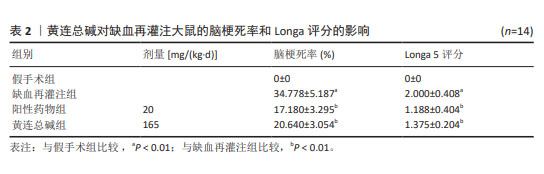
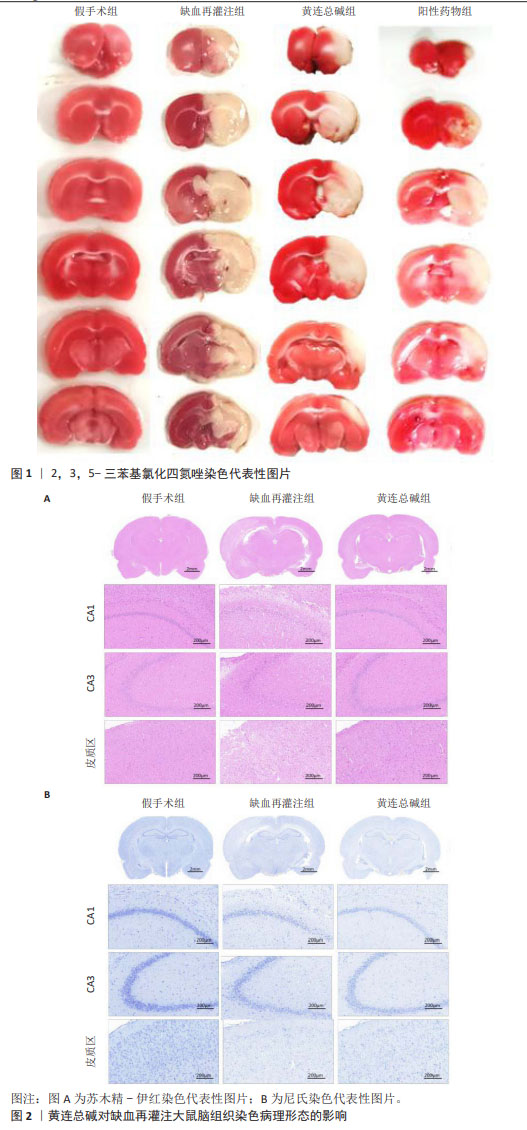
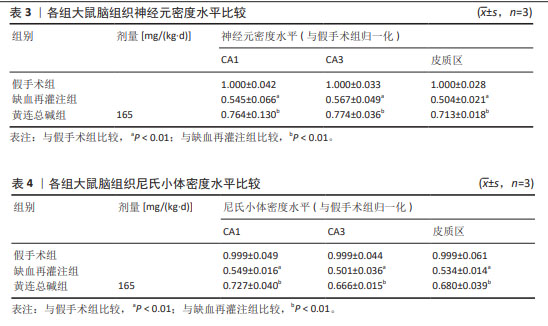
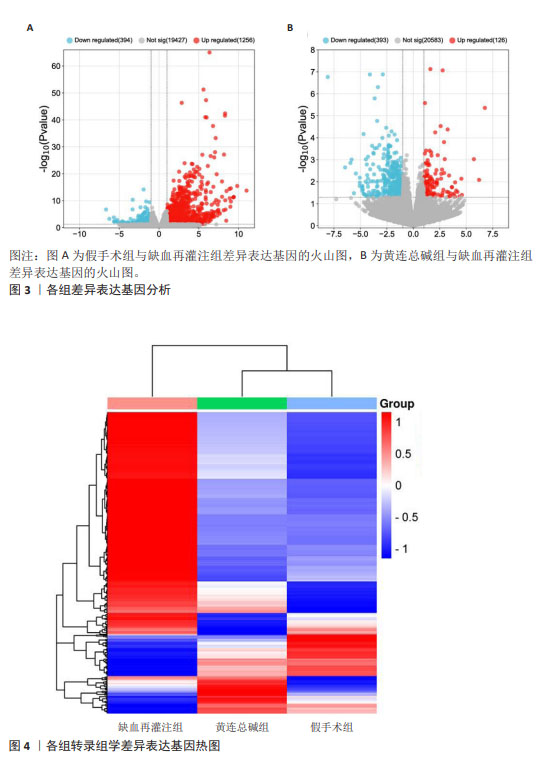
[1] ZHANG JJ,GUO FF, ZHOU R, et al. Proteomics and transcriptome reveal the key transcription factors mediating the protection of Panax notoginseng saponins (PNS) against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Phytomedicine. 2021;92:153613.
