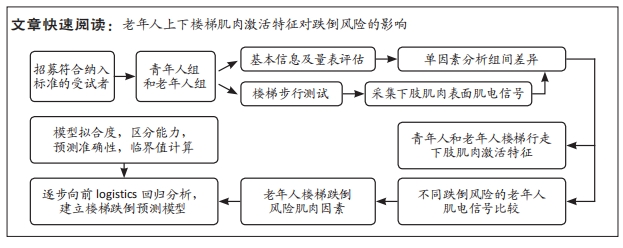
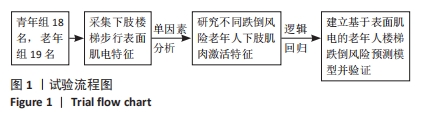
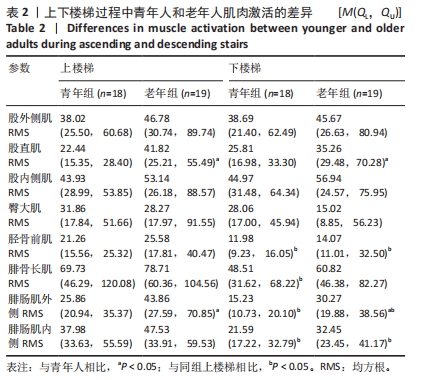
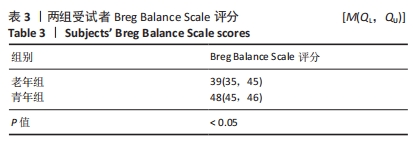
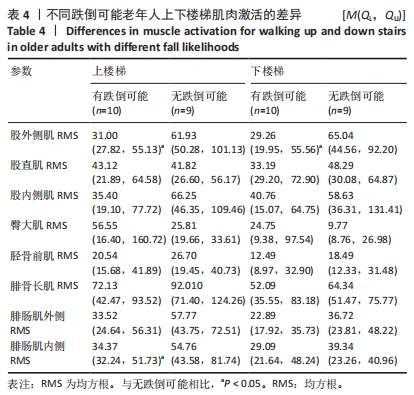
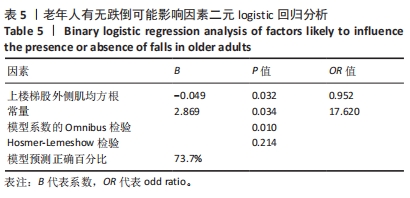
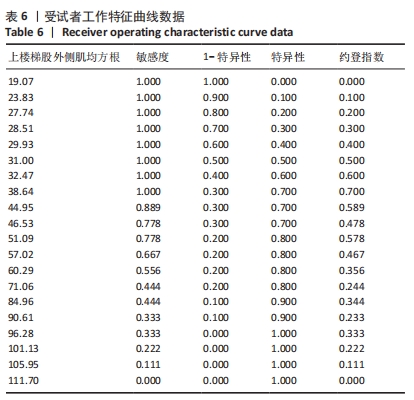
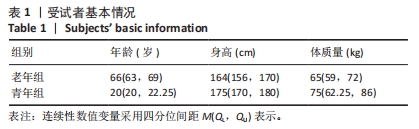
[1] 康宁, 于海军, 陆晓敏, 等. 中国老年人跌倒发生率的Meta分析[J]. 中国循证医学杂志,2022,22(10):1142-1148.
[2] 黄婷苑, 林伟权, 段丹萍, 等. 2018-2020年广东省广州市伤害住院病例流行病学特征[J]. 疾病监测,2023,38(8):995-999.
[3] SOLAIMAN RH, IRFANULLAH E, NAVARRO SM, et al. Rising incidence of stair-related upper extremity fractures among older adults in the United States: a 10-year nationwide analysis. Osteoporos Int. 2023; 34(7):1241-1248.
[4] SCHICK S, HEINRICH D, GRAW M, et al. Fatal falls in the elderly and the presence of proximal femur fractures. Int J Legal Med. 2018;132(6): 1699-1712.
