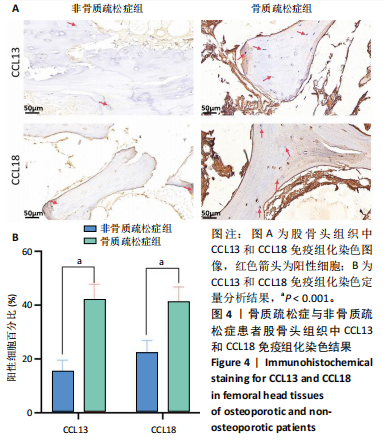
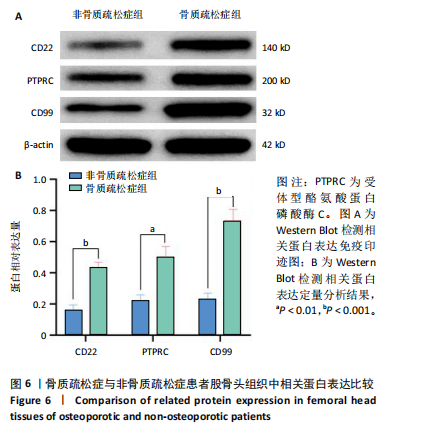
[1] 张玉,游如旭,张聪,等.骨质疏松症治疗药物合理应用专家共识(2023)[J].中国医院药学杂志,2024,44(9):985-1006.
[2] TRÉMOLLIÈRES F. [Menopause hormone therapy and osteoporosis]. Rev Prat. 2020;70(10):1097-1099.
[3] ZHANG W, GAO R, RONG X, et al. Immunoporosis: Role of immune system in the pathophysiology of different types of osteoporosis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:965258.
[4] YATSONSKY II D, PAN K, SHENDGE VB, et al. Linkage of microbiota and osteoporosis: A mini literature review. World J Orthop. 2019;10(3): 123-127.
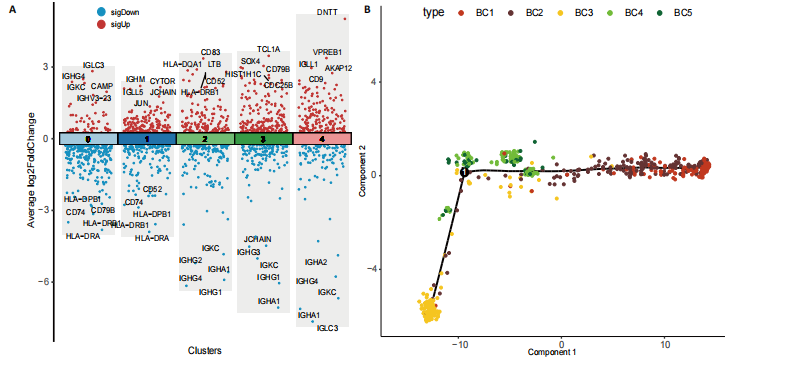
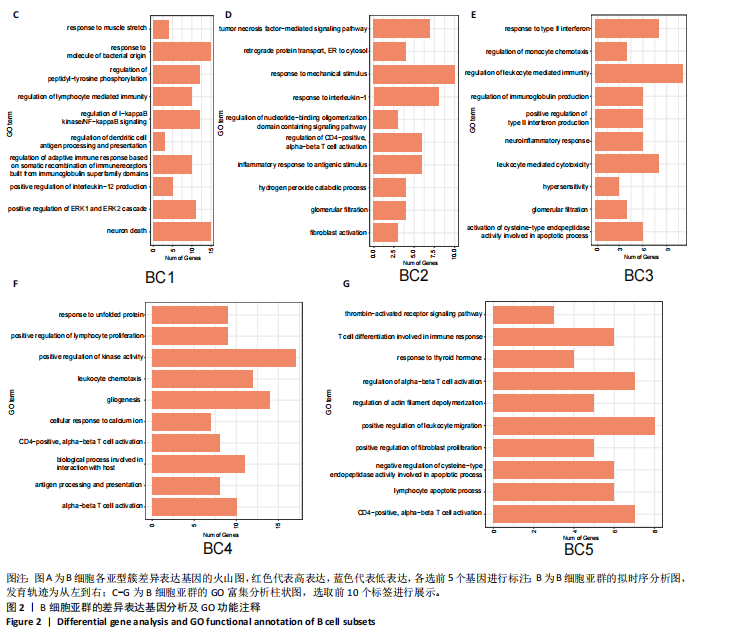
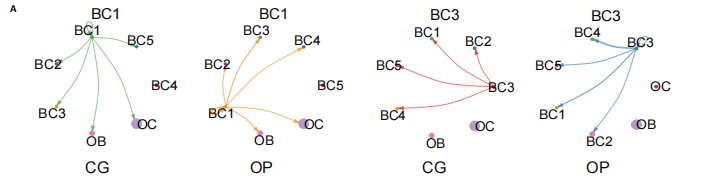
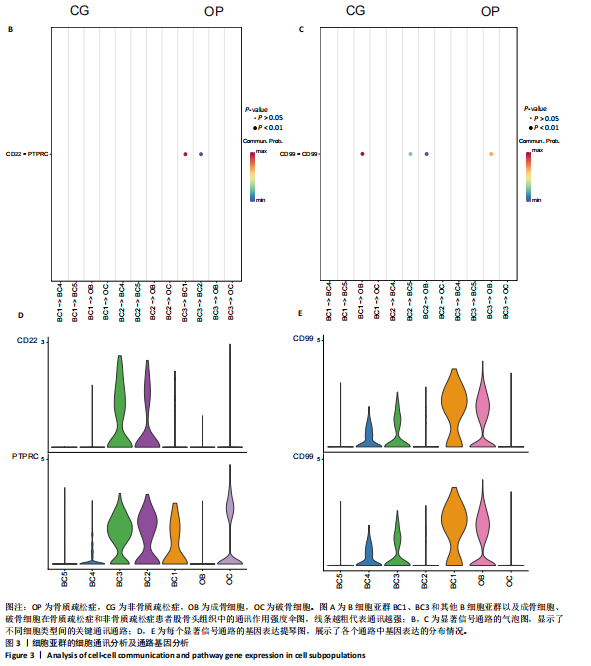
[5] 孙成涛,孙广江,戚晓楠,等.单细胞转录组测序技术在骨质疏松症研究中的应用与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(13):2812-2821.
[6] SAXENA Y, ROUTH S, MUKHOPADHAYA A. Immunoporosis: role of innate immune cells in osteoporosis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:687037.
[7] 陈天宁,杨铁毅,邵进,等.免疫相关基因在绝经后骨质疏松症患者外周血白细胞中的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(25):4033-4038.
[8] SLOVIN S, CARISSIMO A, PANARIELLO F, et al. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Analysis: A Step-by-Step Overview. Methods Mol Biol (Clifton, NJ). 2021;2284:343-365.
[9] LEI Y, TANG R, XU J, et al. Applications of single-cell sequencing in cancer research: progress and perspectives. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14(1):91.
[10] 许业楠,张贤,刘小峰,等.单细胞测序技术在骨质疏松诊疗中的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2024,30(3):463-468.
[11] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会,章振林.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)[J].中国全科医学,2023,26(14):1671-1691.
