中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (42): 6308-6316.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.42.012
• 神经组织构建 nerve tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
TOLL样受体4拮抗剂干预周围神经损伤后的瓦勒变性
熊 乐1,张 蓓1,沈若武2,季爱玉3,孙广强1,边洪琳3,张凤玉1,王 毅1,黄 恒4,李华侨1,周善宇5,沈兆康6,王 忠1
- 青岛大学医学院,1免疫学教研室,2解剖教研室,山东省青岛市 266071;3青岛大学附属医院创伤外科,山东省青岛市 266003;4解放军第401医院手外科,山东省青岛市 266072;5青岛大学医学院整形外科,山东省青岛市 266071;6青岛市第五十八中学,山东省青岛市 266100
Toll-like receptor 4 antagonist protects against Wallerian degeneration after peripheral nerve injury
Xiong Le1, Zhang Bei1, Shen Ruo-wu2, Ji Ai-yu3, Sun Guang-qiang1, Bian Hong-lin3, Zhang Feng-yu1, Wang Yi1, Huang Heng4, Li Hua-qiao1, Zhou Shan-yu5, Shen Zhao-kang6, Wang Zhong1
- 1Department of Immunology, 2Department of Anatomy, 5Department of Plastic Surgery, Qingdao University Medical School, Qingdao 266071, Shandong Province, China; 3Department of Traumatic Surgery, the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266003, Shandong Province, China; 4Department of Hand Surgery, the 401st Hospital of Chinese PLA, Qingdao 266072, Shandong Province, China; 6No. 58 High School of Qingdao, Qingdao 266100, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
TOLL样受体4(TLR4):人类发现的第1个TOLL样受体相关蛋白,由TOLL样受体4基因编码的一种蛋白质,参与激活固有免疫。它可以识别许多革兰阴性细菌的脂多糖(LPS),也可以选择性识别革兰阳性菌,它的配体也包括一些病毒蛋白、多糖及多种内源性蛋白质(如低密度脂蛋白,热休克蛋白等)。
瓦勒变性:即由于各种创伤、牵拉、缺血、高低温、电击等原因,直接使神经纤维受损中断,周围神经损伤后远段发生的轴突坏死、髓鞘分解消失和神经鞘膜增生等一系列蜕变和细胞吞噬过程。
文题释义:
TOLL样受体4(TLR4):人类发现的第1个TOLL样受体相关蛋白,由TOLL样受体4基因编码的一种蛋白质,参与激活固有免疫。它可以识别许多革兰阴性细菌的脂多糖(LPS),也可以选择性识别革兰阳性菌,它的配体也包括一些病毒蛋白、多糖及多种内源性蛋白质(如低密度脂蛋白,热休克蛋白等)。
瓦勒变性:即由于各种创伤、牵拉、缺血、高低温、电击等原因,直接使神经纤维受损中断,周围神经损伤后远段发生的轴突坏死、髓鞘分解消失和神经鞘膜增生等一系列蜕变和细胞吞噬过程。
.jpg) 文题释义:
TOLL样受体4(TLR4):人类发现的第1个TOLL样受体相关蛋白,由TOLL样受体4基因编码的一种蛋白质,参与激活固有免疫。它可以识别许多革兰阴性细菌的脂多糖(LPS),也可以选择性识别革兰阳性菌,它的配体也包括一些病毒蛋白、多糖及多种内源性蛋白质(如低密度脂蛋白,热休克蛋白等)。
