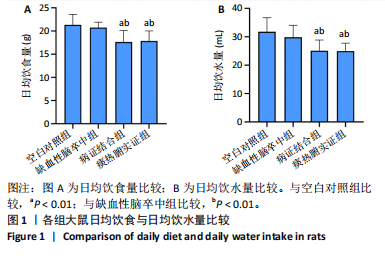
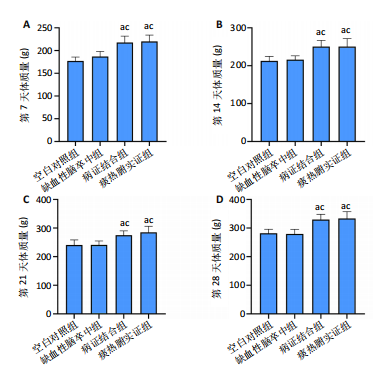
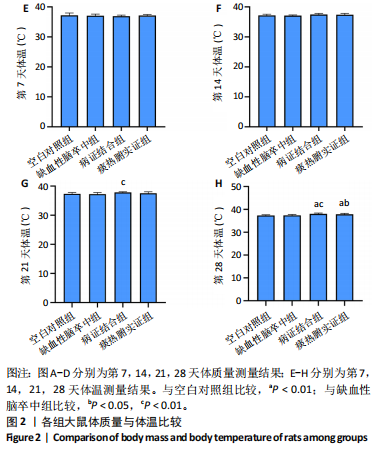
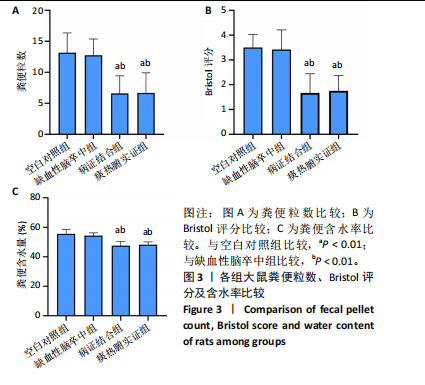
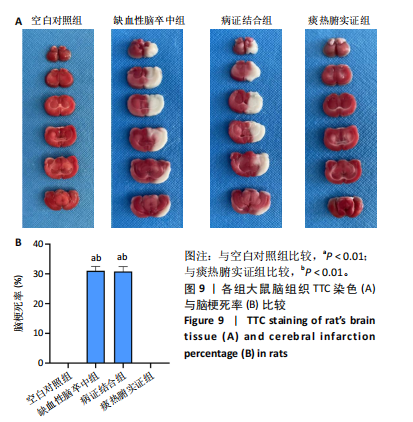
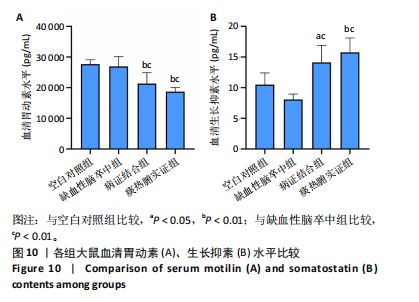
[1] LIU L, CHEN W, ZHOU H, et al. Chinese Stroke Association guidelines for clinical management of cerebrovascular disorders: executive summary and 2019 update of clinical management of ischaemic cerebrovascular diseases. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2020;5(2):159-176.
[2] BENJAMIN EJ, VIRANI SS, CALLAWAY CW, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2018 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2018;137(12):e67-e492.
[3] 王永炎.中风病科研思路方法刍议[J].辽宁中医杂志,1984(9):1-5.
[4] 陈燕清,杨晶晶,曹卓青,等.病证结合动物模型的思考[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2017,23(5):628-629+705.
[5] 王佳帅,李雪梅,曹春然,等.逐瘀通脉胶囊减轻大鼠大脑中动脉阻塞缺血再灌注致运动功能障碍[J]. 实验动物科学,2022,39(6):63-69.
[6] LONGA EZ, WEINSTEIN P , CARLSON S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989;20(1):84-91.
[7] 赵兴杰,李军祥,云逸飞,等.痛泻安肠方调控肠易激综合征小鼠Th17/Treg细胞免疫平衡的研究[J]. 中国中医急症,2022,31(12): 2092-2096+2101.
