| [1] Nagata S. Modification of the stages in total reconstruction of the auricle: Part Ⅰ. Grafting the three dimensional costal cartilage framework for lobule type microtia.Plast Reconstr Surg. 1994;93(2): 221-230.[2] Nagata S. Modification of the stages in total reconstruction of the auricle: Part Ⅱ. Grafting the three dimensional costal cartilage framework for concha type microtia. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1994;93(2): 231-242.[3] Nagata S. Modification of the stages in total reconstruction of the auricle: Part Ⅲ. Grafting the three dimensional costal cartilage framework for small concha-type microtia. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1994;93(2): 243-253.[4] Han H, Wang H, Zhou L, et al. One-stage reconstruction of two atypical small concha-type microtic ears. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2014;78(4):693-696.[5] Wellisz T. Reconstruction of the burned external ear using a Medpor porous polyethylene pivoting helix framework. Plast Reconstr Surg.1993;91(5): 811-818.[6] Baluch N, Nagata S, Park C, et al. Auricular reconstruction for microtia: A review of available methods. Plast Surg (Oakv) 2014;22(1): 39-43.[7] Gandy JR, Lemieux B, Foulad A, et al. Conserving Cartilage In Microtia Repair: The Modular Component Assembly Approach To Rebuilding A Human Ear. JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2016;18(2): 120-127.[8] Anghinoni M, Bailleul C, Magri AS. Auricular reconstruction of congenital microtia: personal experience in 225 cases. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2015;35(3): 191-197.[9] Peiró Ibánez JL, García-Vaquero JA, Acosta Farina D, et al. Auricular alloplastic reconstruction with osteointegrated implants: a new therapy option in microtia. Cir Pediatr. 2000;13(1): 25-29.[10] Mevio E, Facca L, Mullace M, et al. Osseointegrated implants in patients with auricular defects: a case series study. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2015;35(3):186-190.[11] Lovely M, Dathan PC, Gopal D, et al. Implant Retained Auricular Prosthesis with a Modified Hader Bar: A Case Report. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2014;14(2): 187-190.[12] Guttal SS, Shanbhag S, Kulkarni SS, et al. Rehabilitation of a missing ear with an implant retained auricular prosthesis. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2015;15(1): 70-75.[13] Cao Y, Vacanti JP, Paige KT, et al. Transplantation of chondrocytes utilizing a polymercell construct to produce tissue-engineered cartilage in the shape of a human ear. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997;100(2):297-302. [14] Vacanti CA, Cima LG, Ratkowski D, et al. Tissue engineered growth of new cartilage in the shape of a human ear using synthetic polymers seeded with chondrocytes. Mater Res Soc Symp Proc. 1992;252:367-374.