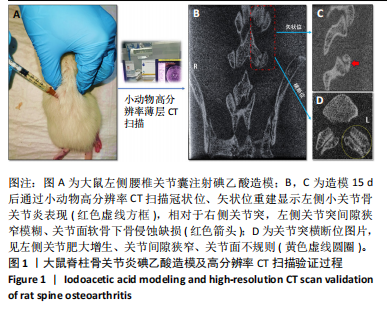
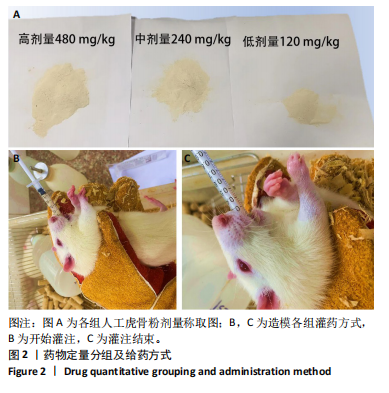
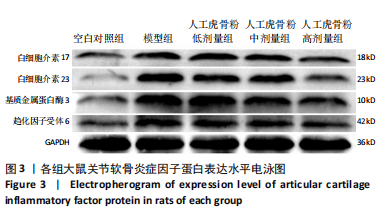
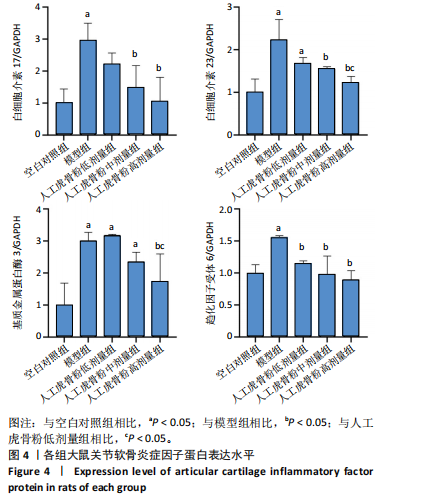
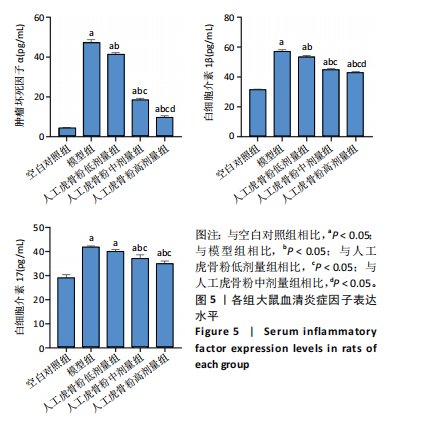
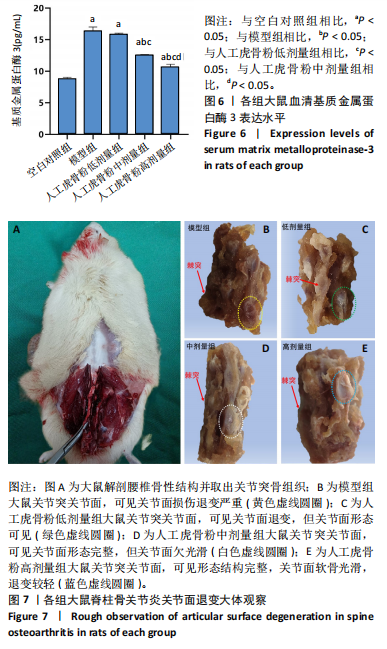
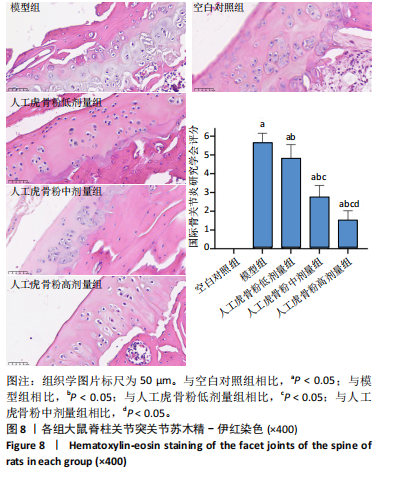
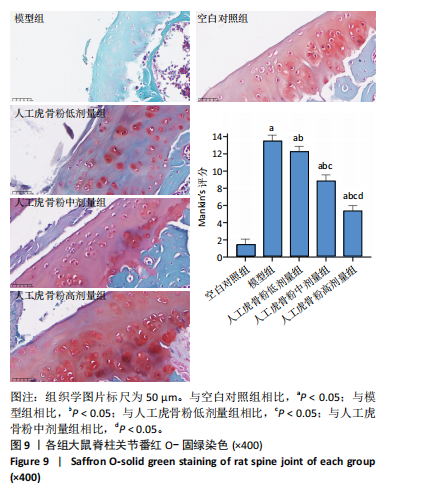
[1] 李锋,宋跃明,方忠,等.脊柱小关节骨关节炎诊治专家共识[J].骨科,2018,9(6):417-422.
