[2] Psaltis PJ, Harbuzariu A, Delacroix S, et al. Resident vascular progenitor cells--diverse origins, phenotype, and function. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2011;4(2): 161-176.
[3] 吴景文,章翔,胡祥. 干细胞临床研究现状与展望[J]. 中华神经外科疾病研究杂志, 2012, 11(3): 193-196.
[4] Patel J, Seppanen E, Chong MS, et al. Prospective surface marker-based isolation and expansion of fetal endothelial colony-forming cells from human term placenta. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013;2(11): 839-847.
[5] Gao X, Chen W, Liang Z, et al. Autotransplantation of circulating endothelial progenitor cells protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rabbit. Int Immunopharmacol. 2011;11(10): 1584-1590.
[6] Chen X, Yin J, Wu X, et al. Effects of magnetically labeled exogenous endothelial progenitor cells on cerebral blood perfusion and microvasculature alterations after traumatic brain injury in rat model. Acta Radiol. 2013;54(3):313-323.
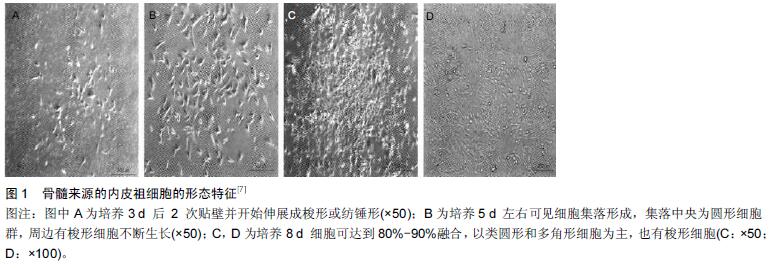
[7] 辛毅,刘小希,赵伟,等.差速贴壁法分离兔骨髓源性间充质干细胞和内皮祖细胞及其生物学特性的研究[J].中国实验血液学杂志, 2013, 21(3): 746-753.
[8] Medina RJ, O'Neill CL, O'Doherty TM, et al. Ex vivo expansion of human outgrowth endothelial cells leads to IL-8-mediated replicative senescence and impaired vasoreparative function. Stem Cells. 2013; 31(8):1657-1668.
[9] Morancho A, Hernández-Guillamon M, Boada C, et al. Cerebral ischaemia and matrix metalloproteinase-9 modulate the angiogenic function of early and late outgrowth endothelial progenitor cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2013c;17(12): 1543-1553.
[10] Kanzler I, Tuchscheerer N, Steffens G, et al. Differential roles of angiogenic chemokines in endothelial progenitor cell-induced angiogenesis. Basic Res Cardiol. 2013108(1):310.
[11] Takahashi M, Matsuoka Y, Sumide K, et al. CD133 is a positive marker for a distinct class of primitive human cord blood-derived CD34-negative hematopoietic stem cells. Leukemia. 2014;28(6):1308-1315.
[12] Wang K, Xu J, Zhang J, et al. Prognostic role of CD133 expression in colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 2012;12:573.
[13] Cheng RB, Ma RJ, Wang ZK, et al. PTEN status is related to cell proliferation and self-renewal independent of CD133 phenotype in the glioma-initiating cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011;349 (1-2):149-157.
[14] Aomatsu N, Yashiro M, Kashiwagi S, et al. CD133 is a useful surrogate marker for predicting chemosensitivity to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45865.
[15] Tanaskovic S, Fernandez S, Price P, et al. CD31 (PECAM-1) is a marker of recent thymic emigrants among CD4+ T-cells, but not CD8+ T-cells or gammadelta T-cells, in HIV patients responding to ART. Immunol Cell Biol. 2010;88(3):321-327.
[16] Goldman O, Han S, Sourisseau M, et al. KDR identifies a conserved human and murine hepatic progenitor and instructs early liver development. Cell Stem Cell. 2013;12(6):748-760.
[17] Fu SL, Pang H, Xu JZ, et al. C/EBPβ mediates osteoclast recruitment by regulating endothelial progenitor cell expression of SDF-1α. PLoS One. 2014; 9(3):e91217.
[18] Cheng CC, Chang SJ, Chueh YN, et al. Distinct angiogenesis roles and surface markers of early and late endothelial progenitor cells revealed by functional group analyses. BMC Genomics. 2013;14:182.
[19] Hur J, Yoon CH, Kim HS, et al. Characterization of two types of endothelial progenitor cells and their different contributions to neovasculogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24(2):288-293.
[20] Li ZF, Fang XG, Yang PF, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells contribute to neointima formation in rabbit elastase-induced aneurysm after flow diverter treatment. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2013;19(5):352-357.
[21] Zhang XY, Su C, Cao Z, et al. CXCR7 upregulation is required for early endothelial progenitor cell-mediated endothelial repair in patients with hypertension. Hypertension. 2014;63(2):383-389.
[22] Suzuki R, Fukuda N, Katakawa M, et al. Effects of an angiotensin II receptor blocker on the impaired function of endothelial progenitor cells in patients with essential hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2014; 27(5):695-701.
[23] Georgescu A, Alexandru N, Andrei E, et al. Circulating microparticles and endothelial progenitor cells in atherosclerosis: pharmacological effects of irbesartan. J Thromb Haemost. 2012;10(4):680-691.
[24] Li Y, Alatan G, Ge Z, et al. Effects of benazepril on functional activity of endothelial progenitor cells from hypertension patients. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2014;36(8): 545-549.
[25] Raptis AE, Markakis KP, Mazioti MC, et al. Effect of aliskiren on circulating endothelial progenitor cells and vascular function in patients with type 2 diabetes and essential hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2015; 28(1):22-29.
