中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (23): 3722-3728.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1229
• 组织构建临床实践 clinical practice in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
随机森林模型分析大学生体质健康影响因素:来源于同济大学568名学生的问卷调查
冯 敏1,冯 辉1,张一雨2,王乐军1
- (1同济大学体育教学部,上海市 200092;2同济大学航空航天与力学学院,上海市 200092)
Factors influencing physical health of college students analyzed by random forest model: questionnaires of 568 students from Tongji University
Feng Min1, Feng Hui1, Zhang Yiyu2, Wang Lejun1
- (1Physical Education Department, 2School of Aerospace Engineering and Applied Mechanics, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
随机森林模型:随机森林模型是一个包含多个决策树的分类器,并且其输出的类别是由个别树输出的类别的众数而定。通过自助法重采样技术,不断生成训练样本和测试样本,由训练样本生成多个分类树组成的随机森林,测试数据的分类结果按分类树投票多少形成的分数而定。主要思想是bagging并行算法,用很多弱模型组合出一种强模型。该模型优点在于:①很多的数据集上表现良好;②能处理高维度数据,并且不用做特征选择;③训练完后,能够给出那些feature比较重要;④训练速度快,容易并行化计算。
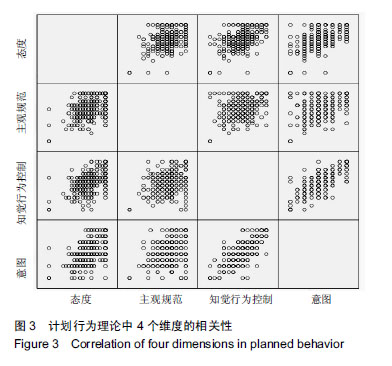
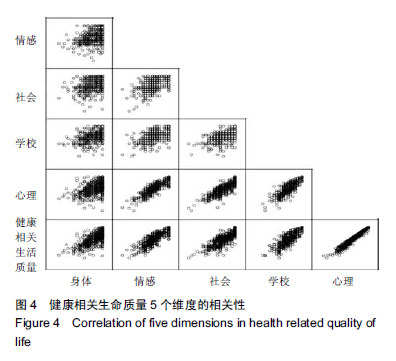
皮尔森相关系数(Pearson correlation coefficient):也称皮尔森积矩相关系数(Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient),是一种线性相关系数。皮尔森相关系数是用来反映两个变量线性相关程度的统计量。相关系数用r表示,其中n为样本量,分别为两个变量的观测值和均值。r描述的是两个变量间线性相关强弱的程度。r的绝对值越大表明相关性越强。
文题释义:
随机森林模型:随机森林模型是一个包含多个决策树的分类器,并且其输出的类别是由个别树输出的类别的众数而定。通过自助法重采样技术,不断生成训练样本和测试样本,由训练样本生成多个分类树组成的随机森林,测试数据的分类结果按分类树投票多少形成的分数而定。主要思想是bagging并行算法,用很多弱模型组合出一种强模型。该模型优点在于:①很多的数据集上表现良好;②能处理高维度数据,并且不用做特征选择;③训练完后,能够给出那些feature比较重要;④训练速度快,容易并行化计算。