[2] 包黎莎,王华芳,杨锦荧,等.人参总皂苷对大鼠骨关节炎的作用[J].浙江临床医学,2021,23(1):4-7
[3] 谭利贤,杜小康,汤润民, 等.脊柱小关节骨关节炎的病因/病理与发病机制研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2022,32(10):954-960.
[4] LINDSEY T, DYDYK AM. Spinal Osteoarthritis. 2023. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): Stat Pearls Publishing, 2024.
[5] GBD 2021 LOW BACK PAIN COLLABORATORS. Global, regional, and national burden of low back pain, 1990–2020, its attributable risk factors, and projections to 2050: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021.Lancet Rheumatol. 2023;5:e316-e329.
[6] MARCH LM, BACHMEIER CJ. Economics of osteoarthritis: a global perspective. Baillieres Clin Rheumatol. 1997;11(4):817-834.
[7] MARTEL-PELLETIER J, BARR AJ, CICUTTINI FM, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16072.
[8] 邹明,张红梅,徐艺筝.膝关节炎患者关节置换术后细菌感染严重程度与IL-1β、TNF-α、IL-6水平的相关性[J].中国微生态学杂志, 2020,32(1):44-46.
[9] LI H, TSOKOS GC. IL-23/IL-17 Axis in Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2021;60(1):31-45.
[10] SCHINOCCA C, RIZZO C, FASANO S, et al. Role of the IL-23/IL-17 Pathway in Rheumatic Diseases: An Overview. Front Immunol. 2021;12:637829.
[11] BUNTE K, BEIKLER T. Th17 Cells and the IL-23/IL-17 Axis in the Pathogenesis of Periodontitis and Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(14):3394.
[12] XIAO J, ZHANG P, CAI FL, et al. IL-17 in osteoarthritis: A narrative review. Open Life Sci. 2023;18(1):20220747.
[13] 李泽琴,杨佳明,高峰,等. 间充质干细胞促进软骨修复治疗骨关节炎的机制及应用进展[J]. 山东医药,2023,63(22):86-90.
[14] ZHU X, SANG L, WU D, et al. Effectiveness and safety of glucosamine and chondroitin for the treatment of osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):170.
[15] SELIG DJ, KRESS AT, HORTON IM, et al. Pharmacokinetics, safety and efficacy of intra-articular non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug injections for the treatment of osteoarthritis: A narrative review. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022;47(8):1122-1133.
[16] SKOU ST, ROOS EM. Physical therapy for patients with knee and hip osteoarthritis: supervised, active treatment is current best practice. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019;37 Suppl 120(5):112-117.
[17] 王彦艳,姚梁怡,蔡立柏, 等.膝骨关节炎非手术治疗患者运动干预的最佳证据总结[J].护理学杂志,2024,39(8):102-106.
