[1] 杨子明,李放,陈华江.颈椎病的分型、诊断及非手术治疗专家共识(2018)[J].中华外科杂志,2018,56(6):401-402.
[2] RAO R. Neck pain, cervical radiculopathy, and cervical myelopathy: pathophysiology, natural history, and clinical evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84(10):1872-1881.
[3] RAO RD, CURRIER BL, ALBERT TJ, et al. Degenerative cervical spondylosis: clinical syndromes, pathogenesis, and management. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(6):1360-1378.
[4] 柯尊华,王静怡.颈椎病流行病学及发病机理研究进展[J].颈腰痛杂志,2014,35(1):62-64.
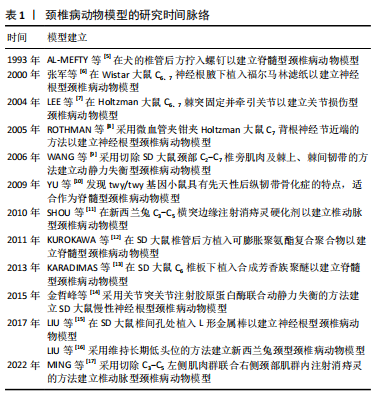
[5] AL-MEFTY O, HARKEY HL, MARAWI I, et al. Experimental chronic compressive cervical myelopathy. J Neurosurg. 1993;79(4):550.
[6] 张军,孙树椿.神经根型颈椎病(急性期)动物模型的建立[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2000,8(1):14-18.
[7] LEE KE, THINNES JH, GOKHIN DS, et al. A novel rodent neck pain model of facet-mediated behavioral hypersensitivity: implications for persistent pain and whiplash injury. J Neurosci Methods. 2004;137(2): 151-159.
[8] ROTHMAN SM, KREIDER RA, WINKELSTEIN BA. Spinal neuropeptide responses in persistent and transient pain following cervical nerve root injury. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(22):2491-2496.
[9] WANG YJ, SHI Q, LU WW, et al. Cervical intervertebral disc degeneration induced by unbalanced dynamic and static forces: a novel in vivo rat model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(14):1532-1538.
[10] YU WR, BAPTISTE DC, LIU T, et al. Molecular mechanisms of spinal cord dysfunction and cell death in the spinal hyperostotic mouse: implications for the pathophysiology of human cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Neurobiol Dis. 2009;33(2):149-163.
[11] SHOU Z, SHEN L, XIONG P. Assessing the validity of a novel model of vertebral artery type of cervical syndrome induced by injecting sclerosing agent next to transverse process of cervical vertebra. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2010;30(1): 85-88.
[12] KUROKAWA R, NAGAYAMA E, MURATA H, et al. Limaprost alfadex, a prostaglandin E1 derivative, prevents deterioration of forced exercise capability in rats with chronic compression of the spinal cord. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(11):865-869.
[13] KARADIMAS SK, MOON ES, YU WR, et al. A novel experimental model of cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM) to facilitate translational research. Neurobiol Dis. 2013;54:43-58.
[14] 金哲峰,徐凡平,朱立国,等.慢性神经根型颈椎病动物模型的建立[J].天津中医药,2015,32(9):558-562.
[15] LIU DL, WANG X, CHU WG, et al. Chronic cervical radiculopathic pain is associated with increased excitability and hyperpolarization-activated current (Ih) in large-diameter dorsal root ganglion neurons. Mol Pain. 2017;13:2071456393.
[16] LIU FS, ZHOU FY, ZHANG Y, et al. Effects of Acupotomy Therapy on mRNA Expressions of Bcl-2, Bax, Caspase-3 in Posterior Cervical Extensor Muscles in Cervical Spondylosis Rabbits. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2017;42(6):514-517.
[17] MING RR, ZHANG YQ, XU Y, et al. Mechanism of Panlongqi Tablets intervening in vertebral artery type of cervical spondylosis in rats through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway based on network pharmacology and experimental verification. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022;47(16): 4454-4461.
[18] ROGERS J. Genomic resources for rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta). Mamm Genome. 2022;33(1):91-99.
[19] XAVIER A, TOUMI H, LESPESSAILLES E. Animal Model for Glucocorticoid Induced Osteoporosis: A Systematic Review from 2011 to 2021. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;23(1):377.
[20] CLAYTON JA, COLLINS FS. Policy: NIH to balance sex in cell and animal studies. Nature. 2014;509(7500):282-283.
[21] HAEFELI M, KALBERER F, SAEGESSER D, et al. The course of macroscopic degeneration in the human lumbar intervertebral disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(14):1522-1531.
[22] FERNÁNDEZ-DE-LAS-PEÑAS C, ALONSO-BLANCO C, HERNÁNDEZ-BARRERA V, et al. Has the prevalence of neck pain and low back pain changed over the last 5 years? A population-based national study in Spain. Spine J. 2013;13(9):1069-1076.
