efferocytosis of large peritoneal macrophages to eliminate ferroptotic monocytes/macrophages in the injured endometria. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024; 15(1):127.
[36] MAO Y, YANG Y, SUN C, et al. Human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells promote endometrium regeneration in a rat model of intrauterine adhesion. Cell Biol Int. 2023;47(1):75-85.
[37] 任莉,张俊俊,孟喜燕.人胎盘间充质干细胞对大鼠子宫内膜损伤的修复作用及对JAK2/STAT3通路的影响[J].中国实用医刊, 2023,50(1):1-5.
[38] LIN Y, DONG S, YE X, et al. Synergistic regenerative therapy of thin endometrium by human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated within hyaluronic acid hydrogels. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):66.
[39] 郝赛楠,夏良君,席瑾,等.电针联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植通过调节SDF-1/CXCR4轴促进薄型子宫内膜修复的机制研究[J].针刺研究,2023,48(9):870-880.
[40] WANG G, REN C, JIANG J. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on repair and receptivity of damaged endometrium in rats. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2021;47(9):3223-3231.
[41] WANG L, YU C, CHANG T, et al. In situ repair abilities of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells and autocrosslinked hyaluronic acid gel complex in rhesus monkeys with intrauterine adhesion. Sci Adv. 2020;6(21):eaba6357.
[42] XU X, XING Q, LIU R, et al. Therapeutic Effects and Repair Mechanism of HGF Gene-Transfected Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Injured Endometrium. Stem Cells Int. 2022;2022:5744538.
[43] ZHANG L, LI Y, DONG YC, et al. Transplantation of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells promotes the recovery of thin endometrium in rats. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):412.
[44] HUANG X, YANG X, HUANG J, et al. Human amnion mesenchymal stem cells promote endometrial repair via paracrine, preferentially than transdifferentiation. Cell Commun Signal. 2024;22(1):301.
[45] WU M, LI Y, WANG Y, et al. HOXA10 Expressing UCMSCs Transplantation Improved Endometrial Receptivity on Endometrial Injury. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;18(7):1001-1012.
[46] FAN J, XIE J, LIAO Y, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells and auto-crosslinked hyaluronic acid gel complex for treatment of intrauterine adhesion. Aging (Albany NY). 2024;16(7):6273-6289.
[47] XU X, KONG DS, TIAN YP, et al. Autocross-linked hyaluronic acid gel and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell composites for the treatment intrauterine adhesions. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;60(6): 1031-1037.
[48] SHAO X, AI G, WANG L, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells transplantation improves endometrial injury repair. Zygote. 2019;27(6):367-374.
[49] HU X, DAI Z, PAN R, et al. Long-term transplantation human menstrual blood mesenchymal stem cell loaded collagen scaffolds repair endometrium histological injury. Reprod Toxicol. 2022;109:53-60.
[50] ZHANG S, ZHANG R, YIN X, et al. MenSCs Transplantation Improve the Viability of Injured Endometrial Cells Through Activating PI3K/Akt Pathway. Reprod Sci. 2023;30(11):3325-3338.
[51] WANG X, BAO H, LIU X, et al. Effects of endometrial stem cell transplantation combined with estrogen in the repair of endometrial injury. Oncol Lett. 2018;16(1):1115-1122.
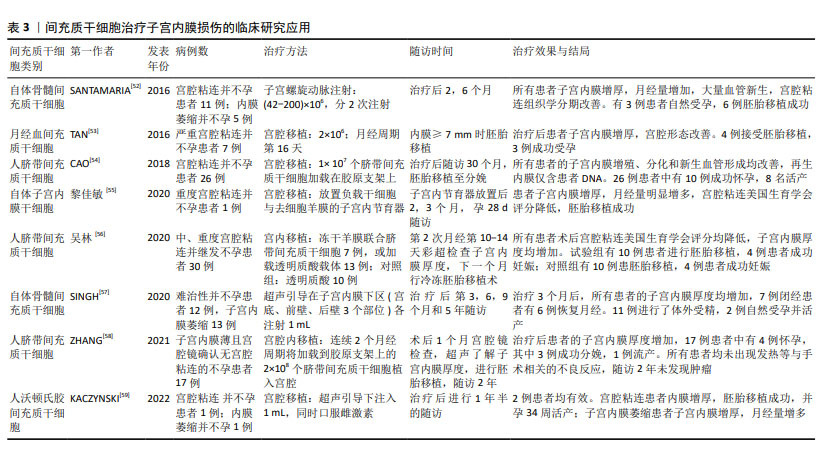
[52] SANTAMARIA X, CABANILLAS S, CERVELLÓ I, et al. Autologous cell therapy with CD133+ bone marrow-derived stem cells for refractory Asherman’s syndrome and endometrial atrophy: a pilot cohort study. Hum Reprod. 2016;31(5):1087-1096.