[2] BOEHME AK, ESENWA C, ELKIND MS. Stroke Risk Factors, Genetics, and Prevention. Circ Res. 2017;120(3):472-495.
[3] CAMPBELL BCV, DE SILVA DA, MACLEOD MR, et al. Ischaemic stroke. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019; 5(1):70.
[4] FU Y, LIU Q, ANRATHER J, et al. Immune interventions in stroke. Nat Rev Neurol. 2015; 11(9):524-535.
[5] SAINI V, GUADA L, YAVAGAL DR. Global Epidemiology of Stroke and Access to Acute Ischemic Stroke Interventions. Neurology. 2021;97(20 Supplement 2):S6-S16.
[6] 石晓花, 莽靖, 徐忠信. 脑缺血再灌注损伤细胞死亡模式的研究进展[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版),2022,48(6):1635-1643.
[7] ZHENG P, ZHANG N, REN D, et al. Integrated spatial transcriptome and metabolism study reveals metabolic heterogeneity in human injured brain. Cell Rep Med. 2023;4(6): 101057.
[8] ZHENG K, LIN L, JIANG W, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals the transcriptional landscape in ischemic stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2022;42(1):56-73.
[9] 丁实, 赵学荣, 赵亮, 等. 黄连素通过B细胞淋巴瘤-2/自噬相关基因复合体抑制自噬减轻脑缺血再灌注损伤的研究[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志,2021,37(9):1094-1097.
[10] HU J, CHAI Y, WANG Y, et al. PI3K p55γ promoter activity enhancement is involved in the anti-apoptotic effect of berberine against cerebral ischemia–reperfusion. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012;674(2):132-142.
[11] KIM M, KIM TW, KIM CJ, et al. Berberine Ameliorates Brain Inflammation in Poloxamer 407-Induced Hyperlipidemic Rats. Int Neurourol J. 2019;23(Suppl 2):S102-S110.
[12] CHENG F, WANG Y, LI J, et al. Berberine improves endothelial function by reducing endothelial microparticles-mediated oxidative stress in humans. Int J Cardiol. 2013;167(3): 936-942.
[13] SARNA LK, WU N, HWANG SY, et al. Berberine inhibits NADPH oxidase mediated superoxide anion production in macrophages. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010;88(3):369-378.
[14] ZHOU R, GUO F, XIANG C, et al. Systematic Study of Crucial Transcription Factors of Coptidis rhizoma Alkaloids against Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021;12(13):2308-2319.
[15] CHEN HY, YE XL, CUI XL, et al. Cytotoxicity and antihyperglycemic effect of minor constituents from Rhizoma Coptis in HepG2 cells. Fitoterapia. 2012;83(1):67-73.
[16] 李淑琴, 朱嘉宝, 武宇洲. 银杏叶提取物防治心脑血管疾病的研究进展[J]. 中国新药杂志,2016,25(1):76-81.
[17] ZHANG JJ, GUO FF, ZHOU R, et al. Proteomics and transcriptome reveal the key transcription factors mediating the protection of Panax notoginseng saponins (PNS) against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Phytomedicine. 2021:153613. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153613.
[18] ZHANG JJ, ZHOU R, CAO GZ, et al. Guhong Injection Prevents Ischemic Stroke-Induced Neuro-Inflammation and Neuron Loss Through Regulation of C5ar1. Front Pharmacol. 2022; 13:818245.
[19] LIU R, DIAO J, HE S, et al. XQ-1H protects against ischemic stroke by regulating microglia polarization through PPARγ pathway in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;57:72-81.