[15] Kasir R, Vernekar VN, Laurencin CT, et al. Regenerative Engineering of Cartilage Using Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Regen Eng Transl Med. 2015;1(1): 42-49. [16] Green JD, Tollemar V, Dougherty M, et al. Multifaceted signaling regulators of chondrogenesis: Implications in cartilage regeneration and tissue engineering. Genes Dis. 2015;2(4): 307-327. [17] Stubbs AJ, Howse EA, Mannava S. Tissue engineering and the future of hip cartilage, labrum and ligamentum teres. J Hip Preserv Surg. 2016;3(1): 23-29. [18] Phull AR, Eo SH, Abbas Q, et al. Applications of Chondrocyte-Based Cartilage Engineering: An Overview. Biomed Res Int. 2016; 2016: 1879837.[19] Steele J, McCullen S, Callanan A, et al. Combinatorial scaffold morphologies for zonal articular cartilage engineering. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(5): 2065-2075. [20] Okano T, Yamada N, Sakai H, et al. A novel recovery system for cultured cells using plasma-treated polystyrene dishes grafted with poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). J Biomed Mater Res. 1993;27(10):1243-1251.[21] Sawa Y, Cherian KM, Mohanty S, et al. An invention of thermo-responsive polymer surface, yielding cell sheet based regenerative therapies in cardiology and ophthalmology. J Stem Cells Regen Med. 2015;11(2): 51-53.[22] Du C, Yao C, Li N, et al. Cell sheet-engineered bones used for the reconstruction of mandibular defects in an animal model. Exp Ther Med. 2015;10(6): 2216-2220.[23] Chen G, Qi Y, Niu L, et al. Application of the cell sheet technique in tissue engineering. Biomed Rep. 2015;3(6): 749–757.[24] Zhou L, Ding R, Li B, et al. Cartilage engineering using chondrocyte cell sheets and its application in reconstruction of microtia. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015; 8(1): 73-80.[25] Lima LH, Morales Y, Cabral T. Ocular Biocompatibility of Poly-N-Isopropylacrylamide (pNIPAM). J Ophthalmol. 2016; 2016: 5356371.[26] Bichara DA, O'Sullivan NA, Pomerantseva I, et al. The tissue-engineered auricle: past, present, and future. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2012;18(1):51-61.[27] Chen CH, Kuo CY, Wang YJ, et al. Dual Function of Glucosamine in Gelatin/Hyaluronic Acid Cryogel to Modulate Scaffold Mechanical Properties and to Maintain Chondrogenic Phenotype for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(11): 1957.[28] Wang S, Xia J, Chen J, et al. Influence of biological scaffold regulation on the proliferation of chondrocytes and the repair of articular cartilage. Am J Transl Res. 2016; 8(11): 4564-4573.[29] Calabrese G, Giuffrida R, Forte S, et al. Bone augmentation after ectopic implantation of a cell-free collagen-hydroxyapatite scaffold in the mouse. Sci Rep. 2016; 6: 36399.[30] Dan Y, Liu O, Liu Y, et al. Development of Novel Biocomposite Scaffold of Chitosan-Gelatin/Nanohydroxyapatite for Potential Bone Tissue Engineering Applications. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2016; 11: 487.[31] Syed-Picard FN, Du Y, Hertsenberg AJ, et al. Scaffold-free tissue engineering of functional corneal stromal tissue. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016. doi: 10.1002/term.2363. [Epub ahead of print][32] Neo PY, Teh TK, Tay AS, et al. Stem cell-derived cell-sheets for connective tissue engineering. Connect Tissue Res. 2016; 57(6):428-442.