| [1]Budai KA, Mirzahosseini A,Béla N,et al. The pharmacotherapy of obesity. Acta Pharm Hung.2015; 85(1): 3-17.[2]Carey VJ, Walters EE, Colditz GA, et al.Body fat distribution and risk of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in women. The Nurses' Health Study. Am J Epidemiol.1997;145(7):614-619.[3]Kissebah AH,Krakower GR.Regional adiposity and morbidity. Physiol Rev.1994;74(4): 761-811.[4]Zimmet P,Alberti&Amp KGMM,Shaw J.Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature.2001;414(6865): 782-787.[5]Racette SB,Evans EM,Weiss EP,et al.Abdominal Adiposity Is a Stronger Predictor of Insulin Resistance Than Fitness Among 50–95 Year Olds. Diabetes Care.2006;29(3): 673-678.[6]Karelis AD,Stpierre DH,Conus F,et al.Metabolic and body composition factors in subgroups of obesity: what do we know. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2004;89(6): 2569-2575.[7]Maillard F,Rousset S,Pereira B,et al.High-intensity interval training reduces abdominal fat mass in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab.2016;42(6): 433-441.[8]Tucker WJ,Sawyer BJ,Jarrett CL,et al.Physiological Responses to High-Intensity Interval Exercise Differing in Interval Duration.J Strength Cond Res.2015; 29(12): 3326-3335.[9]Péronnet F,Massicotte D.Table of nonprotein respiratory quotient: an update.Can J Sport Sci. 1991;16(1): 23-29.[10]Benito PJ,Alvarezsánchez M, Díaz V, et al. Cardiovascular Fitness and Energy Expenditure Response during a Combined Aerobic and Circuit Weight Training Protocol. PLoS One.2016; 11(11): e0164349.[11]Buchheit M,Laursen PB.High-intensity interval training, solutions to the programming puzzle. Part II: anaerobic energy, neuromuscular load and practical applications.Sports Med.2013; 43(10): 927-54.[12]Obradovi? J,Vukadinovi? M,Pantovi? M,et al. HIIT VS MODERATE INTENSITY ENDURANCE TRAINING: IMPACT ON AEROBIC PARAMETERS IN YOUNG ADULT MEN. Acta Kinesiologica. 2016 .[13]Cipryan L,Tschakert G,Hofmann P.Acute and Post-Exercise Physiological Responses to High-Intensity Interval Training in Endurance and Sprint Athletes. J Sports Sci Med. 2017. 16(2): 219-229.[14]Pavey TG, Gartner CE, Coombes JS,et al. Assessing the effectiveness of High Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) for smoking cessation in women: HIIT to quit study protocol.BMC Public Health. 2015;15: 1309.[15]Isaksen K, Munk PS, Valborgland T,et al. Aerobic interval training in patients with heart failure and an implantable cardioverter defibrillator: a controlled study evaluating feasibility and effect. Eur J Prev Cardiol.2015;22(3): 296-303.[16]Buchheit M,Laursen PB.High-Intensity Interval Training, Solutions to the Programming Puzzle. Sports Med. Sports Med.2013;43(5):313-338.[17]Scott CB. Contribution of blood lactate to the energy expenditure of weight training. J Strength Cond Res. 2006;20(2):404-411.[18]Scott CB,Leighton BH,Ahearn KJ,et al.Aerobic,anaerobic,and excess postexercise oxygen consumption energy expenditure of muscular endurance and strength: 1-set of bench press to muscular fatigue. J Strength Cond Res. 2011;25(4):903-908.