[12] WU S, OHBA S, MATSUSHITA Y. Single-Cell RNA-Sequencing Reveals the Skeletal Cellular Dynamics in Bone Repair and Osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(12):9814.
[13] CHEN J, TAN Y, SUN F, et al. Single-cell transcriptome and antigen-immunoglobin analysis reveals the diversity of B cells in non-small cell lung cancer. Genome Biol. 2020;21(1):152.
[14] MITTAL S, GARG B, MEHTA N, et al. Histopathological, Ultrastructural, and Immunohistochemical Findings in Radial Longitudinal Deficiency: A Prospective, Observational Study. J Hand Surg Am. 2022;47(8):789.e1-789.e8.
[15] ISHIHARA S, YAMAMOTO H, IWASAKI T, et al. Histological and immunohistochemical features and genetic alterations in the malignant progression of giant cell tumor of bone: a possible association with TP53 mutation and loss of H3K27 trimethylation. Mod Pathol. 2022;35(5):640-648.
[16] HU L, XIE X, XUE H, et al. MiR-1224-5p modulates osteogenesis by coordinating osteoblast/osteoclast differentiation via the Rap1 signaling target ADCY2. Exp Mol Med. 2022;54(7):961-972.
[17] XU Y, GENG Y, WANG H, et al. Cyclic helix B peptide alleviates proinflammatory cell death and improves functional recovery after traumatic spinal cord injury. Redox Biol. 2023;64:102767.
[18] ZHANG Y, ZHANG J, SUN Z, et al. MAPK8 and CAPN1 as potential biomarkers of intervertebral disc degeneration overlapping immune infiltration, autophagy, and ceRNA. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1188774.
[19] ZHANG W, ZHOU X, HOU W, et al. Reversing the imbalance in bone homeostasis via sustained release of SIRT-1 agonist to promote bone healing under osteoporotic condition. Bioact Mater. 2022;19:429-443.
[20] WANG L, PAN Y, LIU M, et al. Wen-Shen-Tong-Luo-Zhi-Tong Decoction regulates bone-fat balance in osteoporosis by adipocyte-derived exosomes. Pharm Biol. 2023;61(1):568-580.
