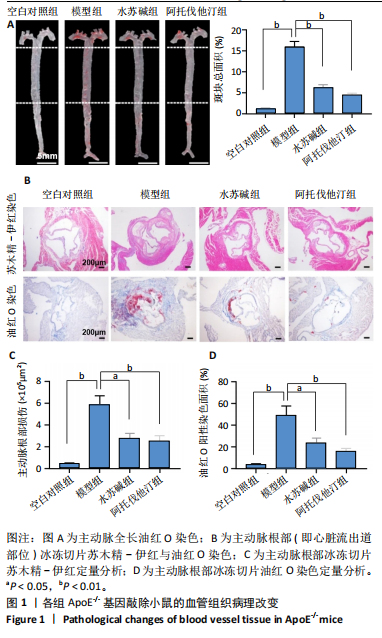
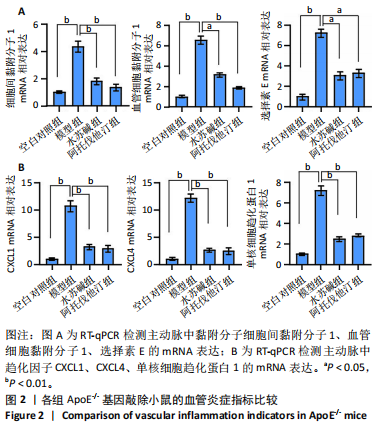
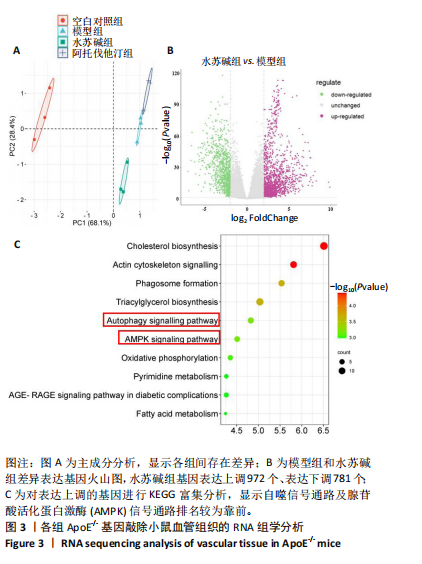
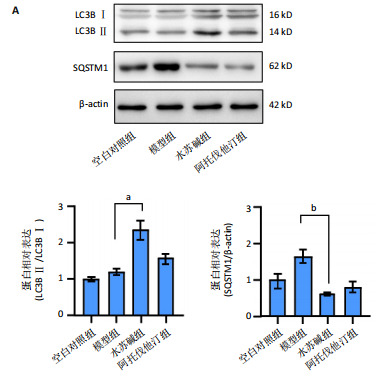
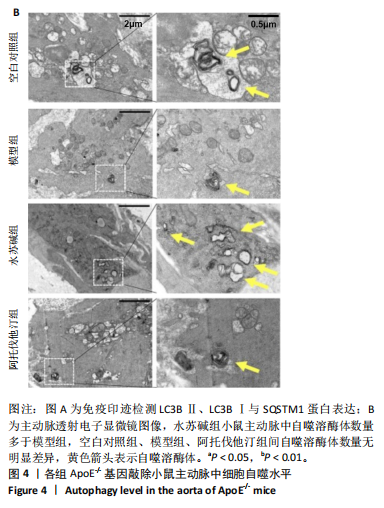
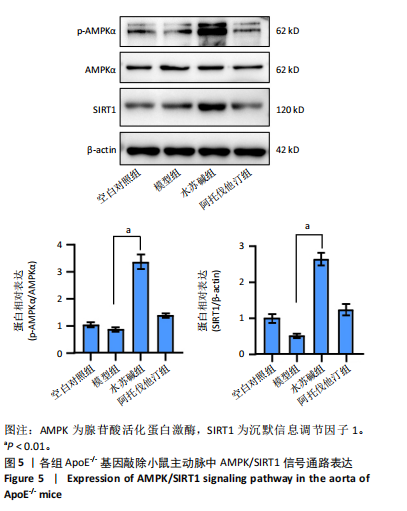
[1] LIN J, GU M, WANG X, et al. Huanglian Jiedu decoction inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell-derived foam cell formation by activating autophagy via suppressing P2RY12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024;328:118125.
[2] WANG XP, REN B, WANG QN, et al. Encephaloduroarteriosynangiosis for Symptomatic Intracranial Atherosclerotic Arterial Steno-Occlusive Disease: Clinical and Radiological Outcomes. J Am Heart Assoc. 2024; 13(15):e034707.