[23] SENGUPTA P. The Laboratory Rat: Relating Its Age With Human’s. Int J Prev Med. 2013;4(6):624-630.
[24] DUTTA S, SENGUPTA P. Rabbits and men: relating their ages. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2018;29(5):427-435.
[25] DUTTA S, SENGUPTA P. Men and mice: Relating their ages. Life Sci. 2016;152:244-248.
[26] YIN J, REN K, HUANG Y, et al. Exploration about changes of IL-10, NF-κB and MMP-3 in a rat model of cervical spondylosis. Mol Immunol. 2018;93:184-188.
[27] SUN Q, LIU F, GAO M, et al. Therapeutic evaluation of acupoint stimulation with needle-scapelon on rat model of degenerative cervical intervertebral discs. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;110:677-684.
[28] UCHIDA K, NAKAJIMA H, WATANABE S, et al. Apoptosis of neurons and oligodendrocytes in the spinal cord of spinal hyperostotic mouse (twy/twy): possible pathomechanism of human cervical compressive myelopathy. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(3):490-497.
[29] KARADIMAS SK, KLIRONOMOS G, PAPACHRISTOU DJ, et al. Immunohistochemical profile of NF-κB/p50, NF-κB/p65, MMP-9,MMP-2, and u-PA in experimental cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(1):4-10.
[30] CHEN B, LIU H, ZHANG LZ, et al. Visual acupotomy intervention mitigates pain reaction by improving intervertebral disc degeneration and inhibiting apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells in rabbits with cervical spondylosis. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022;47(11): 1005-1011.
[31] LI GS, CHEN GH, WANG KH, et al. Neurovascular Unit Compensation from Adjacent Level May Contribute to Spontaneous Functional Recovery in Experimental Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(4):3408.
[32] KANBARA S, OHKAWARA B, NAKASHIMA H, et al. Zonisamide ameliorates progression of cervical spondylotic myelopathy in a rat model. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):13138.
[33] XU P, GONG WM, LI Y, et al. Destructive pathological changes in the rat spinal cord due to chronic mechanical compression. Laboratory investigation. J Neurosurg Spine. 2008;8(3):279-285.
[34] LEE J, SATKUNENDRARAJAH K, FEHLINGS MG. Development and characterization of a novel rat model of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: the impact of chronic cord compression on clinical, neuroanatomical, and neurophysiological outcomes. J Neurotrauma. 2012;29(5):1012-1027.
[35] IBRAHIM S, ADEPUTRA NI, DANIL M, et al. Potential benefit of olive leaf extract in cervical spondylotic myelopathy model. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022;73:103040.
[36] IBRAHIM S, MOUSA A, RIAWAN W. Expression of AIF and Caspase-3 in New Zealand rabbit with Cervical Spondylosis Myelopathy model. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2021;69:102604.
[37] YOSHIZUMI T, MURATA H, YAMAMOTO S, et al. Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor Improves Motor Function in Rats Developing Compression Myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41(23): E1380-E1387.
[38] DHILLON RS, PARKER J, SYED YA, et al. Axonal plasticity underpins the functional recovery following surgical decompression in a rat model of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2016;4(1): 89.
[39] ZHOU LY, YAO M, TIAN ZR, et al. Muscone suppresses inflammatory responses and neuronal damage in a rat model of cervical spondylotic myelopathy by regulating Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission. J Neurochem. 2020;155(2):154-176.
[40] MOON ES, KARADIMAS SK, YU WR, et al. Riluzole attenuates neuropathic pain and enhances functional recovery in a rodent model of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Neurobiol Dis. 2014;62:394-406.
[41] NICHOLSON KJ, ZHANG S, GILLILAND TM, et al. Riluzole effects on behavioral sensitivity and the development of axonal damage and spinal modifications that occur after painful nerve root compression. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;20(6):751-762.
[42] NICHOLSON KJ, GUARINO BB, WINKELSTEIN BA. Transient nerve root compression load and duration differentially mediate behavioral sensitivity and associated spinal astrocyte activation and mGLuR5 expression. Neuroscience. 2012;209:187-195.
[43] SUN W, ZHENG K, LIU B, et al. Neuroprotective Potential of Gentongping in Rat Model of Cervical Spondylotic Radiculopathy Targeting PPAR-γPathway. J Immunol Res. 2017;2017:1-12.
[44] TANG ZY, SHU B, CUI XJ, et al. Changes of cervical dorsal root ganglia induced by compression injury and decompression procedure: a novel rat model of cervical radiculoneuropathy. J Neurotrauma. 2009;26(2): 289-295.
[45] SHEN WS, LI CF, ZHOU ZS, et al. MicroRNA-204 silencing relieves pain of cervical spondylotic radiculopathy by targeting GDNF. Gene Ther. 2020;27(6):254-265.
[46] QIN MX, SU SY, ZHANG X, et al. Effect of mild moxibustion on pain and expression of LC3 and Bax in spinal cord in cervical spondylotic radiculopathy rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022;47(3):244-249.
