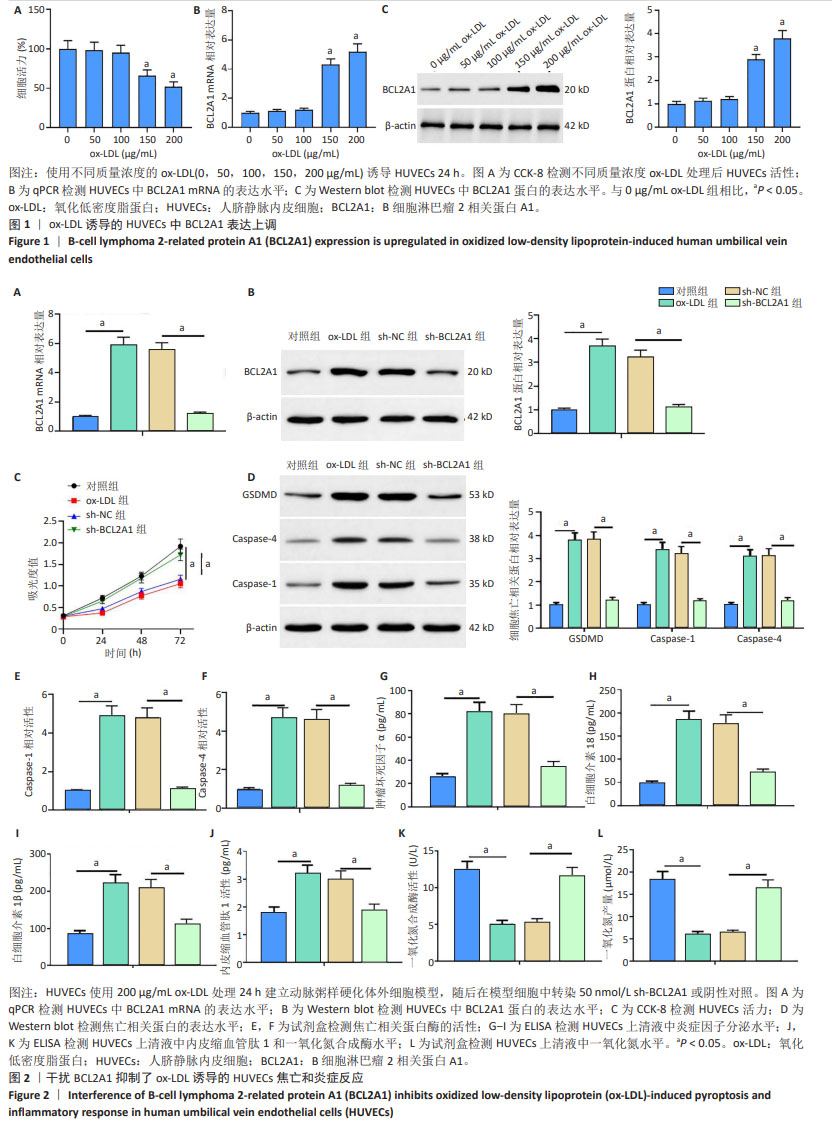
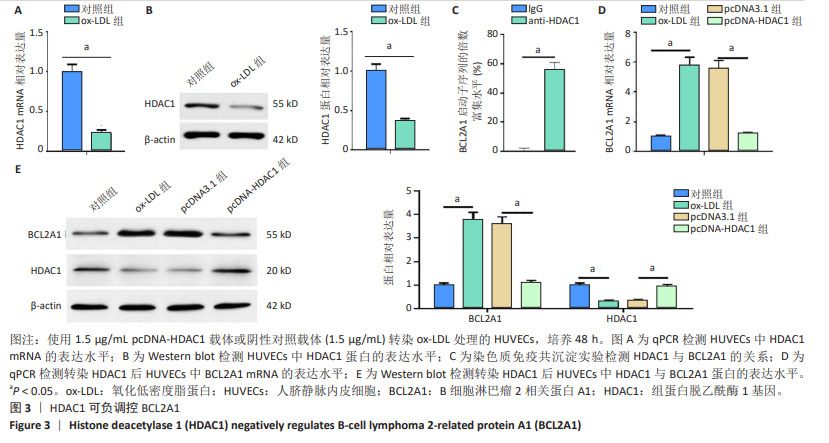
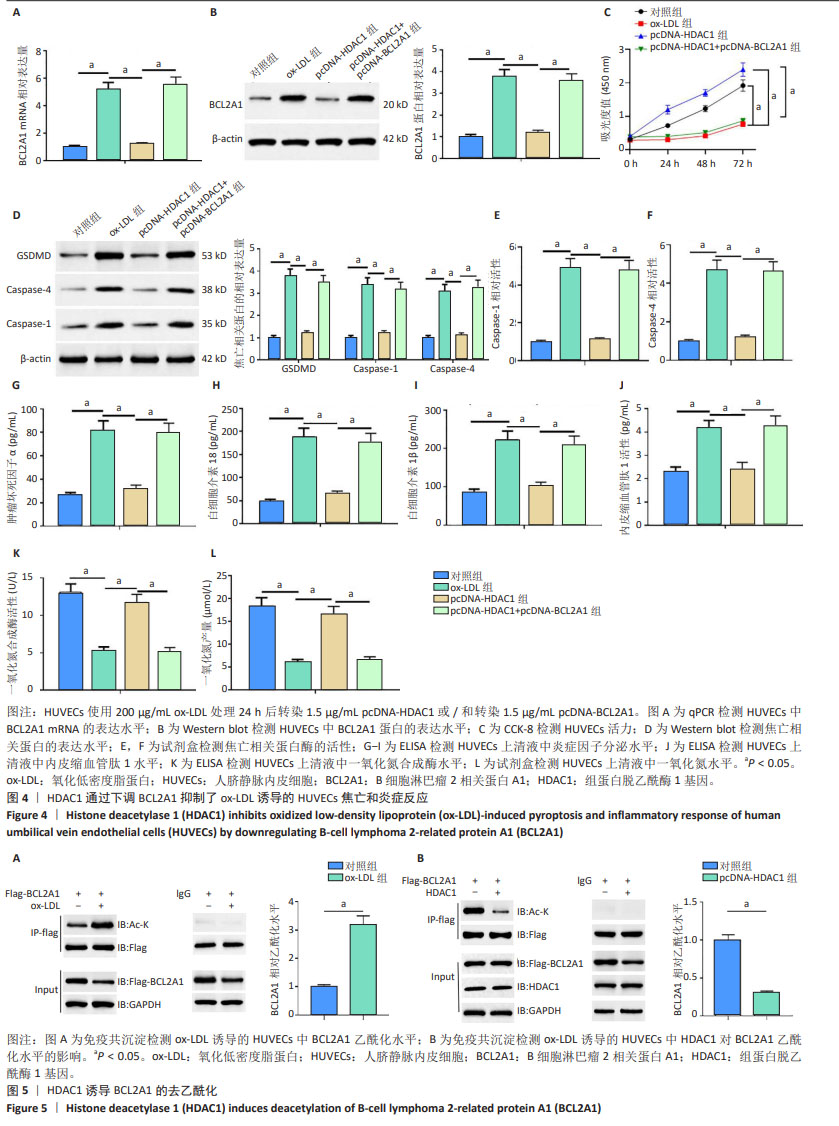
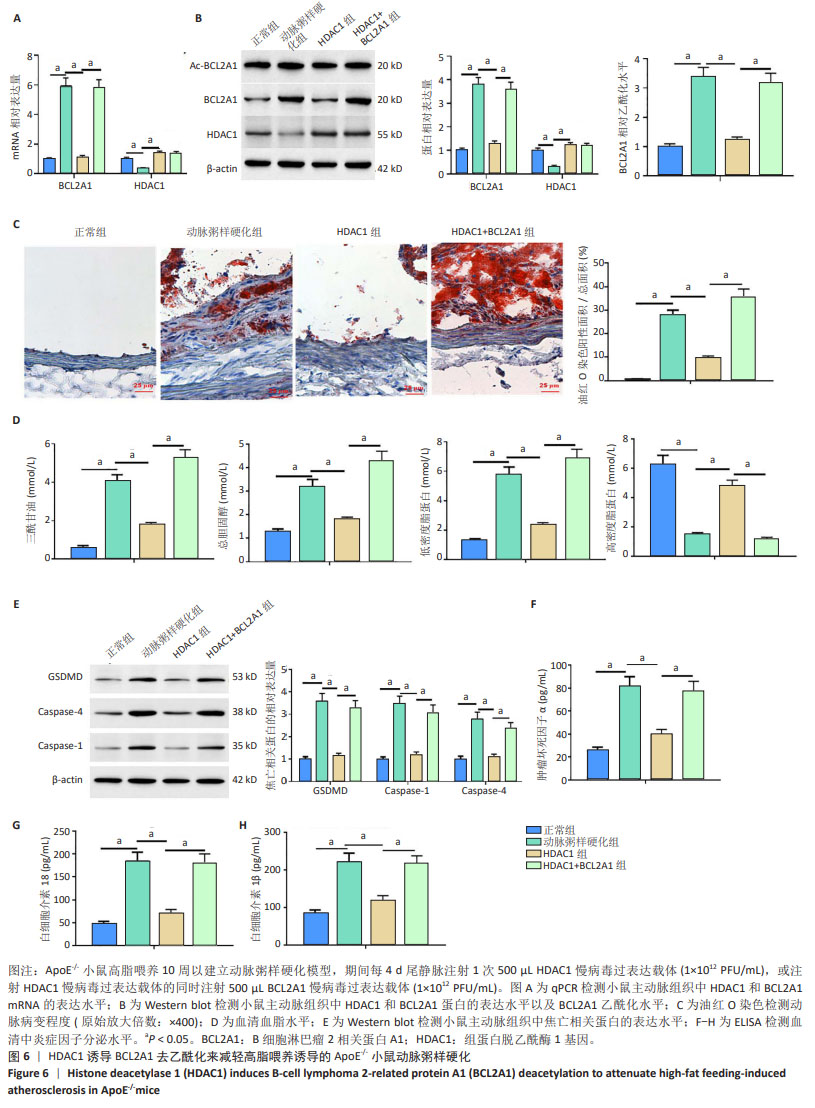
[1] WU J, HE S, SONG Z, et al. Macrophage polarization states in atherosclerosis. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1185587.
[2] ZHANG L, XIA C, YANG Y, et al. DNA methylation and histone post-translational modifications in atherosclerosis and a novel perspective for epigenetic therapy. Cell Commun Signal. 2023;21(1):344.
[3] MA SR, TONG Q, LIN Y, et al. Berberine treats atherosclerosis via a vitamine-like effect down-regulating Choline-TMA-TMAO production pathway in gut microbiota. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):207.
[4] FANG F, NI Y, YU H, et al. Inflammatory endothelium-targeted and cathepsin responsive nanoparticles are effective against atherosclerosis. Theranostics. 2022;12(9):4200-4220.