[18] 刘潞兴,狄鸣远,杨强.中药有效成分治疗骨关节炎机制中的信号通路[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(4):609-614.
[19] 侯德晖,谷光辉,陈允震.人工虎骨粉对SAMP8小鼠肌少症的预防作用[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2023,16(2):123-132.
[20] 魏立友,张宏伟.人工虎骨粉对老年骨质疏松性腰背疼痛的作用[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2017,23(11):1492-1494.
[21] 李超,赵剑波,陈俊雅,等. 金天格胶囊对H2O2诱导的小鼠成骨细胞MC3T3-E1氧化应激损伤及炎症因子的作用[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(10):1448-1452,1532.
[22] 胡培培,黄芳.云南白药通过抗炎作用缓解碘乙酸钠诱导的大鼠膝骨关节炎疼痛[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2019,24(3):254-259.
[23] 黄薇. 人工虎骨粉对胶原诱导关节炎小鼠的治疗作用及其机制初探[D]. 青岛:青岛大学,2023.
[24] GERWIN N, BENDELE AM, GLASSON S, et al. The OARSI histopathology initiative - recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in the rat. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18 Suppl 3:S24-34.
[25] 邬波,马旭,柳椰,等. 膝关节骨关节炎患者软骨炎症因子表达与病变程度的相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(2):236-241.
[26] MOLNAR V, MATIŠIĆ V, KODVANJ I, et al. Cytokines and Chemokines Involved in Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(17):9208.
[27] GLYN-JONES S, PALMER AJ, AGRICOLA R, et al. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2015;386(9991):376-387.
[28] CHEN L, YE L, LIU H, et al. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:1907821.
[29] 邬波,柳椰,焦递进, 等.中医药疗法对膝骨关节炎相关因子影响研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2021,23(1):1-4.
[30] 宋书林,刘胜武,崔向军,等.通滞苏润江胶囊联合托珠单抗治疗类风湿性膝关节炎效果及对IL-6、IL-17、IL-23的影响[J].疑难病杂志,2017,16(3):279-283.
[31] 张雯丽,李慧,闫伟伟.类风湿关节炎患者血清IL-17、TNF-α检测的意义[J].解放军医药杂志,2011,23(5):16-18+111.
[32] 张国华,吕智.类风湿关节炎患者外周血白细胞介素-23和类风湿因子的表达研究[J].中国医药导报,2011,8(18):23-25.
[33] MARTEL-PELLETIER J, BARR AJ, CICUTTINI FM, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16072.
[34] HOUARD X, GOLDRING MB, BERENBAUM F. Homeostatic mechanisms in articular cartilage and role of inflammation in osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2013;15(11):375.
[35] TROEBERG L, NAGASE H. Proteases involved in cartilage matrix degradation in osteoarthritis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1824(1): 133-145.
[36] 范少勇,周明,胡梁深, 等.膝骨关节炎治疗方法研究进展[J].江西中医药,2023,54(10):86-88.
[37] 王鸥,夏维波,成志峰,等.金天格胶囊治疗原发性骨质疏松症的有效性及安全性:随机、双盲双模拟、阳性药平行对照、多中心临床试验[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2022,15(2):142-151.
[38] 王清玉,韩大为.人工虎骨粉的药理作用研究进展[J].中医正骨, 2006(11):70-71.
[39] 包黎莎,王华芳,杨锦荧, 等. 人参总皂苷对大鼠骨关节炎的作用[J].浙江临床医学,2021,23(1):4-7.
[40] 魏立友,樊国峰,孙晓新,等.人工虎骨粉治疗老年脆性骨折的有效性临床研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(5):680-682.
[41] ZHUANG C, WANG Z, CHEN W, et al. Jintiange Capsules Ameliorate Osteoarthritis by Modulating Subchondral Bone Remodeling and Protecting Cartilage Against Degradation. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12: 762543. |