[5] SAMUEL D, ROWE P, HOOD V, et al. The biomechanical functional demand placed on knee and hip muscles of older adults during stair ascent and descent. Gait Posture. 2011;34(2):239-244.
[6] ACKERMANS T, FRANCKSEN N, LEES C, et al. Prediction of Balance Perturbations and Falls on Stairs in Older People Using a Biomechanical Profiling Approach: A 12-Month Longitudinal Study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2021;76(4):638-646.
[7] ACKERMANS T, FRANCKSEN NC, CASANA-ESLAVA RV, et al. A novel multivariate approach for biomechanical profiling of stair negotiation. Exp Gerontol. 2019;124:110646.
[8] PHELAN EA, RITCHEY K. Fall Prevention in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(11):ITC81-ITC96.
[9] MARTINIKORENA I, MARTÍNEZ-RAMÍREZ A, GÓMEZ M, et al. Gait Variability Related to Muscle Quality and Muscle Power Output in Frail Nonagenarian Older Adults. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2016;17(2):162-167.
[10] 王艳春, 郑立新, 周思红. 老年人最大伸膝动作时的肌力与肌电RMS特征[J]. 西安体育学院学报,2017,34(3):336-340.
[11] YUAN S, LARSSON SC. Epidemiology of sarcopenia: Prevalence, risk factors, and consequences. Metabolism. 2023;144:155533.
[12] 周胜如, 盛慧媛, 黄招檬, 等. 老年人上下楼梯的步态特征以及下肢关节运动功能特点[J]. 医用生物力学,2023,38(5):1017-1023.
[13] 赵钦康, 魏俊妮. 中老年跌倒住院患者治疗效果影响因素分析及预测模型建立[J]. 中国公共卫生,2023,39(7):902-907.
[14] DOSTAN A, DOBSON CA, VANICEK N. Relationship between stair ascent gait speed, bone density and gait characteristics of postmenopausal women. PLOS ONE. 2023;18(3):e0283333.
[15] PARK SH. Tools for assessing fall risk in the elderly: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2018;30(1):1-16.
[16] DOWNS S, MARQUEZ J, CHIARELLI P. The Berg Balance Scale has high intra- and inter-rater reliability but absolute reliability varies across the scale: a systematic review. J Physiother. 2013;59(2):93-99.
[17] CHANG MC, LEE BJ, JOO NY, et al. The parameters of gait analysis related to ambulatory and balance functions in hemiplegic stroke patients: a gait analysis study. BMC Neurol. 2021;21(1):38.
[18] MARSHALL RN, MORGAN PT, MARTINEZ-VALDES E, et al. Quadriceps muscle electromyography activity during physical activities and resistance exercise modes in younger and older adults. Exp Gerontol. 2020;136:110965.
[19] DUARTE MB, DA SAG, COSTA K, et al. Anticipatory postural adjustments in older versus young adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst Rev. 2022;11(1):251.
[20] 马刚, 闫士芳, 曹传宝, 等. 老年人下楼梯下肢关节做功模式分析[J]. 医用生物力学,2023,38(5):1010-1016.
[21] SAMUEL D, ROWE P, NICOL A. The functional demand (FD) placed on the knee and hip of older adults during everyday activities. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2013;57(2):192-197.
[22] CASANA J, CALATAYUD J, SILVESTRE A, et al. Knee Extensor Muscle Strength Is More Important Than Postural Balance for Stair-Climbing Ability in Elderly Patients with Severe Knee Osteoarthritis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(7):3637.
[23] TRINLER UK, BATY F, MUNDERMANN A, et al. Stair dimension affects knee kinematics and kinetics in patients with good outcome after TKA similarly as in healthy subjects. J Orthop Res. 2016;34(10):1753-1761.
[24] BUCKLEY JG, HEASLEY KJ, TWIGG P, et al. The effects of blurred vision on the mechanics of landing during stepping down by the elderly. Gait Posture. 2005;21(1):65-71.
