[1] JARAUSCH J, NEUENROTH L, ANDAG R, et al. Influence of Shear Stress, Inflammation and BRD4 Inhibition on Human Endothelial Cells: A Holistic Proteomic Approach. Cells. 2022;11(19):3086.
[2] YE ZM, YANG S, XIA YP, et al. LncRNA MIAT sponges miR-149-5p to inhibit efferocytosis in advanced atherosclerosis through CD47 upregulation. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(2):138.
[3] WANG L, LI H, ZHANG H, et al. Serum-based metabolomics reveals the mechanism of action of isorhynchophylline in the intervention of atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice. Anal Methods. 2024;16(7):1083-1092.
[4] YANG J, CAO RY, GAO R, et al. Physical Exercise Is a Potential “Medicine” for Atherosclerosis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;999:269-286.
[5] CAMACHO-ENCINA M, BOOTH LK, REDGRAVE RE, et al. Cellular Senescence, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Their Link to Cardiovascular Disease. Cells. 2024; 13(4):353.
[6] ZHOU H, HE L, XU G, et al.Mitophagy in cardiovascular disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2020;507:210-218.
[7] GUAN Y, DRAKE JC, YAN Z. Exercise-Induced Mitophagy in Skeletal Muscle and Heart. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2019;47(3):151-156.
[8] 王宁伟,冯红.运动诱导线粒体自噬对慢性疾病健康效应的研究进展[J].天津科技,2022,49(11):18-23+28.
[9] CHEN CCW, ERLICH AT, HOOD DA. Role of parkin and endurance training on mitochondrial turnover in skeletal muscle. Skelet Muscle. 2018;8(1):10.
[10] 张沛文. 运动预适应心肌保护PINK1/Parkin信号通路的研究[D].桂林:广西师范大学,2023.
[11] 张泰瑜. PHB2在预运动训练干预下MPTP致小鼠帕金森发病线粒体机制中的作用[D].天津:天津体育学院,2020.
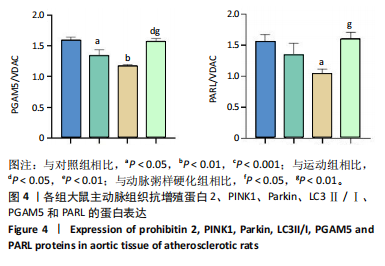
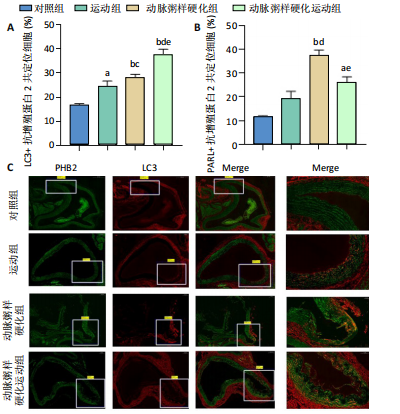
[12] WEI Y, CHIANG WC, SUMPTER R, et al. Prohibitin 2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane mitophagy receptor. Cell. 2017;168(1-2):224-238.
[13] YAN C, GONG L, CHEN L, et al. PHB2 (prohibitin2) promotes PINK1-PRKN/Parkin-dependent mitophagy by the PARL-PGAM5-PINK1 axis. Autophagy. 2020;16(3): 419-434.
[14] 周红,吴晓燕,袁艺标,等.三种剂量维生素D3结合高脂饲料建立大鼠动脉粥样硬化模型的比较[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2012,20(11):995-998.
[15] 林小晶,汪燕,王凡.有氧运动降低动脉粥样硬化大鼠血清和组织Lp-PLA2水平及意义[J].中国体育科技,2019,55(1):28-36.
[16] 刘善云,王敏,张洪侠,等.耐力训练对ApoE~(-/-)致AS小鼠IL-18和IL-10表达的影响[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2016,32(3):225-228+291.
[17] YOO SZ, NO MH, HEO JW, et al. Effects of Acute Exercise on Mitochondrial Function, Dynamics, and Mitophagy in Rat Cardiac and Skeletal Muscles. Int Neurourol J. 2019;23(Suppl 1):S22-S31.
[18] 王琳琳,范君,叶陈宇,等.血脂与老年冠心病患者颈动脉粥样硬化斑块的相关性[J].检验医学,2021,36(6):618-622.
[19] FERENCE BA, GINSBERG HN, GRAHAM I, et al. Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. 1. Evidence from genetic, epidemiologic, and clinical studies. A consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur Heart J. 2017;38(32):2459-2472.
[20] 伍莎,彭道泉.动脉粥样硬化性心血管病一级预防的血脂管理[J].中国医学前沿杂志(电子版),2019,11(5):15-20.
[21] 刘君雯,何奇芳.有氧运动对大鼠高脂血症及动脉粥样硬化相关生化指标的影响[J].现代预防医学,2014,41(23):4354-4356.
[22] POZNYAK AV, IVANOVA EA, SOBENIN IA, et al. The Role of Mitochondria in Cardiovascular Diseases. Biology (Basel). 2020;9(6):137.
[23] ZHOU X, LI R, CHEN R, et al. Altered Mitochondrial Dynamics, Biogenesis, and Functions in the Paclitaxel-Resistant Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Line A549/Taxol. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:918216.
[24] SUN L, XU H, WANG Y, et al. The mitochondrial-targeted peptide SBT-20 ameliorates inflammation and oxidative stress in chronic renal failure. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(18):18238-18250.
[25] TOWERS CG, WODETZKI DK, THORBURN J, et al. Mitochondrial-derived vesicles compensate for loss of LC3-mediated mitophagy. Dev Cell. 2021;56(14):2029-2042.
[26] 陈林波,马凯丽,陈佺,等.线粒体自噬的分子机制[J].中国科学:生命科学,2019,49(9):1045-1053.
[27] LU Y, LI Z, ZHANG S, et al. Cellular mitophagy: Mechanism, roles in diseases and small molecule pharmacological regulation. Theranostics. 2023;13(2):736-766.
[28] SEKINE S, KANAMARU Y, KOIKE M, et al. Rhomboid protease PARL mediates the mitochondrial membrane potential loss-induced cleavage of PGAM5. Biol Chem. 2012;287(41):34635-34645.
[29] WANG S, LONG H, HOU L, et al. The mitophagy pathway and its implications in human diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023; 8(1):304.
[30] LO SC, HANNINK M. PGAM5 tethers a ternary complex containing Keap1 and Nrf2 to mitochondria. Exp Cell Res. 2008;314(8):1789-1803. |