皮尔森相关系数(Pearson correlation coefficient):也称皮尔森积矩相关系数(Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient),是一种线性相关系数。皮尔森相关系数是用来反映两个变量线性相关程度的统计量。相关系数用r表示,其中n为样本量,分别为两个变量的观测值和均值。r描述的是两个变量间线性相关强弱的程度。r的绝对值越大表明相关性越强。
.jpg) 文题释义:
随机森林模型:随机森林模型是一个包含多个决策树的分类器,并且其输出的类别是由个别树输出的类别的众数而定。通过自助法重采样技术,不断生成训练样本和测试样本,由训练样本生成多个分类树组成的随机森林,测试数据的分类结果按分类树投票多少形成的分数而定。主要思想是bagging并行算法,用很多弱模型组合出一种强模型。该模型优点在于:①很多的数据集上表现良好;②能处理高维度数据,并且不用做特征选择;③训练完后,能够给出那些feature比较重要;④训练速度快,容易并行化计算。
皮尔森相关系数(Pearson correlation coefficient):也称皮尔森积矩相关系数(Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient),是一种线性相关系数。皮尔森相关系数是用来反映两个变量线性相关程度的统计量。相关系数用r表示,其中n为样本量,分别为两个变量的观测值和均值。r描述的是两个变量间线性相关强弱的程度。r的绝对值越大表明相关性越强。
文题释义:
随机森林模型:随机森林模型是一个包含多个决策树的分类器,并且其输出的类别是由个别树输出的类别的众数而定。通过自助法重采样技术,不断生成训练样本和测试样本,由训练样本生成多个分类树组成的随机森林,测试数据的分类结果按分类树投票多少形成的分数而定。主要思想是bagging并行算法,用很多弱模型组合出一种强模型。该模型优点在于:①很多的数据集上表现良好;②能处理高维度数据,并且不用做特征选择;③训练完后,能够给出那些feature比较重要;④训练速度快,容易并行化计算。
皮尔森相关系数(Pearson correlation coefficient):也称皮尔森积矩相关系数(Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient),是一种线性相关系数。皮尔森相关系数是用来反映两个变量线性相关程度的统计量。相关系数用r表示,其中n为样本量,分别为两个变量的观测值和均值。r描述的是两个变量间线性相关强弱的程度。r的绝对值越大表明相关性越强。摘要
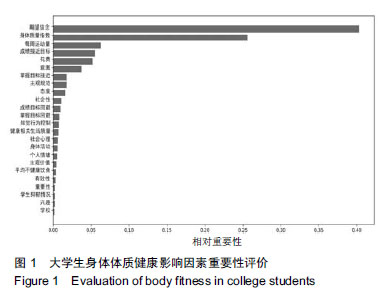
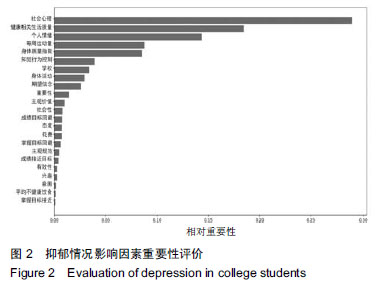
背景:由于影响大学生体质因素复杂多样,且各影响因素之间有直接或间接相关作用,许多隐性因素常被忽略。大部分影响因素的研究分析往往是对影响因素做了“归纳”,较少对于不同维度影响因素的“影响力”进行分析。
目的:运用随机森林模型分析大学生体质健康影响因素。
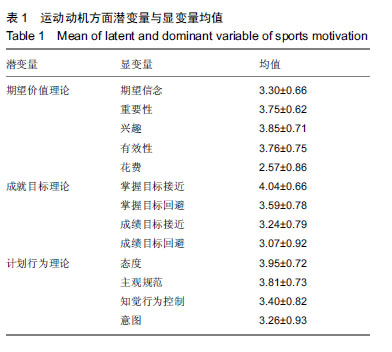
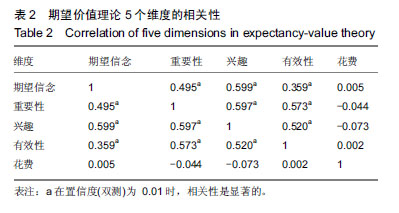
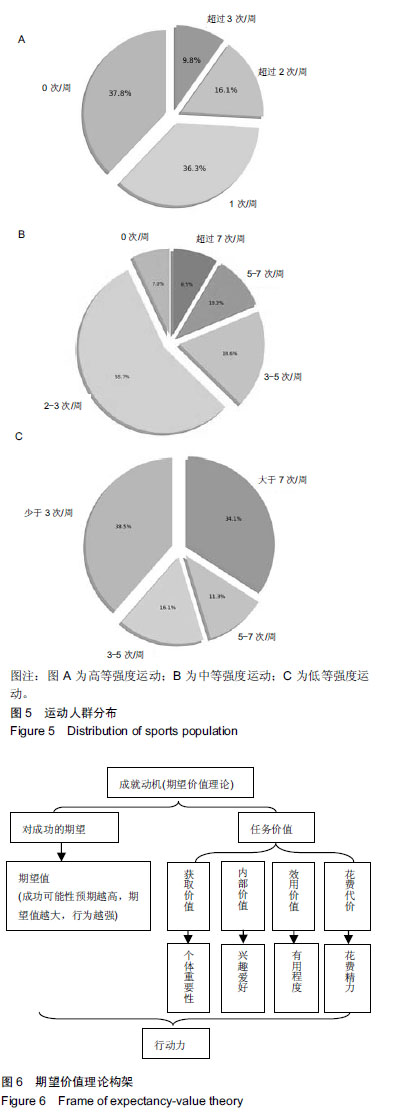