[3] KNEUER JM, GRAJEK IA, WINKLER M, et al. Novel Long Noncoding RNA HEAT4 Affects Monocyte Subtypes, Reducing Inflammation and Promoting Vascular Healing. Circulation. 2024. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.124.069315.
[4] DONG M, CHEN M, ZHANG Y, et al. Oscillatory shear stress promotes endothelial senescence and atherosclerosis via STING activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024;715:149979.
[5] KOKAI D, MARKOVIC FILIPOVIC J, OPACIC M, et al. In vitro and in vivo exposure of endothelial cells to dibutyl phthalate promotes monocyte adhesion. Food Chem Toxicol. 2024;188:114663.
[6] LI W, BAI P, LI W. UHRF1 inhibition mitigates vascular endothelial cell injury and ameliorates atherosclerosis in mice via regulating the SMAD7/YAP1 axis. Mol Immunol. 2024;170:119-130.
[7] CHENG F, ZHOU Y, WANG M, et al. A review of pharmacological and pharmacokinetic properties of stachydrine. Pharmacol Res. 2020;155: 104755.
[8] LIAO L, TANG Y, LI B, et al. Stachydrine, a potential drug for the treatment of cardiovascular system and central nervous system diseases. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;161:114489.
[9] MENG J, ZHOU C, ZHANG W, et al. Stachydrine prevents LPS-induced bone loss by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis via NF-kappaB and Akt signalling. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(10):6730-6743.
[10] LIU FC, YU HP, LEE HC, et al. The Modulation of Phospho-Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase and Phospho-Protein Kinase B Signaling Pathways plus Activity of Macrophage-Stimulating Protein Contribute to the Protective Effect of Stachydrine on Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(3):1484.
[11] PAREKH T, TSAI M, SPIRO S. Choline degradation in Paracoccus denitrificans: identification of sources of formaldehyde. J Bacteriol. 2024;206(4):e0008124.
[12] ZENG H, XU D, SONG Y, et al. Synthesis, characterization and anti-breast cancer activities of stachydrine derivatives. Eur J Med Chem. 2023;259:115679.
[13] XIE X, YANG C, CUI Q, et al. Stachydrine Mediates Rapid Vascular Relaxation: Activation of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Involving AMP-Activated Protein Kinase and Akt Phosphorylation in Vascular Endothelial Cells. J Agric Food Chem. 2019;67(35):9805-9811.
[14] KIM H, APPEL LJ, LICHTENSTEIN AH, et al. Metabolomic Profiles Associated With Blood Pressure Reduction in Response to the DASH and DASH-Sodium Dietary Interventions. Hypertension. 2023; 80(7):1494-1506.
[15] NAJEM MY, RYS RN, LAURANCE S, et al. Extracellular RNA Induces Neutrophil Recruitment Via Toll-Like Receptor 3 During Venous Thrombosis After Vascular Injury. J Am Heart Assoc. 2024;13(15): e034492.
[16] SHAPIRA KE, SHAPIRA G, SCHMUKLER E, et al. Autophagy is induced and modulated by cholesterol depletion through transcription of autophagy-related genes and attenuation of flux. Cell Death Discov. 2021;7(1):320.
[17] OU H, LIU C, FENG W, et al. Role of AMPK in atherosclerosis via autophagy regulation. Sci China Life Sci. 2018;61(10):1212-1221.
[18] TIAN Z, NING H, WANG X, et al. Endothelial Autophagy Promotes Atheroprotective Communication Between Endothelial and Smooth Muscle Cells via Exosome-Mediated Delivery of miR-204-5p. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024;44(8):1813-1832.
[19] MANTA CP, LEIBING T, FRIEDRICH M, et al. Targeting of Scavenger Receptors Stabilin-1 and Stabilin-2 Ameliorates Atherosclerosis by a Plasma Proteome Switch Mediating Monocyte/Macrophage Suppression. Circulation. 2022;146(23):1783-1799.
[20] JANG E, HO T WW, BRUMELL J, et al. IL-1beta Induces LDL Transcytosis by a Novel Pathway Involving LDLR and Rab27a. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024;44(9):2053-2068.
[21] KANE J, VOS WG, BOSMANS LA, et al. Peritoneal Dialysis Aggravates and Accelerates Atherosclerosis in Uremic ApoE(-/-) Mice. J Am Heart Assoc. 2024;13(14):e034066.
[22] TIAN S, MIAO M, BAI M, et al. Effect of stachydrine hydrochloride to the prostate hyperplasia model in mice. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2019;26(4): 782-789.