[20] XU D, HOU K, LI F, et al. XQ-1H alleviates cerebral ischemia in mice through inhibition of apoptosis and promotion of neurogenesis in a Wnt/β-catenin signaling dependent way. Life Sci. 2019;235:116844.
[21] WANG Y, PEI DS, JI HX, et al. Protective effect of a standardized Ginkgo extract (ginaton) on renal ischemia/reperfusion injury via suppressing the activation of JNK signal pathway. Phytomedicine. 2008;15(11):923-931.
[22] LO EH, DALKARA T, MOSKOWITZ MA. Mechanisms, challenges and opportunities in stroke. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003;4(5):399-415.
[23] MOSKOWITZ MA, LO EH, IADECOLA C. The Science of Stroke: Mechanisms in Search of Treatments. Neuron. 2010;67(2):181-198.
[24] 巩婷婷, 司凯, 刘会平, 等. MAPK级联调控细胞生长及其在免疫,炎症及癌症中作用的研究进展[J]. 中南大学学报(医学版), 2022, 47(12):1721-1728.
[25] 许川山, 余茜, 吴士明, 等. MAPK级联传导途径与脑缺血性损害[J]. 现代康复,2001 (13):62-63.
[26] ZHANG M, GONG JX, WANG JL, et al. p38 MAPK Participates in the Mediation of GLT-1 Up-regulation During the Induction of Brain Ischemic Tolerance by Cerebral Ischemic Preconditioning. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;54(1): 1-14.
[27] GELDERBLOM M, WEYMAR A, BERNREUTHER C, et al. Neutralization of the IL-17 axis diminishes neutrophil invasion and protects from ischemic stroke. Blood. 2012;120(18): 3793-3802.
[28] SUN L, ZHANG H, WANG W, et al. Astragaloside IV Exerts Cognitive Benefits and Promotes Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Stroke Mice by Downregulating Interleukin-17 Expression via Wnt Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11: 421.
[29] ZHANG Q, LUO T, YUAN D, et al. Retraction Note: Qilongtian ameliorate bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice via inhibiting IL-17 signal pathway. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):11263.
[30] 潘玲珍,闫智勇,左长英,等.长期使用地西泮对神经活性配体受体相互作用信号通路的影响[J]. 中国药科大学学报,2011, 42(5):443-446.
[31] ZHANG S, WANG X, YANG Q, et al. Isopropyl 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxypropanoate plays an anti-hypoxic role through regulating neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction signaling pathway in larval zebrafish. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;161:114570.
[32] ZAN XY, LI L. Construction of lncRNA-mediated ceRNA network to reveal clinically relevant lncRNA biomarkers in glioblastomas. Oncol Lett. 2019;17(5):4369-4374.
[33] HU S, CAO Q, XU P, et al. Rolipram stimulates angiogenesis and attenuates neuronal apoptosis through the cAMP/cAMP-responsive element binding protein pathway following ischemic stroke in rats. Exp Ther Med. 2016;11(3):1005-1010.
[34] LIU C, DU L, ZHANG S, et al. Network pharmacology and experimental study of phenolic acids in salvia miltiorrhiza bung in preventing ischemic stroke. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1108518.
[35] WANG YL, ZHU XL, SUN MH, et al. Effects of astaxanthin onaxonal regeneration via cAMP/PKA signaling pathway in mice with focal cerebral infarction. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(3 Suppl):135-143.
[36] ZHOU XQ, ZENG XN, KONG H, et al. Neuroprotective effects of berberine on stroke models in vitro and in vivo. Neurosci Lett. 2008;447(1):31-36.
[37] ZHU JR, LU HD, GUO C, et al. Berberine attenuates ischemia–reperfusion injury through inhibiting HMGB1 release and NF-κB nuclear translocation. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica. 2018;39(11):1706-1715.
[38] JIN X, WANG RH, WANG H, et al. Brain protection against ischemic stroke using choline as a new molecular bypass treatment. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica. 2015;36(12):1416-1425.
[39] WANG J, TANG M, XIE X, et al. Efficacy of ferulic acid in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke injury in rats: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol. 2023; 14: 1278036.