[25] MACIE A, MATSON T, SCHINKEL-IVY A. Age affects the relationships between kinematics and postural stability during gait. Gait Posture. 2023;102:86-92.
[26] HUANG CH, AYDEMIR B, FOUCHER KC. Sagittal plane ankle kinetics are associated with dynamic hip range of motion and gait efficiency in women with hip osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2023;41(3):555-561.
[27] PEREIRA DB, SOUZA TSD, FUZINATO CT, et al. Effect of a programme of muscular endurance, balance and gait exercises with and without the use of flexible and minimalist shoes in older women with medial knee osteoarthritis: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2022;12(9):e061267.
[28] WINGER ME, CASEROTTI P, CAULEY J, et al. Lower Leg Power and Grip Strength Are Associated With Increased Fall Injury Risk in Older Men: The Osteoporotic Fractures in Men Study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2023;78(3):479-485.
[29] OMANA H, BEZAIRE K, BRADY K, et al. Functional Reach Test, Single-Leg Stance Test, and Tinetti Performance-Oriented Mobility Assessment for the Prediction of Falls in Older Adults: A Systematic Review. Phys Ther. 2021;101(10):pzab173.
[30] TIELAND M, TROUWBORST I, CLARK BC. Skeletal muscle performance and ageing. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2018;9(1):3-19.
[31] GOODPASTER BH, PARK SW, HARRIS TB, et al. The Loss of Skeletal Muscle Strength, Mass, and Quality in Older Adults: The Health, Aging and Body Composition Study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2006; 61(10):1059-1064.
[32] BLASZCZYSZYN M, BORYSIUK Z, PIECHOTA K, et al. Wavelet coherence as a measure of trunk stabilizer muscle activation in wheelchair fencers. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2021;13(1):140.
[33] SONG Z, OU J, SHU L, et al. Fall Risk Assessment for the Elderly Based on Weak Foot Features of Wearable Plantar Pressure. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2022;30:1060-1070.
[34] ULLRICH M, ROTH N, KUDERLE A, et al. Fall Risk Prediction in Parkinson’s Disease Using Real-World Inertial Sensor Gait Data. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2023;27(1):319-328.
[35] GREENE BR, REDMOND SJ, CAULFIELD B. Fall Risk Assessment Through Automatic Combination of Clinical Fall Risk Factors and Body-Worn Sensor Data. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2017;21(3):725-731.
[36] 王志灼, 谷莉, 周谋望. 中国老年人跌倒风险因素识别及评估工具应用的研究进展[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2021,36(11):1440-1444.
[37] 周君桂, 范建中. Morse跌倒评估量表与Berg平衡量表应用于老年患者预测跌倒风险的效果分析[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2012,27(2): 130-133.
[38] 刘善云, 陈东烨, 连志强, 等. 核心力量练习对男性老年人下肢肌力、平衡能力与跌倒风险的干预效果[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2015,34(12):1139-1142.
[39] 柯鹏辉, 韩刘虎, 胡军, 等. 腰椎间盘突出症病人经椎间孔镜手术前后步态与站立平衡稳定性研究[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志,2023, 29(5):353-358.
[40] 王金仙, 姚瑞, 龙永姣, 等. 老年人步态、平衡特征与跌倒关系的研究现状及热点分析[J]. 护理研究,2020,34(13):2264-2270.
[41] 戴婷, 张孟喜, 李欢, 等. 老年人跌倒风险相关评估的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学,2019,22(27):3347-3352.
[42] 胡惠菊, 韩静, 唐启群, 等. Morse跌倒评估量表与STEADI跌倒风险自评量表在养老机构老年人中的应用比较[J]. 护理学报,2021, 28(19):8-12.
[43] 岳跃学, 贾玉玲, 王秀红. 老年人跌倒风险预测模型研究进展[J]. 护理研究,2022,36(16):2944-2948.
[44] 张琪, 刘腊梅. 老年人步态与平衡评估工具研究进展[J]. 中国慢性病预防与控制,2022,30(4):307-311. |