[23] LEOW SS, KHOO JS, LEE WK, et al. RNA-Seq transcriptome profiling of Nile rat livers reveals novel insights on the anti-diabetic mechanisms of Water-Soluble Palm Fruit Extract. J Appl Genet. 2024. doi: 10.1007/s13353-024-00880-1.
[24] ZULOAGA R, DETTLEFF P, BASTIAS-MOLINA M, et al. RNA-Seq-Based Analysis of Cortisol-Induced Differential Gene Expression Associated with Piscirickettsia salmonis Infection in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Myotubes. Animals (Basel). 2021;11(8):2399.
[25] MA D, LIU S, LIU K, et al. MDFI promotes the proliferation and tolerance to chemotherapy of colorectal cancer cells by binding ITGB4/LAMB3 to activate the AKT signaling pathway. Cancer Biol Ther. 2024;25(1):2314324.
[26] XU H, DU Z, LI Z, et al. MUC1-EGFR crosstalk with IL-6 by activating NF-kappaB and MAPK pathways to regulate the stemness and paclitaxel-resistance of lung adenocarcinoma. Ann Med. 2024;56(1):2313671.
[27] LU Y, GAO L, ZHANG W, et al. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester restores mitochondrial homeostasis against peritoneal fibrosis induced by peritoneal dialysis through the AMPK/SIRT1 pathway. Ren Fail. 2024; 46(1):2350235.
[28] KARLIN H, SOODA M, LARSON M, et al. Plasma Extracellular MicroRNAs Associated With Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors in Middle-Aged and Older Adults. J Am Heart Assoc. 2024;13(12):e033674.
[29] SANTULLI G, VARZIDEH F, FORZANO I, et al. Functional and Clinical Importance of SGLT2-inhibitors in Frailty: From the Kidney to the Heart. Hypertension. 2023;80(9):1800-1809.
[30] ZHU X, WU Y, ZHANG X, et al. Stachydrine ameliorates hypoxia reoxygenation injury of cardiomyocyte via enhancing SIRT1-Nrf2 pathway. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2023;18(1):265.
[31] LU S, LIANG Y, YANG S, et al. Stachydrine Hydrochloride Regulates the NOX2-ROS-Signaling Axis in Pressure-Overload-Induced Heart Failure. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(18):14369.
[32] ZHOU F, LIU F, LIU J, et al. Stachydrine promotes angiogenesis by regulating the VEGFR2/MEK/ERK and mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis signaling pathways in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131:110724.
[33] HU Y, HE K, ZHU H. Chinese herbal medicinal ingredients affect secretion of NO, IL-10, ICAM-1 and IL-2 by endothelial cells. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2015;37(3):324-328.
[34] LI WW, GUO ZM, WANG BC, et al. PCSK9 induces endothelial cell autophagy by regulating the PI3K/ATK pathway in atherosclerotic coronary heart disease. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2024. doi: 10.3233/CH-242172.
[35] AKHTAR S, SAGAR K, SINGH A, et al. Inflammation-induced sialin mediates nitrate efflux in dysfunctional endothelium affecting NO bioavailability. Nitric Oxide. 2024;146:37-47.
[36] ZHU L, GUO L, XU J, et al. Postprandial Triglyceride-Rich Lipoproteins-Induced Lysosomal Dysfunction and Impaired Autophagic Flux Contribute to Inflammation in White Adipocytes. J Nutr. 2024;154(5): 1619-1630.
[37] BARANGI S, HAYES AW, KARIMI G. The role of lncRNAs/miRNAs/Sirt1 axis in myocardial and cerebral injury. Cell Cycle. 2023;22(9):1062-1073.
[38] CHENG J, PAN W, ZHENG Y, et al. Piezocatalytic Schottky Junction Treats Atherosclerosis by a Biomimetic Trojan Horse Strategy. Adv Mater. 2024;36(19):e2312102.
[39] HUI B, HOU X, LIU R, et al. Gypenoside inhibits ox-LDL uptake and foam cell formation through enhancing Sirt1-FOXO1 mediated autophagy flux restoration. Life Sci. 2021;264:118721.
[40] XU H, FU J, TU Q, et al. The SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin attenuates atherosclerosis progression by inducing autophagy. J Physiol Biochem. 2024;80(1):27-39.
[41] LI D, ZHANG Y, MA J, et al. Adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase regulates ABCG1-mediated oxysterol efflux from endothelial cells and protects against hypercholesterolemia-induced endothelial dysfunction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010;30(7):1354-1362. |