[53] TAN J, LI P, WANG Q, et al. Autologous menstrual blood-derived stromal cells transplantation for severe Asherman’s syndrome. Hum Reprod. 2016;31(12):2723-2729.
[54] CAO Y, SUN H, ZHU H, et al. Allogeneic cell therapy using umbilical cord MSCs on collagen scaffolds for patients with recurrent uterine adhesion: a phase I clinical trial. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):192.
[55] 黎佳敏,林姣,彭婀娜,等.去细胞羊膜载体复合自体子宫内膜干细胞治疗重度宫腔粘连1例报道[J].生殖医学杂志,2020,29(4): 541-544.
[56] 吴林.冻干羊膜联合人脐带间充质干细胞治疗中重度宫腔粘连的研究[D].衡阳:南华大学,2020.
[57] SINGH N, SHEKHAR B, MOHANTY S, et al. Autologous Bone Marrow-Derived Stem Cell Therapy for Asherman’s Syndrome and Endometrial Atrophy: A 5-Year Follow-up Study. J Hum Reprod Sci. 2020;13(1):31-37.
[58] ZHANG Y, SHI L, LIN X, et al. Unresponsive thin endometrium caused by Asherman syndrome treated with umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on collagen scaffolds: a pilot study. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):420.
[59] KACZYNSKI JB, RZEPKA JK. Endometrial regeneration in Asherman’s syndrome and endometrial atrophy using Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Ginekol Pol. 2022;93(11):904-909.
[60] WANG X, WU J, XIE Y, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles facilitate endometrial injury repair by carrying the E3 ubiquitin ligase WWP1. Biochem Cell Biol. 2022; 100(4):357-369.
[61] LI J, PAN Y, YANG J, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α-primed mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote M2 macrophage polarization via Galectin-1 and modify intrauterine adhesion on a novel murine model. Front Immunol. 2022;13:945234.
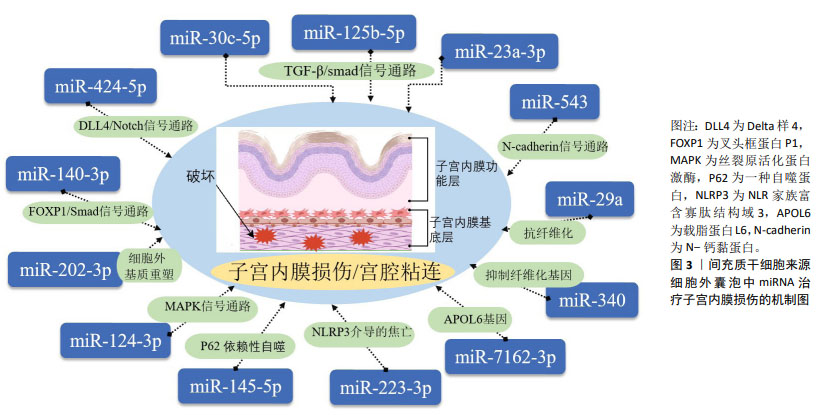
[62] XIONG Z, HU Y, JIANG M, et al. Hypoxic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell exosomes promote angiogenesis and enhance endometrial injury repair through the miR-424-5p-mediated DLL4/Notch signaling pathway. PeerJ. 2024;12:e16953.
[63] CHEN Y, ZHENG S, ZHAO X, et al. Unveiling the protective effects of BMSCs/anti-miR-124-3p exosomes on LPS-induced endometrial injury. Funct Integr Genomics. 2024;24(2):32.
[64] MANSOURI-KIVAJ N, NAZARI A, ESFANDIARI F, et al. Homogenous subpopulation of human mesenchymal stem cells and their extracellular vesicles restore function of endometrium in an experimental rat model of Asherman syndrome. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):61.
[65] LIU Y, ZHANG S, XUE Z, et al. Bone mesenchymal stem cells-derived miR-223-3p-containing exosomes ameliorate lipopolysaccharide-induced acute uterine injury via interacting with endothelial progenitor cells. Bioengineered. 2021;12(2):10654-10665.