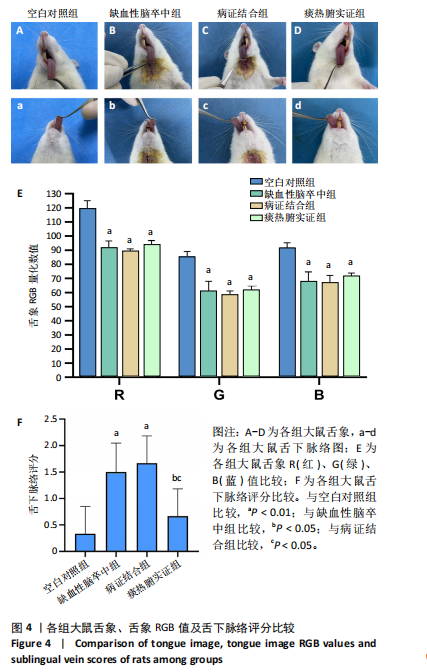
[8] 林筱洁,万浩宇,李志威,等.丹红注射液对缺血性中风大鼠舌象的干预研究[J].中国中医急症,2019,28(5):757-761.
[9] 康洁,高碧珍.病证结合动物模型研究概况[J].中华中医药学刊, 2009,27(11):2357-2359.
[10] 孙晓霞,任威铭,陈宁,等.2型糖尿病阴虚证病证结合动物模型的建立与评价[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2023,43(2):200-211.
[11] 陈沛,江澜,耿花蕾,等.中风病痰热腑实证的研究现状[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2019,17(18):2770-2773.
[12] 甘佳乐,徐武清,刘敬霞.病证结合脑梗死动物模型探讨[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2016,18(9):101-104.
[13] OSTROVA IV, KALABUSHEV SN, RYZHKOV IA, et al. A novel thromboplastin-based rat model of ischemic stroke. Brain Sci. 2021; 11(11):1475.
[14] PAWLETKO K, JEDRZEJOWSKA-SZYPULKA H, BOGUS K, et al. A novel improved thromboembolism-based rat stroke model that meets the latest standards in preclinical studies. Brain Sci. 2022;12(12):1671.
[15] LIN X, ZHAO P, LIN Z, et al. Establishment of a modified and standardized ferric chloride-induced rat carotid artery thrombosis model. ACS Omega. 2022;7(10):8919-8927.
[16] 石春明,李会仓,刘淑霞.黄竹清脑颗粒对痰热腑实证急性脑出血大鼠海马CA1区脑片的神经元密度的影响[J]. 四川中医,2013, 31(5):55-56.
[17] 蔚永运,申亚峰,赵楠.涤痰通腑汤对脑梗死大鼠的保护作用[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2013,27(4):341-343.
[18] 宋文英,古金晓,梁笑笑,等.基于真实世界中风痰热腑实的证候演变规律研究[J].中医药学报,2023,51(7):46-51.
[19] 刘悦,姚明江,付国静,等.角叉菜胶诱导大鼠血瘀证模型再评价[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2023,29(12):2005-2009.
[20] 黄婷婷,韩笑,刘建勋,等.益气活血方对气虚血瘀证大鼠血管内皮功能的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2019,25(8): 40-46.
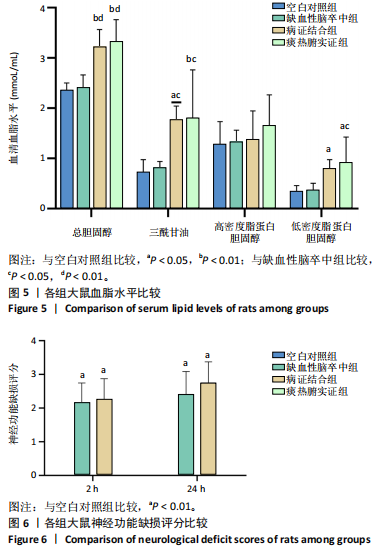
[21] 王安琪,张思薇,陈文娜,等.不同中医证型冠心病患者血脂与脂蛋白水平的关系[J].辽宁中医杂志,2019,46(12):2577-2579.
[22] 陈小光,陈美春,万晓华,等.冠心病中医痰证与血脂相关性的Meta分析[J].世界中西医结合杂志,2019,14(1):13-17.