[21] LI T, YUAN J, XU P, et al. PMAIP1, a novel diagnostic and potential therapeutic biomarker in osteoporosis. Aging. 2024;16(4):3694-3715.
[22] JI C, DONG Q, LIU H, et al. Acyl-protein thioesterase1 alleviates senile osteoporosis by promoting osteoblast differentiation via depalmitoylation of BMPR1a. Regen Ther. 2023;24:351-360.
[23] ARRON JR, CHOI Y. Osteoimmunology-bone versus immune system. Nature. 2000;408(6812):535-536.
[24] ANARGYROU K, FOTIOU D, VASSILAKOPOULOS TP, et al. Low Bone Mineral Density and High Bone Turnover in Patients With Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (NHL) Who Receive Frontline Therapy: Results of a Multicenter Prospective Study. Hemasphere. 2019;3(6):e303.
[25] Weitzmann MN. The Role of Inflammatory Cytokines, the RANKL/OPG Axis, and the Immunoskeletal Interface in Physiological Bone Turnover and Osteoporosis. Scientifica (Cairo). 2013;2013:125705.
[26] FISCHER V, HAFFNER-LUNTZER M. Interaction between bone and immune cells: Implications for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022;123:14-21.
[27] SUN W, MEEDNU N, ROSENBERG A, et al. B cells inhibit bone formation in rheumatoid arthritis by suppressing osteoblast differentiation. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):5127.
[28] CAI S, CHEN Y, HU Z, et al. The landscape of T and B lymphocytes interaction and synergistic effects of Th1 and Th2 type response in the involved tissue of IgG4-RD revealed by single cell transcriptome analysis. J Autoimmun. 2022;133:102944.
[29] BASHIROVA AA, ZHENG W, AKDAG M, et al. Population-specific diversity of the immunoglobulin constant heavy G chain (IGHG) genes. Genes Immun. 2021; 22(7-8):327-334.
[30] PRAZMA CM, YAZAWA N, FUJIMOTO Y, et al. CD83 expression is a sensitive marker of activation required for B cell and CD4+ T cell longevity in vivo. J Immunol. 2007;179(7):4550-4562.
[31] ZHANG H, WANG R, WANG G, et al. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals B Cells Are Important Regulators in Fracture Healing. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:666140.
[32] VELOUNIAS RL, TULL TJ. Human B-cell subset identification and changes in inflammatory diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 2022;210(3):201-216.
[33] ZHAI Y, CHEN L, ZHAO Q, et al. Cysteine carboxyethylation generates neoantigens to induce HLA-restricted autoimmunity. Science. 2023;379(6637):eabg2482.
[34] FENG M, WANG X, ZHOU S, et al. CD83+B cells alleviate uveitis through inhibiting DCs by sCD83. Immunology. 2023;170(1):134-153.
[35] XU K, WANG R, XIE H, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals cell heterogeneity and transcriptome profile of breast cancer lymph node metastasis. Oncogenesis. 2021;10(10):66.
[36] PASELLO M, MANARA MC, SCOTLANDI K. CD99 at the crossroads of physiology and pathology. J Cell Commun Signal. 2018;12(1):55-68.
[37] LI L, DAI F, WANG L, et al. CCL13 and human diseases. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1176639.
[38] LIN F, XUE DT, XIE T, et al. HMGB1 promotes cellular chemokine synthesis and potentiates mesenchymal stromal cell migrationvia Rap1 activation. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14(2):1283-1289.
[39] WU X, LIU Y, JIN S, et al. Single-cell sequencing of immune cells from anticitrullinated peptide antibody positive and negative rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):4977.
[40] DU Y, CAI Y, LV Y, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing unveils the communications between malignant T and myeloid cells contributing to tumor growth and immunosuppression in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Cancer Lett. 2022;551:215972.
[41] LI H, HE Z, DENG B, et al. Cytokines and chemokines involved in HLA-B27-positive ankylosing spondylitis-associated acute anterior uveitis. Mol Vis. 2023;29:378-385.
[42] CIECHANOWSKA A, MIKA J. CC Chemokine Family Members’ Modulation as a Novel Approach for Treating Central Nervous System and Peripheral Nervous System Injury-A Review of Clinical and Experimental Findings. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(7):3788.
[43] HUANG Y, HUANG J, ZHANG P, et al. Integrated analysis of hub gene expression in multiple myeloma. J BUON. 2021;26(5):2040-2052.
[44] PANG J, YU Q, CHEN Y, et al. Integrating Single-cell RNA-seq to construct a Neutrophil prognostic model for predicting immune responses in non-small cell lung cancer. J Transl Med. 2022;20(1):531.
[45] ZHANG Q, YU B, ZHANG Y, et al. Combination of single-cell and bulk RNA seq reveals the immune infiltration landscape and targeted therapeutic drugs in spinal cord injury. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1068359. |