方法:对同济大学568名大学生进行问卷调查,包括godin的休闲运动锻炼问卷/量表、期望价值理论量表、2X2 成就目标理论量表、计划行为理论量表、健康相关的生活质量量表、久坐的工作日量表、CES-D 抑郁量表、皮茨伯格睡眠质量量表、饮食方面(自编)。结合体质健康测试,包括身高、体质量、肺活量、坐位体前屈、1 min仰卧起坐(女)、引体向上(男)、立定跳远、50 m、800 m(女)、1 000 m(男)指标。建立随机森林模型对影响因素进行降维,再用皮尔森相关分析对降维后的变量进行相关性分析,找到重要影响因素及重要影响因素之间的相互作用。
结果与结论:①由随机森林模型发现在影响身体体质健康因素中,运动动机方面影响力最大,尤其是内在动机方面;②对心理健康方面影响最为突出的是健康相关生活质量方面的社会心理因素;③每周运动量直接影响大学生身体和心理两方面健康;④相关性分析中发现花费精力因素(被包括在期望价值理论中)常被忽略,行为意图的清晰程度直接影响知觉行为控制;⑤结果说明,运动动机对大学生身体体质健康影响程度最大,尤其是内在动机影响更深远。需加强花费影响因素的实证研究;大学生抑郁倾向比例越来越高,在关于大学生体质健康方面研究中不可忽略心理干预,可从健康相关生活质量和每周运动量两方面进行干预。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
随机森林模型:随机森林模型是一个包含多个决策树的分类器,并且其输出的类别是由个别树输出的类别的众数而定。通过自助法重采样技术,不断生成训练样本和测试样本,由训练样本生成多个分类树组成的随机森林,测试数据的分类结果按分类树投票多少形成的分数而定。主要思想是bagging并行算法,用很多弱模型组合出一种强模型。该模型优点在于:①很多的数据集上表现良好;②能处理高维度数据,并且不用做特征选择;③训练完后,能够给出那些feature比较重要;④训练速度快,容易并行化计算。
皮尔森相关系数(Pearson correlation coefficient):也称皮尔森积矩相关系数(Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient),是一种线性相关系数。皮尔森相关系数是用来反映两个变量线性相关程度的统计量。相关系数用r表示,其中n为样本量,分别为两个变量的观测值和均值。r描述的是两个变量间线性相关强弱的程度。r的绝对值越大表明相关性越强。
文题释义:
随机森林模型:随机森林模型是一个包含多个决策树的分类器,并且其输出的类别是由个别树输出的类别的众数而定。通过自助法重采样技术,不断生成训练样本和测试样本,由训练样本生成多个分类树组成的随机森林,测试数据的分类结果按分类树投票多少形成的分数而定。主要思想是bagging并行算法,用很多弱模型组合出一种强模型。该模型优点在于:①很多的数据集上表现良好;②能处理高维度数据,并且不用做特征选择;③训练完后,能够给出那些feature比较重要;④训练速度快,容易并行化计算。
皮尔森相关系数(Pearson correlation coefficient):也称皮尔森积矩相关系数(Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient),是一种线性相关系数。皮尔森相关系数是用来反映两个变量线性相关程度的统计量。相关系数用r表示,其中n为样本量,分别为两个变量的观测值和均值。r描述的是两个变量间线性相关强弱的程度。r的绝对值越大表明相关性越强。