[40] ZHONG F, CHEN Y, CHEN J, et al. Jatrorrhizine: A Review of Sources, Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics and Toxicity. Front Pharmacol. 2022;12:783127.
[41] LIANG H, CHANG X, XIA R, et al. Magnoflorine attenuates cerebral ischemia-induced neuronal injury via autophagy/sirt1/AMPK signaling pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:2131561.
[42] TANG C, HONG J, HU C, et al. Palmatine protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by activation of the AMPK/Nrf2 pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:6660193.
[43] PEREIRA JF, DE SOUSA NEVES JC, FONTELES AA, et al. Palmatine, a natural alkaloid, attenuates memory deficits and neuroinflammation in mice submitted to permanent focal cerebral ischemia. J Neuroimmunol. 2023;381:578131.
[44] COLAIZZO D, FOFI L, TISCIA G, et al. The COX-2 G/C− 765 polymorphism may modulate the occurrence of cerebrovascular ischemia. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2006;17(2):93-96.
[45] LIN W, WANG Y, CHEN Y, et al. Role of calcium signaling pathway-related gene regulatory networks in ischemic stroke based on multiple WGCNA and single-cell analysis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:8060477.
[46] ZHOU Z, LU C, MENG S, et al. Silencing of PTGS2 exerts promoting effects on angiogenesis endothelial progenitor cells in mice with ischemic stroke via repression of the NF-κB signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(12):23448-23460.
[47] CUI Q, ZHANG YL, MA YH, et al. A network pharmacology approach to investigate the mechanism of Shuxuening injection in the treatment of ischemic stroke. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;257:112891.
[48] 尚津锋, 焦家康, 李倩楠, 等. 白杨素通过抑制铁死亡减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 中国中药杂志,2023,48(6): 597-1605.
[49] REX D, DAGAMAJALU S, GOUDA MM, et al. A comprehensive network map of IL-17A signaling pathway. J Cell Commun Signal. 2023; 17(1):209-215.
[50] LI JK, NIE L, ZHAO YP, et al. IL-17 mediates inflammatory reactions via p38/c-Fos and JNK/c-Jun activation in an AP-1-dependent manner in human nucleus pulposus cells. J Transl Med. 2016:14:77.
[51] BALKAYA M, CHO S. Genetics of stroke recovery: BDNF val66met polymorphism in stroke recovery and its interaction with aging. Neurobiol Dis. 2019;126:36-46.
[52] BÉJOT Y, MOSSIAT C, GIROUD M, et al. Circulating and Brain BDNF Levels in Stroke Rats. Relevance to Clinical Studies. PLOS ONE. 2011;6(12):e29405.
[53] DI LAZZARO V, PELLEGRINO G, DI PINO G, et al. Val66Met BDNF gene polymorphism influences human motor cortex plasticity in acute stroke. Brain Stimul. 2015;8(1):92-96.
[54] 何恩浩, 曾燕, 陈星星. Hap1在神经系统疾病中的研究进展[J]. 生命科学,2023,35(5): 592-600.
[55] PLOUGHMAN M, ATTWOOD Z, WHITE N, et al. Endurance exercise facilitates relearning of forelimb motor skill after focal ischemia. Eur J Neurosci. 2007;25(11):3453-3460.
[56] ZHAO D, ZHANG M, YANG L, et al. GPR68 improves nerve damage and myelination in an immature rat model induced by sevoflurane anesthesia by activating cAMP/CREB to mediate BDNF. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2022;13(3):423-431.
[57] EARLEY S, GONZALES AL, CRNICH R. Endothelium-dependent cerebral artery dilation mediated by TRPA1 and Ca2+-Activated K+ channels. Circ Res. 2009;104(8):987-994.
[58] PIRES PW, EARLEY S. Neuroprotective effects of TRPA1 channels in the cerebral endothelium following ischemic stroke. eLife. 2018;7:e35316.
[59] PIRES PW, SULLIVAN MN, EARLEY S. Endothelial TRPA1 Channel is Protective Against Ischemia and Hemorrhagic Strokes in Mice. Stroke. 2016;47(suppl_1):A141-A141. |