[47] LIN YY, SU SY, XU YY, et al. Effect of wheat-grain moxibustion on the expression of Beclin-1/GRP78 in spinal dorsal horn in rats with cervical spondylotic radiculopathy. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2022;42(5):533-539.
[48] CAI HQ, LIN XY, CHEN HY, et al. Direct moxibustion exerts an analgesic effect on cervical spondylotic radiculopathy by increasing autophagy via the Act A/Smads signaling pathway. Brain Behav. 2022;12(4):e2545.
[49] XIE H, HUANG Y, NONG L, et al. X-ray dynamic observation of cervical degenerative disease induced by unbalanced dynamic and static forces in rats 1. Acta Cir Bras. 2017;32(9):736-745.
[50] LIAO J, KE M, XU T, et al. Electroacupuncture inhibits apoptosis in annulus fibrosis cells through suppression of the mitochondria-dependent pathway in a rat model of cervical intervertebral disc degradation. Genet Mol Biol. 2012;35(3):686-692.
[51] LIAO J, ZHANG L, ZHENG J, et al. Electroacupuncture inhibits annulus fibrosis cell apoptosis in vivo via TNF-alpha-TNFR1-caspase-8 and integrin beta1/Akt signaling pathways. J Tradit Chin Med. 2014;34(6): 684-690.
[52] YIN J, HUANG Y, GAO G, et al. Changes and significance of inflammatory cytokines in a rat model of cervical spondylosis. Exp Ther Med. 2018; 15(1):400-406.
[53] ZHAO K, CHEN M, LIU T, et al. Rhizoma drynariae total flavonoids inhibit the inflammatory response and matrix degeneration via MAPK pathway in a rat degenerative cervical intervertebral disc model. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;138:111466.
[54] HUANG LS, HUANG PP, TONG XB, et al. Effects of Chiropractics on Intervertebral Disk Extracell Matrix and Metabolic Enzymes in Rats with Cervical Spondylosis. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2017;42(4):321-326.
[55] WANG YX, LIN YK, PENG N, et al. Experimental study of improved sclerotherapy injection in rat model of vertebral arteriocervical spondylopathy. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2023;36(2):185-188.
[56] WANG C, ZHU JC, XIONG YZ, et al. Experimental study on improvement of blood supply timeliness of rabbits with vertebral artery type of cervical spondylosis by massage. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2018;31(8): 769-774.
[57] ITA ME, CROSBY ND, BULKA BA, et al. Painful Cervical Facet Joint Injury Is Accompanied by Changes in the Number of Excitatory and Inhibitory Synapses in the Superficial Dorsal Horn That Differentially Relate to Local Tissue Injury Severity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017;42(12): E695-E701.
[58] KALLAKURI S, SINGH A, LU Y, et al. Tensile stretching of cervical facet joint capsule and related axonal changes. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(4): 556-563.
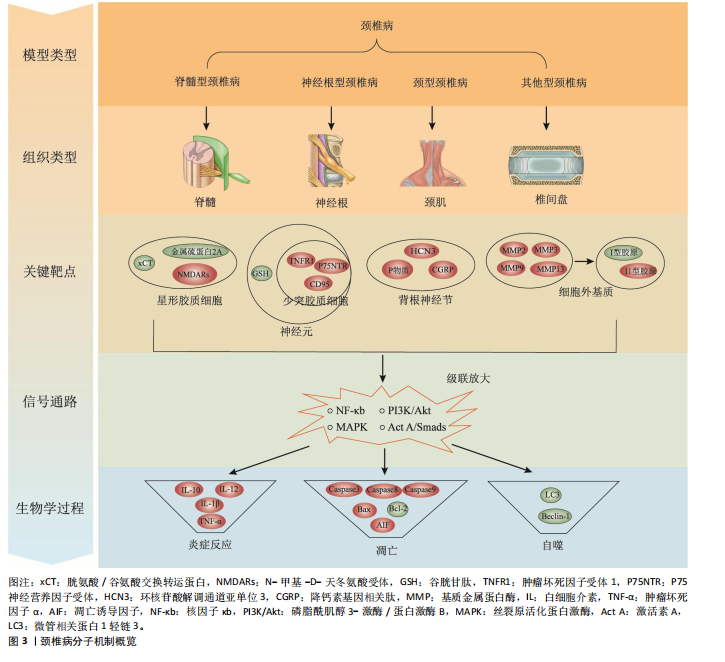
[59] 王辉昊,詹红生.颈椎病中医实验动物模型的研究进展[J].中华中医药杂志,2022,37(6):3335-3339.
[60] 王诗军,李钰婷,李淳德.颈椎病动物模型的建立及其应用研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(40):6067-6073.
[61] 朱立国,唐彬,魏戌,等.神经根型颈椎病动物模型的研究进展及评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(35):5700-5705. |