[5] XU YJ, ZHENG L, HU YW, et al. Pyroptosis and its relationship to atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta. 2018;476:28-37.
[6] DUAN H, ZHANG Q, LIU J, et al. Suppression of apoptosis in vascular endothelial cell, the promising way for natural medicines to treat atherosclerosis. Pharmacol Res. 2021;168:105599.
[7] ZHANG Q, LIU J, DUAN H, et al. Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling: An important molecular mechanism of herbal medicine in the treatment of atherosclerosis via the protection of vascular endothelial cells from oxidative stress. J Adv Res. 2021;34:43-63.
[8] ZENG X, LIU D, HUO X, et al. Pyroptosis in NLRP3 inflammasome-related atherosclerosis. Cell Stress. 2022;6(10):79-88.
[9] VOGLER M. BCL2A1: the underdog in the BCL2 family. Cell Death Differ. 2012;19(1):67-74.
[10] LI J, SUN L, XIE F, et al. MiR-3976 regulates HCT-8 cell apoptosis and parasite burden by targeting BCL2A1 in response to Cryptosporidium parvum infection. Parasit Vectors. 2023;16(1):221.
[11] LIN P, LI J, YE F, et al. KCNN4 induces multiple chemoresistance in breast cancer by regulating BCL2A1. Am J Cancer Res. 2020;10(10): 3302-3315.
[12] SU W, ZHAO Y, WEI Y, et al. Exploring the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis Complicated With Atherosclerosis via Microarray Data Analysis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:667690.
[13] DUMAN M, VAQUIÉ A, NOCERA G, et al. EEF1A1 deacetylation enables transcriptional activation of remyelination. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):3420.
[14] CHEN J, ZHU Z, XU S, et al. HDAC1 participates in polycystic ovary syndrome through histone modification by regulating H19/miR-29a-3p/NLRP3-mediated granulosa cell pyroptosis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2023;573:111950.
[15] MURTHY SRK, CHENG X, ZHUANG T, et al. BCL2A1 regulates Canady Helios Cold Plasma-induced cell death in triple-negative breast cancer. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):4038.
