| [1] Sica A, Mantovani A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. J Clin Invest.2012;122(3): 787-795.
[2] Xue J, Schmidt SV, Sander J, et al.Transcriptome-based network analysis reveals a spectrum model of human macrophage activation.Immunity. 2014;40(2):274-288.
[3] Mantovani A, Sica A, Locati M. Macrophage polarization comes of age. Immunity.2005; 23(4): 344-346.
[4] Vernon MA, Mylonas KJ, Hughes J. Macrophages and renal fibrosis. Semin Nephrol. 2010; 30(3): 302-317.
[5] Whyte CS, Bishop ET, Rückerl D, et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS)1 is a key determinant of differential macrophage activation and function. J Leukoc Biol.2011; 90(5): 845-854.
[6] Phipps KD, Gebremeskel S, Gillis J, et al. Alternatively activated M2 macrophages improve autologous Fat Graft survival in a mouse model through induction of angiogenesis. Plast Reconstr Surg.2015;135(1):140-149.
[7] Okizaki S, Ito Y, Hosono K, et al. Suppressed recruitment of alternatively activated macrophages reduces TGF-β1 and impairs wound healing in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2015;70:317-325.
[8] Wilson HM.Macrophages heterogeneity in atherosclerosis- implications for therapy.J Cell Mol Med. 2010; 14(8):2055- 2065.
[9] Wynn TA. Fibrotic disease and the T(H)1/T(H)2 paradigm.Nat Rev Immunol.2004; 4(8): 583-594.
[10] Shibahara K, Asano M, Ishida Y, et al. Isolation of a novel mouse gene MA-3 that is induced upon programmed cell death. Gene. 1995;166(2):297-301.
[11] Palamarchuk A, Efanov A, Maximov V, et al. Akt phosphorylates and regulates Pdcd4 tumor suppressor protein. Cancer Res. 2005; 65 (24):11282-11286.
[12] Lankat-Buttgereit B, Göke R. The tumour suppressor Pdcd4: recent advances in the elucidation of function and regulation. Biol Cell. 2009;101(6):309-317.
[13] White K, Dempsie Y, Caruso P, et al. Endothelial apoptosis in pulmonary hypertension is controlled by a microRNA/ programmed cell death 4/caspase-3 axis. Hypertension. 2014; 64 (1):185-194.
[14] Yasuda M, Schmid T, Rübsamen D, et al. Downregulation of programmed cell death 4 by inflammatory conditions contributes to the generation of the tumor promoting microenvironment. Mol Carcinog. 2010;49(9):837-848.
[15] Wang X, Zhang L, Wei Z, et al. The inhibitory action of PDCD4 in lipopolysaccharide /D-galactosamine-induced acute liver injury. Lab Invest. 2013; 93(3):291-302.
[16] Yasuda M, Schmid T, Rübsamen D, et al. Downregulation of programmed cell death 4 by inflammatory conditions contributes to the generation of the tumor promoting microenvironment. Mol Carcinog. 2010;49(9):837-848.
[17] Hwang SK, Baker AR, Young MR, et al. Tumor suppressor PDCD4 inhibits NF-κB-dependent transcription in human glioblastoma cells by direct interaction with p65. Carcinogenesis. 2014; 35 (7):1469-1480.
[18] Erwig LP, Stewart KN, Rees AJ. Macrophages from inflamed but not normal glomeruli are unresponsive to anti-inflammatory cytokines. Am J Pathol. 2000;156(1): 295-301.
[19] Ke X, Hu G, Fang W,et al. Yin inhibits the LPS-induced activation of the IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway in human intestinal Caco-2 cells. Int J Mol Med. 2015;35(4):1133-1137.
[20] de Oliveira JR, Favarin DC, Tanaka SC, et al. AT-RvD1 Modulates CCL-2 and CXCL-8 Production and NF-κB, STAT-6,SOCS1, and SOCS3 Expression on Bronchial Epithelial Cells Stimulated with IL-4.Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015:178369.
[21] Whyte CS, Bishop ET, Rückerl D, et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS)1 is a key determinant of differential macrophage activation and function. J Leukoc Biol. 2011; 90(5): 845-854.
|
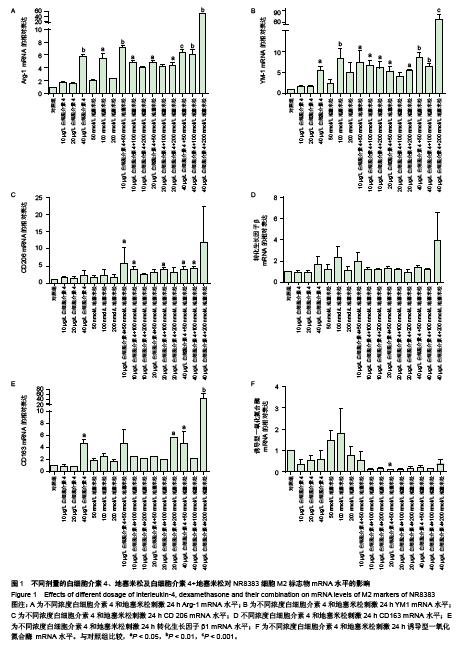
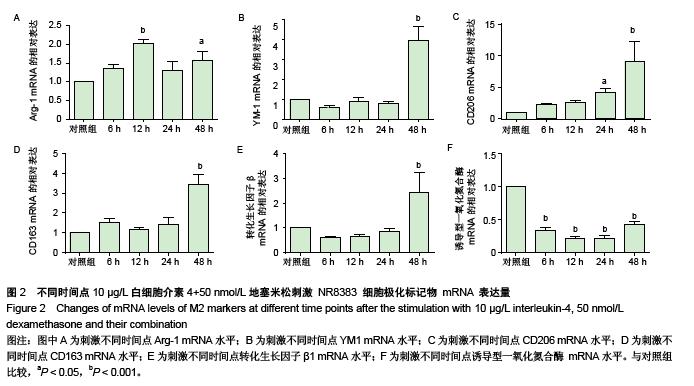
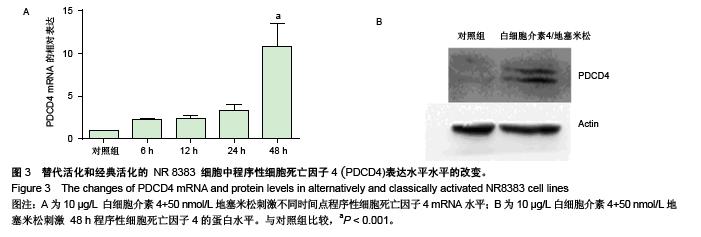
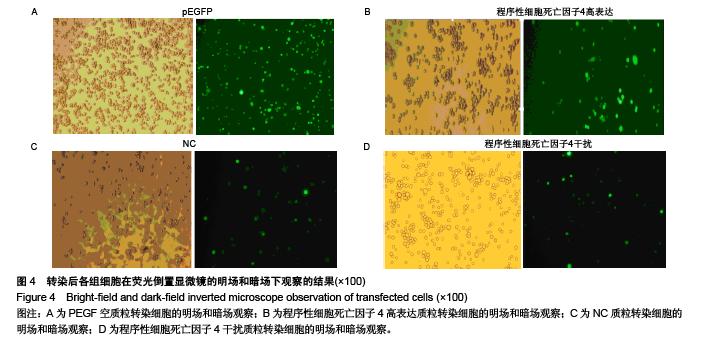
.jpg)

.jpg)

.jpg)