[66] TAN Q, XIA D, YING X. miR-29a in Exosomes from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Inhibit Fibrosis during Endometrial Repair of Intrauterine Adhesion. Int J Stem Cells. 2020;13(3):414-423.
[67] XIAO B, ZHU Y, HUANG J, et al. Exosomal transfer of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived miR-340 attenuates endometrial fibrosis. Biol Open. 2019;8(5):bio039958.
[68] XIONG Z, MA Y, HE J, et al. Apoptotic bodies of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibit endometrial stromal cell fibrosis by mediating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Heliyon. 2023; 9(11):e20716.
[69] XIN L, WEI C, TONG X, et al. In situ delivery of apoptotic bodies derived from mesenchymal stem cells via a hyaluronic acid hydrogel: A therapy for intrauterine adhesions. Bioact Mater. 2021;12:107-119.
[70] YUAN D, GUO T, QIAN H, et al. Exosomal miR-543 derived from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates endometrial fibrosis in intrauterine adhesion via downregulating N-cadherin. Placenta. 2023;131:75-81.
[71] WANG S, LIU T, NAN N, et al. Exosomes from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Facilitates Injured Endometrial Restoring in Early Repair Period through miR-202-3p Mediating Formation of ECM. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023;19(6):1954-1964.
[72] SHI Q, WANG D, DING X, et al. Exosome-shuttled miR-7162-3p from human umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells repair endometrial stromal cell injury by restricting APOL6. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2021;707:108887.
[73] SONG M, MA L, ZHU Y, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes inhibits fibrosis in human endometrial stromal cells via miR-140-3p/FOXP1/Smad axis. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):8321.
[74] WANG J, HU R, XING Q, et al. Exosomes Derived from Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Mifepristone-Induced Human Endometrial Stromal Cell Injury. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:6091269.
[75] LIU H, ZHANG X, ZHANG M, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosomes Repair Uterine Injury by Targeting Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling. ACS Nano. 2024;18(4):3509-3519.
[76] ZHAO S, QI W, ZHENG J, et al. Exosomes Derived from Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells Restore Functional Endometrium in a Rat Model of Intrauterine Adhesions. Reprod Sci. 2020;27(6):1266-1275.
[77] SUN H, DONG J, FU Z, et al. TSG6-Exo@CS/GP Attenuates Endometrium Fibrosis by Inhibiting Macrophage Activation in a Murine IUA Model. Adv Mater. 2024;36(21):e2308921.
[78] ZHANG S , CHANG Q , LI P , et al. Concentrated small extracellular vesicles from menstrual blood-derived stromal cells improve intrauterine adhesion, a pre-clinical study in a rat model. Nanoscale. 2021;13(15):7334-7347.
[79] ZHOU L, DONG L, LI H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes ameliorate TGF-β1-induced endometrial fibrosis by altering their miRNA profile. Am J Transl Res. 2023;15(5):3203-3216.
[80] 王艳阳,刘婵,余丽梅,等.间充质干细胞及细胞外囊泡治疗肺纤维化的现状与未来[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(25):4079-4086.
[81] 熊正花,刘贝贝,杨琳娟,等.低氧处理骨髓间充质干细胞来源的外泌体对宫腔粘连模型大鼠的疗效研究[J].中华妇产科杂志, 2023,58(12):911-921.
[82] LONG L, JI D, HU C, et al. Microneedles for in situ tissue regeneration. Mater Today Bio. 2023;19:100579.
[83] LI X, LV HF, ZHAO R, et al. Recent developments in bio-scaffold materials as delivery strategies for therapeutics for endometrium regeneration. Mater Today Bio. 2021 ;11:100101.
[84] 邬浩明,王瑶,陈圆梦,等.宫腔粘连中水凝胶促内膜修复的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(17):2774-2781.
[85] LiU T, HE B, XU X. Repairing and Regenerating Injured Endometrium Methods. Reprod Sci. 2023;30(6):1724-1736.
[86] ÇIL N, YAKA M, ÜNAL MS, et al. Adipose derived mesenchymal stem cell treatment in experimental asherman syndrome induced rats. Mol Biol Rep. 2020;47(6):4541-4552.
[87] XIAO B, YANG W, LEI D, et al. PGS Scaffolds Promote the In Vivo Survival and Directional Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Restoring the Morphology and Function of Wounded Rat Uterus. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8(5):e1801455.
|