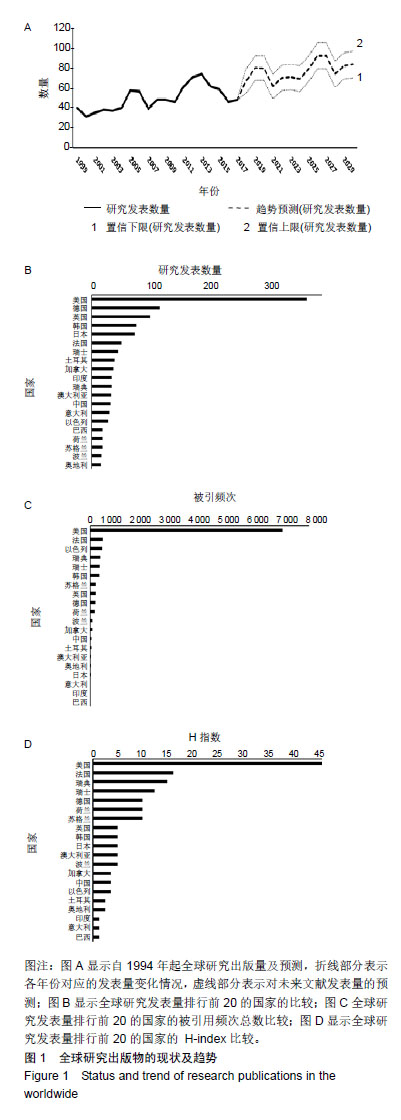
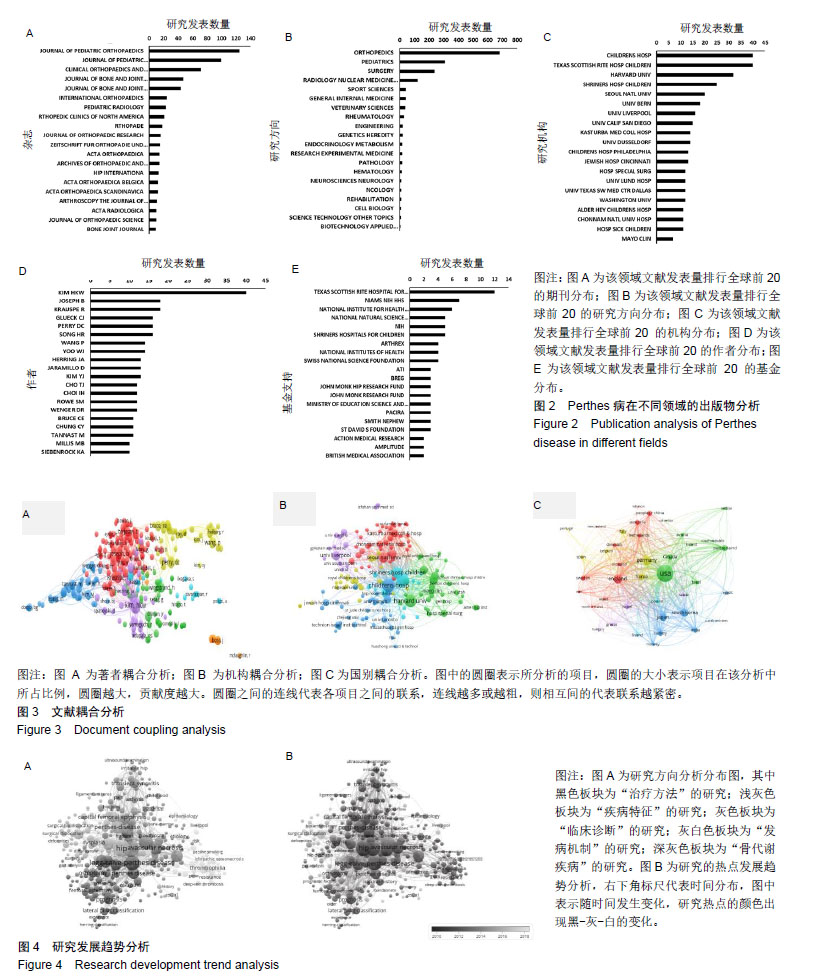
| [1]吴在德,吴肇汉.外科学[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社,2011:839[2]Wiig O. Perthes' disease in Norway. A prospective study on 425 patients. Acta Orthop Suppl. 2009;80(333):1-44.[3]Perry DC, Bruce CE, Pope D, et al. Comorbidities in Perthes' disease: a case control study using the General Practice Research database. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(12):1684.[4]Loder RT, Skopelja EN. The Epidemiology and Demographics of Legg-Calvé-Perthes' Disease. ISRN Orthop. 2011;2011(1): 504393-504393.[5]Tannast M, Macintyre N, Steppacher SD, et al. A systematic approach to analyse the sequelae of LCPD. Hip Int. 2013;23 Suppl 9(Suppl 9): S61-70.[6]Mazloumi SM, Ebrahimzadeh MH, Kachooei AR. Evolution in diagnosis and treatment of Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. Arch Bone Joint Surg. 2014; 2(2):86-92.[7]Rampal V, Clément JL, Solla F. Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease: classifications and prognostic factors. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab. 2017;14(1):74-82. [8]Waldenström H. The definite form of the coxa plana. Acta Radiol. 1922;4(1): 384-394.[9]Catterall A. The natural history of Perthes’disease. J Bone Joint Surg Br.1971;53B: 37-53.[10]Salter RB, Thompson GH. Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. The prognostic significance of the subchondral fracture and a two-group classification of the femoral head involvement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984;66(4): 479-489.[11]Herring JA, Neustadt JB, Williams JJ, et al. The lateral pillar classification of Legg-Calve -Perthes disease. J Pediatr Orthop. 1992; 12:143-150.[12]Herring JA, Kim HT, Browne R. Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. Part I: Classification of radiographs with use of the modified lateral pillar and Stulberg classifications. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A(10): 2103.[13]Mose K. Methods of measuring in Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease with special regard to the prognosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980;(150): 103-109.[14]Mazloumi SM, Ebrahimzadeh MH, Kachooei AR. Evolution in diagnosis and treatment of Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. Arch Bone Joint Surg. 2014; 2(2):86-92.[15]Jamil K, Zacharin M, Foster B, et al. Protocol for a randomised control trial of bisphosphonate (zoledronic acid) treatment in childhood femoral head avascular necrosis due to Perthes disease. BMJ Paediatr Open. 2017;1(1): e000084.[16]吴生康,何鹤皋. 高压氧治疗 38 例儿童股骨头缺血性坏死[J]. 中华航海医学与高气压医学杂志,2005,12(1) : 60-62.[17]俞松,黄辉.Perthes病的病因与临床诊疗现状[J].临床外科杂志, 2017,25 (12):952-954.