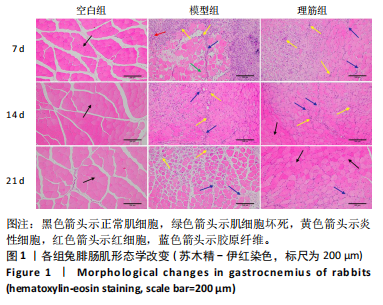
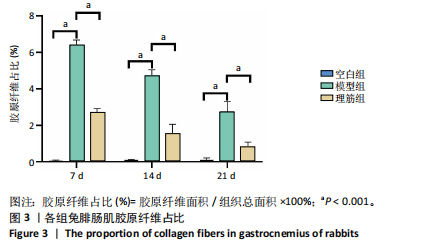
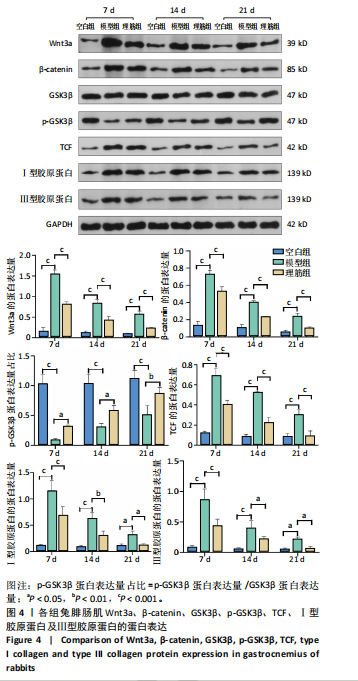
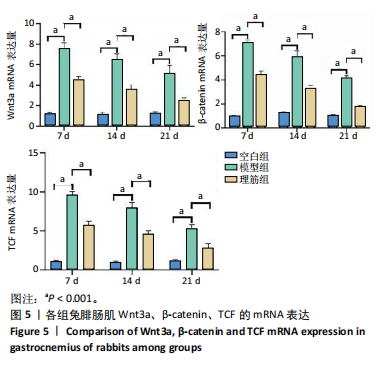
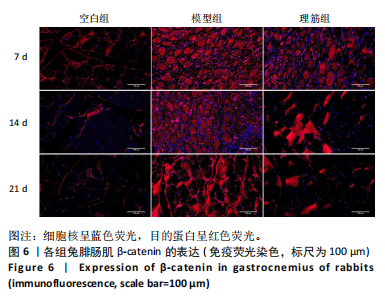
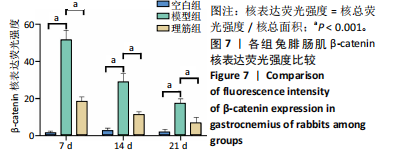
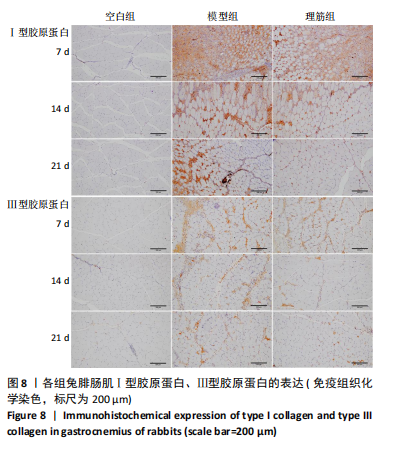
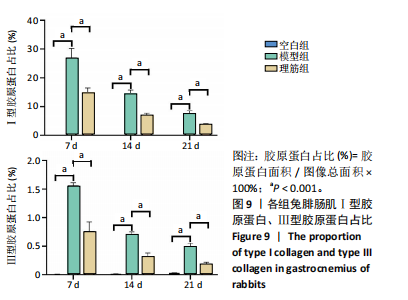
[1] 卜婷婷,汪松.白藜芦醇在骨骼肌损伤修复中的研究进展[J].海南医学, 2022,33(11):1451-1454.
[2] 杜田昊,刘佳,杨旭,等.骨骼肌损伤微波热疗机制的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2023,31(23):2166-2171.
[3] 卢雅梦,雷静,尤浩军.骨骼肌损伤后疼痛机制及非药物治疗研究进展[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2023,29(2):138-143.
[4] 黄敬伟.经筋疗法[M].北京:中国中医药出版社,2010:77-85.
[5] 王波,游永豪,张阳,等.理筋手法联合体外冲击波治疗青年运动员三角纤维软骨复合体损伤[J].陕西中医药大学学报,2024,47(2):105-109.
[6] 杨平,马惠昇,穆静,等.回医理筋疗法治疗腰椎间盘突出症的临床疗效[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2016,38(3):233-235.
[7] 马惠昇,穆静.回医理筋-肩部筋伤[M].北京:中国中医药出版社,2016.
[8] 黄博,阮磊,王兰兰,等.推拿治疗骨骼肌损伤的分子生物学机制研究进展[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2023,43(4):753-758.
[9] QIN JJ, NIU MD, CHA Z, et al. TRAIL and Celastrol Combinational Treatment Suppresses Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Human Glioblastoma Cells via Targeting Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Pathway. Chin J Integr Med. 2024;30(4):322-329.