[19]尹伟.24式太极拳呼吸及能量代谢特点研究[D]. 北京:北京体育大学, 2010.[20]董晓虹,陈宇婷,韩娟.基于不同体重和运动方法的底物代谢与能量消耗特征研究[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2016,35(5): 411-416+422.[21]王爱华,徐国栋.基于近红外光谱技术的递增负荷运动中局部肌氧变化与气体交换率比较研究[J].广州体育学院学报,2011,31(5): 84-88.[22]张勇.运动与脂肪氧化动力学及最大脂肪氧化研究[D].上海:上海体育学院,2013.[23]Larsen I,Welde B,Martins C,et al.High- and moderate-intensity aerobic exercise and excess post-exercise oxygen consumption in men with metabolic syndrome.Scand J Med Sci Sports.2014; 24(3): e174-e179.[24]Murphy MH,Hardman AE.Training effects of short and long bouts of brisk walking in sedentary women. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1998;30(1): 152-157.[25]Goto K,Ishii N,Mizuno A,et al.Enhancement of fat metabolism by repeated bouts of moderate endurance exercise.J Appl Physiol (1985).2007;102(6): 2158.[26]Ahmed K, Tunaru S, Tang C, et al. An autocrine lactate loop mediates insulin-dependent inhibition of lipolysis through GPR81. Cell Metab.2010;11(4): 311-319.[27]Rooney K,Trayhurn P.Lactate and the GPR81 receptor in metabolic regulation: implications for adipose tissue function and fatty acid utilisation by muscle during exercise.British Journal of Nutrition.2011;106(9): 1310-1316. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
高强度间歇运动:是指进行多次短时间高强度运动训练,在每2次训练之间以相对较低的强度运动或者完全无负荷休息形成间歇期,常采用全力冲刺或90%左右最大摄氧量强度。单组运动时间和间歇期可持续几秒到几分钟不等,按间歇周期长短可分为短间歇高强度间歇运动和长间歇高强度间歇运动。
气体代谢:是指机体消耗氧和产生二氧化碳的过程。组织细胞在生命活动过程中需要不断获取能量,其来源是体内营养物质(蛋白质、糖类和脂肪)的氧化。为维持体内正常的氧化过程,需经常供给氧和排出二氧化碳。测定单位时间内氧耗量和二氧化碳产生量可计算出能量代谢率。
文题释义:
高强度间歇运动:是指进行多次短时间高强度运动训练,在每2次训练之间以相对较低的强度运动或者完全无负荷休息形成间歇期,常采用全力冲刺或90%左右最大摄氧量强度。单组运动时间和间歇期可持续几秒到几分钟不等,按间歇周期长短可分为短间歇高强度间歇运动和长间歇高强度间歇运动。
气体代谢:是指机体消耗氧和产生二氧化碳的过程。组织细胞在生命活动过程中需要不断获取能量,其来源是体内营养物质(蛋白质、糖类和脂肪)的氧化。为维持体内正常的氧化过程,需经常供给氧和排出二氧化碳。测定单位时间内氧耗量和二氧化碳产生量可计算出能量代谢率。.jpg) 文题释义:
高强度间歇运动:是指进行多次短时间高强度运动训练,在每2次训练之间以相对较低的强度运动或者完全无负荷休息形成间歇期,常采用全力冲刺或90%左右最大摄氧量强度。单组运动时间和间歇期可持续几秒到几分钟不等,按间歇周期长短可分为短间歇高强度间歇运动和长间歇高强度间歇运动。
气体代谢:是指机体消耗氧和产生二氧化碳的过程。组织细胞在生命活动过程中需要不断获取能量,其来源是体内营养物质(蛋白质、糖类和脂肪)的氧化。为维持体内正常的氧化过程,需经常供给氧和排出二氧化碳。测定单位时间内氧耗量和二氧化碳产生量可计算出能量代谢率。
文题释义:
高强度间歇运动:是指进行多次短时间高强度运动训练,在每2次训练之间以相对较低的强度运动或者完全无负荷休息形成间歇期,常采用全力冲刺或90%左右最大摄氧量强度。单组运动时间和间歇期可持续几秒到几分钟不等,按间歇周期长短可分为短间歇高强度间歇运动和长间歇高强度间歇运动。
气体代谢:是指机体消耗氧和产生二氧化碳的过程。组织细胞在生命活动过程中需要不断获取能量,其来源是体内营养物质(蛋白质、糖类和脂肪)的氧化。为维持体内正常的氧化过程,需经常供给氧和排出二氧化碳。测定单位时间内氧耗量和二氧化碳产生量可计算出能量代谢率。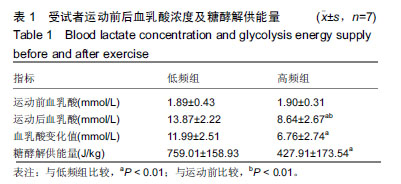
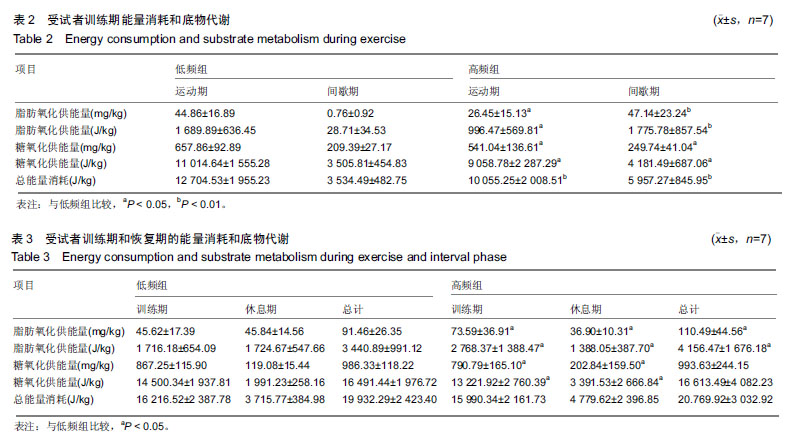
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
高强度间歇运动:是指进行多次短时间高强度运动训练,在每2次训练之间以相对较低的强度运动或者完全无负荷休息形成间歇期,常采用全力冲刺或90%左右最大摄氧量强度。单组运动时间和间歇期可持续几秒到几分钟不等,按间歇周期长短可分为短间歇高强度间歇运动和长间歇高强度间歇运动。
气体代谢:是指机体消耗氧和产生二氧化碳的过程。组织细胞在生命活动过程中需要不断获取能量,其来源是体内营养物质(蛋白质、糖类和脂肪)的氧化。为维持体内正常的氧化过程,需经常供给氧和排出二氧化碳。测定单位时间内氧耗量和二氧化碳产生量可计算出能量代谢率。
文题释义:
高强度间歇运动:是指进行多次短时间高强度运动训练,在每2次训练之间以相对较低的强度运动或者完全无负荷休息形成间歇期,常采用全力冲刺或90%左右最大摄氧量强度。单组运动时间和间歇期可持续几秒到几分钟不等,按间歇周期长短可分为短间歇高强度间歇运动和长间歇高强度间歇运动。
气体代谢:是指机体消耗氧和产生二氧化碳的过程。组织细胞在生命活动过程中需要不断获取能量,其来源是体内营养物质(蛋白质、糖类和脂肪)的氧化。为维持体内正常的氧化过程,需经常供给氧和排出二氧化碳。测定单位时间内氧耗量和二氧化碳产生量可计算出能量代谢率。