瓦勒变性:即由于各种创伤、牵拉、缺血、高低温、电击等原因,直接使神经纤维受损中断,周围神经损伤后远段发生的轴突坏死、髓鞘分解消失和神经鞘膜增生等一系列蜕变和细胞吞噬过程。
文题释义:
TOLL样受体4(TLR4):人类发现的第1个TOLL样受体相关蛋白,由TOLL样受体4基因编码的一种蛋白质,参与激活固有免疫。它可以识别许多革兰阴性细菌的脂多糖(LPS),也可以选择性识别革兰阳性菌,它的配体也包括一些病毒蛋白、多糖及多种内源性蛋白质(如低密度脂蛋白,热休克蛋白等)。
瓦勒变性:即由于各种创伤、牵拉、缺血、高低温、电击等原因,直接使神经纤维受损中断,周围神经损伤后远段发生的轴突坏死、髓鞘分解消失和神经鞘膜增生等一系列蜕变和细胞吞噬过程。摘要
背景:外周神经损伤后发生瓦勒变性,其机制复杂,从免疫学角度对其进行调控可以影响神经早期修复效果。
目的:分析特异性拮抗Toll样受体4(TLR4)对于大鼠坐骨神经损伤早期瓦勒变性及轴突再生的影响。
方法:将50只Wistar大鼠随机分成3组:处理组及模型组横断大鼠右侧坐骨神经后,行神经外膜端端吻合;假手术组仅游离出坐骨神经,然后关闭切口。术前1 h及术后7 d处理组大鼠每天尾静脉注射0.15 mg/kg Toll样受体4拮抗剂TAK-242,模型组及假手术组大鼠尾静脉注射同等体积生理盐水。于术后24 h、3 d、4 d和7d取术侧坐骨神经。
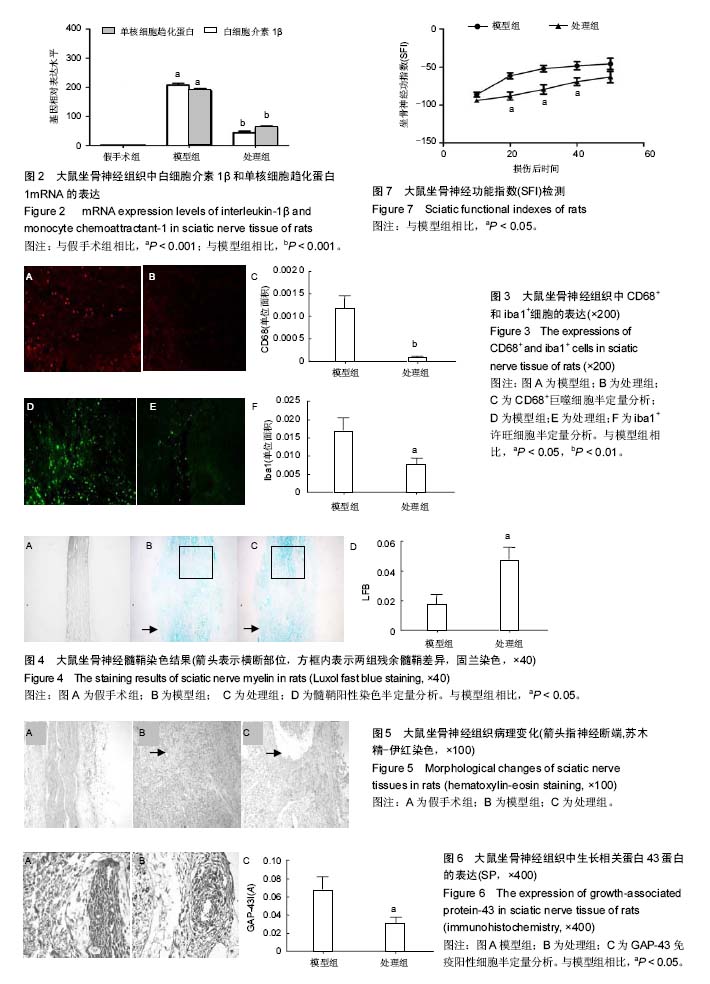
结果与结论:①实时定量PCR显示,与假手术组相比,术后24 h模型组白细胞介素1β mRNA和单核细胞趋化蛋白1 mRNA的表达均明显升高(P < 0.001,P < 0.001),与模型组相比,术后24 h处理组白细胞介素1β mRNA和单核细胞趋化蛋白1 mRNA的表达明显降低(P < 0. 001,P < 0. 001);②免疫荧光可见,与模型组相比,术后3 d处理组中CD68+细胞和iba1+细胞表达均显著下调(P < 0. 01,P < 0.05);③固兰染色可见,在术后7 d,模型组和处理组坐骨神经断端均出现脱髓鞘反应,但与模型组相比,处理组神经断端髓鞘碎片清除率明显降低(P < 0.05);④苏木精-伊红染色可见,在术后7 d,模型组坐骨神经断端较多炎性细胞浸润,许旺细胞增殖活跃,神经纤维大量再生通过吻合口,断端修复正常,处理组神经断端炎性细胞较少,纤维组织增生较少,吻合口有缝隙,断端修复能力减弱;⑤免疫组织化学可见,与模型组相比,术后4 d处理组中生长相关蛋白43蛋白表达均显著下调(P < 0.05);⑥坐骨神经功能指数显示,与模型组相比,处理组大鼠在术后20,30和40 d同期比较明显降低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。⑦结果证实,Toll样受体4拮抗剂导致大鼠坐骨周围神经损伤早期再生延迟,其机制可能是抑制了瓦勒变性过程中的的Toll样受体4信号通路。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-2714-3637(熊乐)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
TOLL样受体4(TLR4):人类发现的第1个TOLL样受体相关蛋白,由TOLL样受体4基因编码的一种蛋白质,参与激活固有免疫。它可以识别许多革兰阴性细菌的脂多糖(LPS),也可以选择性识别革兰阳性菌,它的配体也包括一些病毒蛋白、多糖及多种内源性蛋白质(如低密度脂蛋白,热休克蛋白等)。
瓦勒变性:即由于各种创伤、牵拉、缺血、高低温、电击等原因,直接使神经纤维受损中断,周围神经损伤后远段发生的轴突坏死、髓鞘分解消失和神经鞘膜增生等一系列蜕变和细胞吞噬过程。
文题释义:
TOLL样受体4(TLR4):人类发现的第1个TOLL样受体相关蛋白,由TOLL样受体4基因编码的一种蛋白质,参与激活固有免疫。它可以识别许多革兰阴性细菌的脂多糖(LPS),也可以选择性识别革兰阳性菌,它的配体也包括一些病毒蛋白、多糖及多种内源性蛋白质(如低密度脂蛋白,热休克蛋白等)。
瓦勒变性:即由于各种创伤、牵拉、缺血、高低温、电击等原因,直接使神经纤维受损中断,周围神经损伤后远段发生的轴突坏死、髓鞘分解消失和神经鞘膜增生等一系列蜕变和细胞吞噬过程。