[26] Liu HF, Qi XW, Ma LL, et al. Atorvastatin improves endothelial progenitor cell function and reduces pulmonary hypertension in patients with chronic pulmonary heart disease. Exp Clin Cardiol. 2013; 18(1):e40-43.
[27] Chen J, Xiao X, Chen S, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 priming enhances the function of endothelial progenitor cells and their therapeutic efficacy. Hypertension. 2013;61(3):681-689.
[28] Liu X, Zhang GX, Zhang XY, et al. Lacidipine improves endothelial repair capacity of endothelial progenitor cells from patients with essential hypertension. Int J Cardiol. 2013;168(4):3317-3326.
[29] Xia WH, Li J, Su C, et al. Physical exercise attenuates age-associated reduction in endothelium-reparative capacity of endothelial progenitor cells by increasing CXCR4/JAK-2 signaling in healthy men. Aging Cell. 2012;11(1): 111-119.
[30] Xie HH, Zhou S, Chen DD, et al. GTP cyclohydrolase I/BH4 pathway protects EPCs via suppressing oxidative stress and thrombospondin-1 in salt-sensitive hypertension. Hypertension. 2010; 56(6):1137-1144.
[31] Chen DD, Dong YG, Yuan H, et al. Endothelin 1 activation of endothelin A receptor/NADPH oxidase pathway and diminished antioxidants critically contribute to endothelial progenitor cell reduction and dysfunction in salt-sensitive hypertension. Hypertension. 2012;59(5):1037-1043.
[32] Peng J, Liu B, Ma QL, et al. Dysfunctional endothelial progenitor cells in cardiovascular diseases: role of NADPH oxidase. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2015; 65(1):80-87.
[33] Yang Z, Xia WH, Zhang YY, et al. Shear stress-induced activation of Tie2-dependent signaling pathway enhances reendothelialization capacity of early endothelial progenitor cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012;52(5):1155-1163.
[34] Beijk MA, Klomp M, van Geloven N, et al. Two-year follow-up of the Genous™ endothelial progenitor cell capturing stent versus the Taxus Liberté stent in patients with de novo coronary artery lesions with a high-risk of restenosis: a randomized, single-center, pilot study. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2011;78(2): 189-195.
[35] Povsic TJ, Junge C, Nada A, et al. A phase 3, randomized, double-blinded, active-controlled, unblinded standard of care study assessing the efficacy and safety of intramyocardial autologous CD34+ cell administration in patients with refractory angina: design of the RENEW study. Am Heart J. 2013;165(6):854-861.
[36] Losordo DW, Kibbe MR, Mendelsohn F, et al. A randomized, controlled pilot study of autologous CD34+ cell therapy for critical limb ischemia. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2012;5(6):821-830.
[37] Shuai L, Li X, He Q, et al. Angiogenic effect of endothelial progenitor cells transfected with telomerase reverse transcriptase on peritubular microvessel in five out of six subtotal nephrectomy rats. Ren Fail. 2012;34(10):1270-1280.
[38] Cui B, Huang L, Fang Y, et al. Transplantation of endothelial progenitor cells overexpressing endothelial nitric oxide synthase enhances inhibition of neointimal hyperplasia and restores endothelium-dependent vasodilatation. Microvasc Res. 2011;81(1):143-150.
[39] Fu SS, Li FJ, Wang YY, et al. Kallikrein gene-modified EPCs induce angiogenesis in rats with ischemic hindlimb and correlate with integrin αvβ3 expression. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e73035.
[40] Yao Y, Sheng Z, Li Y, et al. Tissue kallikrein-modified human endothelial progenitor cell implantation improves cardiac function via enhanced activation of akt and increased angiogenesis. Lab Invest. 2013; 93(5):577-591.
[41] Deshane J, Chen S, Caballero S, et al. Stromal cell-derived factor 1 promotes angiogenesis via a heme oxygenase 1-dependent mechanism. J Exp Med. 2007;204(3):605-618.
[42] Brunt KR, Wu J, Chen Z, et al. Ex vivo Akt/HO-1 gene therapy to human endothelial progenitor cells enhances myocardial infarction recovery. Cell Transplant. 2012;21(7):1443-1461.
[43] Yoshida Y, Fukuda N, Maeshima A, et al. Treatment with valsartan stimulates endothelial progenitor cells and renal label-retaining cells in hypertensive rats. J Hypertens. 2011;29(1):91-101.
[44] Pelliccia F, Pasceri V, Cianfrocca C, et al. Angiotensin II receptor antagonism with telmisartan increases number of endothelial progenitor cells in normotensive patients with coronary artery disease: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Atherosclerosis. 2010;210(2):510-515.
[45] Cacciatore F, Bruzzese G, Vitale DF, et al. Effects of ACE inhibition on circulating endothelial progenitor cells, vascular damage, and oxidative stress in hypertensive patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2011; 67(9):877-883.
[46] de Ciuceis C, Pilu A, Rizzoni D, et al. Effect of antihypertensive treatment on circulating endothelial progenitor cells in patients with mild essential hypertension. Blood Press. 2011;20(2):77-83.
[47] Fernandes T, Nakamuta JS, Magalhães FC, et al. Exercise training restores the endothelial progenitor cells number and function in hypertension: implications for angiogenesis. J Hypertens. 2012;30(11):2133- 2143.
[48] Yang Z, Xia WH, Su C, et al. Regular exercise-induced increased number and activity of circulating endothelial progenitor cells attenuates age-related decline in arterial elasticity in healthy men. Int J Cardiol. 2013; 165(2):247-254.
[49] Lavoie JR, Stewart DJ. Genetically modified endothelial progenitor cells in the therapy of cardiovascular disease and pulmonary hypertension. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2012;10(3):289-299.
.jpg)
.jpg)