[18]Perry DC, Skellorn PJ, Bruce CE. The lognormal age of onset distribution in Perthes' disease: an analysis from a large well-defined cohort . Bone Joint J. 2016;98-B (5):710.[19]Sweileh WM, Al-Jabi SW, Zyoud SH, et al. Bibliometric analysis of global publications in medication adherence (1900-2017). Int J Pharm Pract. 2019;27(2):112-120.[20]Xing D, Zhao Y, Dong S, et al. Global research trends in stem cells for osteoarthritis: a bibliometric and visualized study. Int J Rheum Dis. 2018; 21(7):1372-1384.[21]Hirsch JE. An index to quantify an individual's scientific research output Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(46):16569-16572.[22]Zou X, Yue WL, Vu HL. Visualization and analysis of mapping knowledge domain of road safety studies. Accid Anal Prev. 2018; 118:131-145.[23]Somberg JC. A perspective on the support of scientific research. Am J Ther. 2013;20(3):231. [24]Kim HKW, Kaste S, Dempsey M, et al. A comparison of non-contrast and contrast-enhanced MRI in the initial stage of Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. Pediatr Radiol. 2013;43(9): 1166-1173.[25]Du J, Lu A, Dempsey M, et al. MR perfusion index as a quantitative method of evaluating epiphyseal perfusion in Legg-Calve-Perthes disease and correlation with short-term radiographic outcome: a preliminary study. J Pediatr Orthop. 2013;33(7):707.[26]Kim HKW, Wiesman KD, Kulkarni V, et al. Perfusion MRI in early stage of Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease to predict lateral pillar involvement: a preliminary study. J Bone Joint Surg. 2014;96(14): 1152-1160.[27]Joseph B. Prognostic factors and outcome measures in Perthes disease. Orthop Clin North Am. 2011;42(3):303-315.[28]Siebenrock KA, Anwander H, Zurmühle CA, et al. Head reduction osteotomy with additional containment surgery improves sphericity and containment and reduces pain in Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(4):1274-1283.[29]Aydin BK, Sofu H, Konya MN, et al. Clinical and radiographic outcomes after femoral varusderotation osteotomy for Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease at 25 years follow-up: what are the determinants of outcome in the long term? Hip Int. 2016;26(3): 301-306. [30]Herring J. Legg-Calve-Perthes disease, Part II; multicenter study of the effect of treatment on outcome. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014; 86(10): 2121-2134.[31]Daniel AB, Orth HSM, Kamath A, et al. Environmental tobacco and wood smoke increase the risk of Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(9):2369-2375.[32]Joseph B, Varghese G, Mulpuri K, et al. Natural evolution of Perthes disease: a study of 610 children under 12 years of age at disease onset. J Pediatr Orthop. 2003;23(5):590-600. |
.jpg)
.jpg)