[23] 周小文,王雅欣,闫振乾,等.茯苓-泽泻药对对高脂血症痰浊证ApoE(-/-)小鼠肝、肾组织中水通道蛋白的作用研究[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2022,28(6):886-891.
[24] 魏佳,曾华霖,林书颖,等.代谢综合征痰证大鼠模型建立与评价的实验研究[J].辽宁中医杂志,2022,49(6):195-199.
[25] 张斐,黄成宝,张晓芳,等.二陈汤对高脂血症痰证模型大鼠脂肪酸代谢的影响[J].中医杂志,2020,61 (3):241-245.
[26] 李芹,张会永,周鹤,等.健脾化痰方对高脂血症脾虚痰浊证模型小型猪血管内皮功能的影响[J].中医杂志,2020,61(10): 886-889+895.
[27] GAO Y, LI J, SU M, et al. Acupuncture with smoothing liver and regulating qi for post-stroke slow transit constipation and its gastrointestinal hormone level. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2017;37(2):125-129.
[28] KITAZAWA T, KAIYA H. Motilin comparative study: Structure, distribution, receptors, and gastrointestinal motility. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:700884.
[29] 刘梦茹,邱仁静,田耀洲,等.运脾柔肝方对便秘型肠易激综合征大鼠胃动素、生长抑素影响的实验研究[J].中国医药导报,2020, 17(8):4-8+16+198.
[30] 陈凯旋,张龙江,李鹏超,等.加味增液汤治疗气阴两虚型慢传输型便秘的疗效评价及对胃肠功能的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2021,27(13):72-77.
[31] 张志亮,常廷民.补脾益肠丸联合复方谷氨酰胺治疗腹泻型肠易激综合征的临床研究[J].现代药物与临床,2019,34(4):1059-1064.
[32] SHAMSI BH, CHATOO M, XU XK, et al. Versatile functions of somatostatin and somatostatin receptors in the gastrointestinal system. Front Endocrinol. 2021;12:652363.
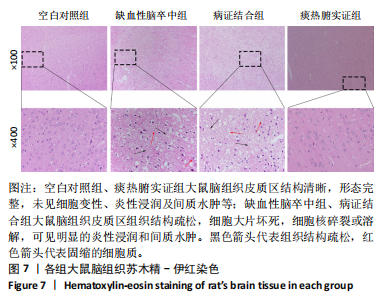
[33] 卢小叶,吕倩忆,李棋龙,等.Zea-longa评分与改良garcia评分应用于针刺治疗ciri大鼠神经功能缺损评估的研究[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2021,41(9):1356-1360.
[34] ZHAO H, ZHANG T, ZHANG H, et al. Exercise-with-melatonin therapy improves sleep disorder and motor dysfunction in a rat model of ischemic stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2024;19(6):1336-1343.
[35] SHA R, ZHANG B, HAN X, et al. Electroacupuncture alleviates ischemic brain injury by inhibiting the mir-223/nlrp3 pathway. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:4723-4733.
[36] YANG Y, HE B, ZHANG X, et al. Geraniin protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis via regulation of the nrf2/ho-1 pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:2152746.
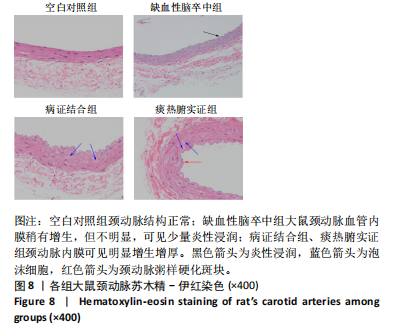
[37] 朱惠斌,陈懿,葛金文.建立一种脑梗死血瘀证大鼠模型的实验研究[J].湖南中医药导报,2004,10(6):77-79+83.
[38] 李豆,梁欣怡,张维,等.颈动脉粥样硬化对缺血性脑卒中影响的相关研究进展[J].海南医学,2023,34(11):1656-1660.
[39] 胡皓月,冯占辉,廖付军.颈动脉粥样硬化与缺血性进展性脑卒中的研究进展[J].中西医结合心血管病电子杂志,2017,5(23):12-13.
[40] LIU Y, ZHU Y, JIA W, et al. Association between lipid profiles and presence of carotid plaque. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):18011. |