[33] Shimizu T, Yamato M, Kikuchi A, et al. Cell sheet engineering for myocardial tissue reconstruction. Biomaterials. 2003;24 (13): 2309-2316.[34] Vacanti CA, Vacanti JP. Bone and cartilage reconstruction with tissue engineering approaches. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1994;27(1):263-276.[35] Langer R, Vacanti JP. Tissue engineering. Science. 1993; 260(5110):920-926.[36] Hubbell JA. Biomaterials in tissue engineering. Biotechnology (N Y). 1995;13(6):565-576.[37] Kanai N, Yamato M, Okano T. Cell sheets engineering for esophageal regenerative medicine. Ann Transl Med. 2014; 2(3):28.[38] Matsuura K, Utoh R, Nagase K, et al. Cell sheet approach for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. J Control Release. 2014;190:228-239.[39] Shimizu T. Cell sheet-based tissue engineering for fabricating 3-dimensional heart tissues. Circ J. 2014;78(11):2594-2603.[40] Sato M. Articular cartilage therapy using cell sheet. Clin Calcium. 2013;23(12):1751-1757. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
细胞膜片:细胞膜片技术是通过物理的方法将扩增融合的细胞从培养皿底壁分离,获得膜片状细胞结构的一种技术。与传统胰酶消化收集细胞的方法相比,运用该技术收集到的细胞保留了体外培养过程中分泌的胞外基质、建立的细胞-基质连接以及细胞间连接等结构。
组织工程:从机体获取少量的活体组织细胞,在体外进行培养扩增,然后将扩增的细胞与具有良好生物相容性、可降解性和可吸收的生物材料(支架)按一定的比例混合,使细胞黏附在生物材料(支架)上形成细胞-材料复合物;将该复合物植入机体的组织或器官病损部位,随着生物材料在体内逐渐被降解和吸收,植入的细胞在体内不断增殖并分泌细胞外基质,最终形成相应的组织或器官,从而达到修复创伤和重建功能的目的。
文题释义:
细胞膜片:细胞膜片技术是通过物理的方法将扩增融合的细胞从培养皿底壁分离,获得膜片状细胞结构的一种技术。与传统胰酶消化收集细胞的方法相比,运用该技术收集到的细胞保留了体外培养过程中分泌的胞外基质、建立的细胞-基质连接以及细胞间连接等结构。
组织工程:从机体获取少量的活体组织细胞,在体外进行培养扩增,然后将扩增的细胞与具有良好生物相容性、可降解性和可吸收的生物材料(支架)按一定的比例混合,使细胞黏附在生物材料(支架)上形成细胞-材料复合物;将该复合物植入机体的组织或器官病损部位,随着生物材料在体内逐渐被降解和吸收,植入的细胞在体内不断增殖并分泌细胞外基质,最终形成相应的组织或器官,从而达到修复创伤和重建功能的目的。.jpg) 文题释义:
细胞膜片:细胞膜片技术是通过物理的方法将扩增融合的细胞从培养皿底壁分离,获得膜片状细胞结构的一种技术。与传统胰酶消化收集细胞的方法相比,运用该技术收集到的细胞保留了体外培养过程中分泌的胞外基质、建立的细胞-基质连接以及细胞间连接等结构。
组织工程:从机体获取少量的活体组织细胞,在体外进行培养扩增,然后将扩增的细胞与具有良好生物相容性、可降解性和可吸收的生物材料(支架)按一定的比例混合,使细胞黏附在生物材料(支架)上形成细胞-材料复合物;将该复合物植入机体的组织或器官病损部位,随着生物材料在体内逐渐被降解和吸收,植入的细胞在体内不断增殖并分泌细胞外基质,最终形成相应的组织或器官,从而达到修复创伤和重建功能的目的。
文题释义:
细胞膜片:细胞膜片技术是通过物理的方法将扩增融合的细胞从培养皿底壁分离,获得膜片状细胞结构的一种技术。与传统胰酶消化收集细胞的方法相比,运用该技术收集到的细胞保留了体外培养过程中分泌的胞外基质、建立的细胞-基质连接以及细胞间连接等结构。
组织工程:从机体获取少量的活体组织细胞,在体外进行培养扩增,然后将扩增的细胞与具有良好生物相容性、可降解性和可吸收的生物材料(支架)按一定的比例混合,使细胞黏附在生物材料(支架)上形成细胞-材料复合物;将该复合物植入机体的组织或器官病损部位,随着生物材料在体内逐渐被降解和吸收,植入的细胞在体内不断增殖并分泌细胞外基质,最终形成相应的组织或器官,从而达到修复创伤和重建功能的目的。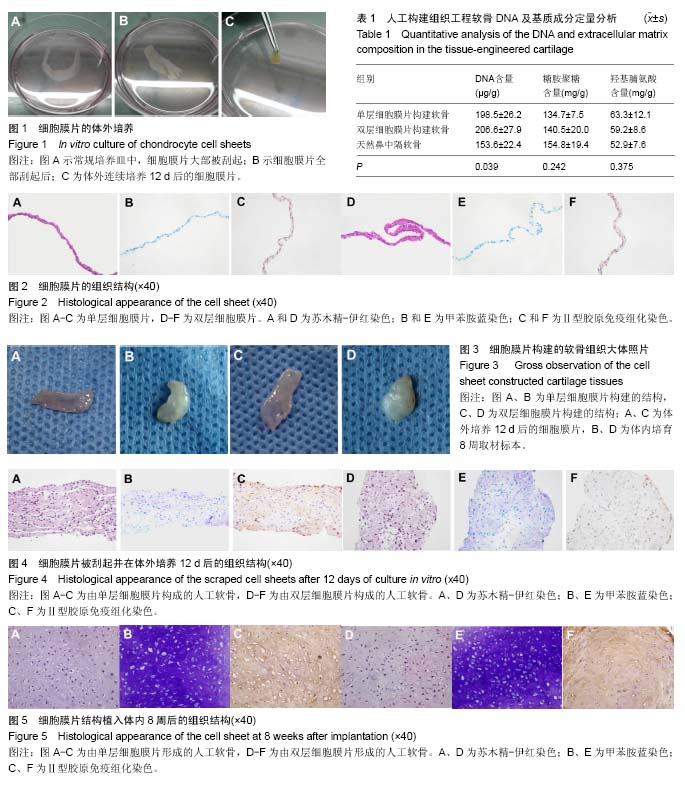
.jpg) 文题释义:
细胞膜片:细胞膜片技术是通过物理的方法将扩增融合的细胞从培养皿底壁分离,获得膜片状细胞结构的一种技术。与传统胰酶消化收集细胞的方法相比,运用该技术收集到的细胞保留了体外培养过程中分泌的胞外基质、建立的细胞-基质连接以及细胞间连接等结构。
组织工程:从机体获取少量的活体组织细胞,在体外进行培养扩增,然后将扩增的细胞与具有良好生物相容性、可降解性和可吸收的生物材料(支架)按一定的比例混合,使细胞黏附在生物材料(支架)上形成细胞-材料复合物;将该复合物植入机体的组织或器官病损部位,随着生物材料在体内逐渐被降解和吸收,植入的细胞在体内不断增殖并分泌细胞外基质,最终形成相应的组织或器官,从而达到修复创伤和重建功能的目的。
文题释义:
细胞膜片:细胞膜片技术是通过物理的方法将扩增融合的细胞从培养皿底壁分离,获得膜片状细胞结构的一种技术。与传统胰酶消化收集细胞的方法相比,运用该技术收集到的细胞保留了体外培养过程中分泌的胞外基质、建立的细胞-基质连接以及细胞间连接等结构。
组织工程:从机体获取少量的活体组织细胞,在体外进行培养扩增,然后将扩增的细胞与具有良好生物相容性、可降解性和可吸收的生物材料(支架)按一定的比例混合,使细胞黏附在生物材料(支架)上形成细胞-材料复合物;将该复合物植入机体的组织或器官病损部位,随着生物材料在体内逐渐被降解和吸收,植入的细胞在体内不断增殖并分泌细胞外基质,最终形成相应的组织或器官,从而达到修复创伤和重建功能的目的。