[10] SON Y, LORENZ WW, PATON CM. Linoleic acid-induced ANGPTL4 inhibits C2C12 skeletal muscle differentiation by suppressing Wnt/β-catenin. J Nutr Biochem. 2023;116:109324.
[11] 黄何平.生长因子对骨骼肌损伤与修复的作用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(29):4402-4408.
[12] 李冬军,李明,赵连魁.病理性瘢痕形成机制的研究进展[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2021,30(8):908-912.
[13] 孙畅,徐鹏喆,苏洪于,等.基于Wnt通路治疗心肌纤维化的药物研究[J].中国心血管病研究,2024,22(4):351-356.
[14] MURPHY MM, KEEFE AC, LAWSON JA, et al. Transiently active Wnt/β-catenin signaling is not required but must be silenced for stem cell function during muscle regeneration. Stem Cell Reports. 2014;3(3):475-488.
[15] 刘志华.回医理筋手法对家兔骨骼肌损伤修复过程中IGF-1表达的影响[D]. 银川:宁夏医科大学,2015.
[16] 李开颖,魏晓歌,宋斐,等.理筋手法调控兔骨骼肌损伤修复中瘢痕形成的作用机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(8):1600-1608.
[17] 李岩,王岩,马天成,等.机械性骨骼肌损伤实验动物模型的造模方法和特点[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2024,30(4):601-604 .
[18] 徐明奎,许日明,林业武,等.柚皮素调控巨噬细胞极化和肌卫星细胞增殖修复骨骼肌损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(14):2133-2138.
[19] HUANG Y, LI H, HU T, et al. Implantable Electronic Medicine Enabled by Bioresorbable Microneedles for Wireless Electrotherapy and Drug Delivery. Nano Lett. 2022;22(14):5944-5953.
[20] TOMAZONI SS, FRIGO L, DOS REIS FERREIRA TC, et al. Effects of photobiomodulation therapy and topical non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug onskeletal muscle injury induced by contusion in rats-part 2: biochemical aspects. Lasers Med Sci. 2017;32(8):1879-1887.
[21] LI RH, LI J, KAN SL, et al. The Protective Effects of Fasciotomy on Reperfusion Injury of Skeletal Muscle of Rabbits. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:7238960.
[22] 刘仁建.按摩对损伤骨骼肌生长因子bFGF、IGF-Ⅰ及致瘢痕因子TGF-β1、COL-Ⅰ的影响研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2014.
[23] 史欢.理筋手法对兔骨骼肌静力性损伤的骨架蛋白修复作用及镇痛效应研究[D].银川:宁夏医科大学,2019.
[24] 周红海,于栋.中医筋伤学[M].北京:中国中医药出版社,2021.
[25] NUSSE R, CLEVERS H. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling, Disease, and Emerging Therapeutic Modalities. Cell. 2017;169(6):985-999.
[26] HAYAT R, MANZOOR M, HUSSAIN A. Wnt signaling pathway: A comprehensive review. Cell Biol Int. 2022;46(6):863-877.
[27] LIU J, XIAO Q, XIAO J, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signalling: function, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):3.
[28] LAW SM, ZHENG JJ. Premise and peril of Wnt signaling activation through GSK-3β inhibition. iScience. 2022;25(4):104159.
[29] TORRES-AGUILA NP, SALONNA M, HOPPLER S, et al. Evolutionary diversification of the canonical Wnt signaling effector TCF/LEF in chordates. Dev Growth Differ. 2022;64(3):120-137.
[30] STEWART RA, RAMAKRISHNAN AB, CADIGAN KM. Diffusion and function of Wnt ligands. PLoS Genet. 2019;15(6):e1008154.
[31] AKIYAMA T. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000; 11(4):273-282.
[32] CHEN N, WANG J. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling and Obesity. Front Physiol. 2018; 9:792.
[33] CLEVERS H, NUSSE R. Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disease. Cell. 2012; 149(6):1192-1205.
[34] HUANG P, YAN R, ZHANG X, et al. Activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway for disease therapy: Challenges and opportunities. Pharmacol Ther. 2019;196:79-90.
[35] MADSEN SF, SAND JMB, JUHL P, et al. Fibroblasts are not just fibroblasts: clear differences between dermal and pulmonary fibroblasts’ response to fibrotic growth factors. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):9411.
[36] CISTERNAS P, HENRIQUEZ JP, BRANDAN E, et al. Wnt signaling in skeletal muscle dynamics: myogenesis, neuromuscular synapse and fibrosis. Mol Neurobiol. 2014;49(1):574-589.
[37] JONES AE, PRICE FD, LE GRAND F, et al. Wnt/β-catenin controls follistatin signalling to regulate satellite cell myogenic potential. Skelet Muscle. 2015; 5:14.
[38] 陈平,何振富,王斐,等.Collagen1和Collagen3在牦牛肺纤维化组织中的表达研究[J].核农学报,2023,37(6):1158-1165.
[39] BRACK AS, CONBOY MJ, ROY S, et al. Increased Wnt signaling during aging alters muscle stem cell fate and increases fibrosis. Science. 2007;317(5839): 807-810.
[40] 阮磊,黄博,王兰兰,等.推拿㨰法对兔骨骼肌钝挫伤修复及Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的影响[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2023,43(9):1685-1692.
[41] KORKUT C, BUDNIK V. WNTs tune up the neuromuscular junction. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009;10(9):627-634. |