[16] ZHENG Q, GAN G, GAO X, et al. Targeting the IDO-BCL2A1-Cytochrome c Pathway Promotes Apoptosis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2021;14:1673-1687.
[17] HE M, MAO G, XIANG Y, et al. MicroRNA-664a-3p inhibits the proliferation of ovarian granulosa cells in polycystic ovary syndrome and promotes apoptosis by targeting BCL2A1. Ann Transl Med. 2021; 9(10):852.
[18] HOU X, ZHANG Z, MA Y, et al. Mechanism of hydroxysafflor yellow A on acute liver injury based on transcriptomics. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:966759.
[19] MÉTAIS JY, WINKLER T, GEYER JT, et al. BCL2A1a over-expression in murine hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells decreases apoptosis and results in hematopoietic transformation. PLoS One. 2012;7(10): e48267.
[20] NATH P, MODAK S, AKTAR T, et al. Olive leaves extract alleviates inflammation and modifies the intrinsic apoptotic signal in the leukemic bone marrow. Front Immunol. 2023;13:1054186.
[21] QIAN Z, ZHAO Y, WAN C, et al. Pyroptosis in the Initiation and Progression of Atherosclerosis. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:652963.
[22] LIN L, ZHANG MX, ZHANG L, et al. Autophagy, Pyroptosis, and Ferroptosis: New Regulatory Mechanisms for Atherosclerosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;9:809955.
[23] ZHU J, CHEN H, LE Y, et al. Salvianolic acid A regulates pyroptosis of endothelial cells via directly targeting PKM2 and ameliorates diabetic atherosclerosis. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1009229.
[24] JIANG X, MA C, GAO Y, et al. Tongxinluo attenuates atherosclerosis by inhibiting ROS/NLRP3/caspase-1-mediated endothelial cell pyroptosis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;304:116011.
[25] YUN WJ, LI J, YIN NC, et al. The facilitating effects of KRT80 on chemoresistance, lipogenesis, and invasion of esophageal cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2024;25(1):2302162.
[26] JIANG T, QIN T, GAO P, et al. SIRT1 attenuates blood-spinal cord barrier disruption after spinal cord injury by deacetylating p66Shc. Redox Biol. 2023;60:102615.
[27] GUO Z, YU X, ZHAO S, et al. SIRT6 deficiency in endothelial cells exacerbates oxidative stress by enhancing HIF1α accumulation and H3K9 acetylation at the Ero1α promoter. Clin Transl Med. 2023;13(8): e1377.
[28] LUO D, LI W, XIE C, et al. Capsaicin Attenuates Arterial Calcification Through Promoting SIRT6-Mediated Deacetylation and Degradation of Hif1α (Hypoxic-Inducible Factor-1 Alpha). Hypertension. 2022;79(5): 906-917.
[29] SUNG JY, KIM SG, KANG YJ, et al. SIRT1-dependent PGC-1α deacetylation by SRT1720 rescues progression of atherosclerosis by enhancing mitochondrial function. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2024;1869(3):159453.
[30] LI N, LIU B, HE R, et al. HDAC3 promotes macrophage pyroptosis via regulating histone deacetylation in acute lung injury. iScience. 2023;26(7):107158.
[31] WU Z, WANG Y, LU S, et al. SIRT3 alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting pyroptosis via regulating the deacetylation of FoxO3a. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2023;82:102244.
[32] LIU J, YAN Y, ZHENG D, et al. Inhibiting microRNA-200a-3p attenuates pyroptosis via targeting the SIRT1/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway in H2O2-induced HAEC. Aging (Albany NY). 2023;15(20):11184-11200.
[33] YAO F, LV X, JIN Z, et al. Sirt6 inhibits vascular endothelial cell pyroptosis by regulation of the Lin28b/let-7 pathway in atherosclerosis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;110:109056.
[34] DUNAWAY LS, POLLOCK JS. HDAC1: an environmental sensor regulating endothelial function. Cardiovasc Res. 2022;118(8):1885-1903.
[35] ZHANG X, LU J, ZHANG Q, et al. CircRNA RSF1 regulated ox-LDL induced vascular endothelial cells proliferation, apoptosis and inflammation through modulating miR-135b-5p/HDAC1 axis in atherosclerosis. Biol Res. 2021;54(1):11.
[36] WANG H, SUGIMOTO K, LU H, et al. HDAC1-mediated deacetylation of HIF1α prevents atherosclerosis progression by promoting miR-224-3p-mediated inhibition of FOSL2. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;23: 577-591. |