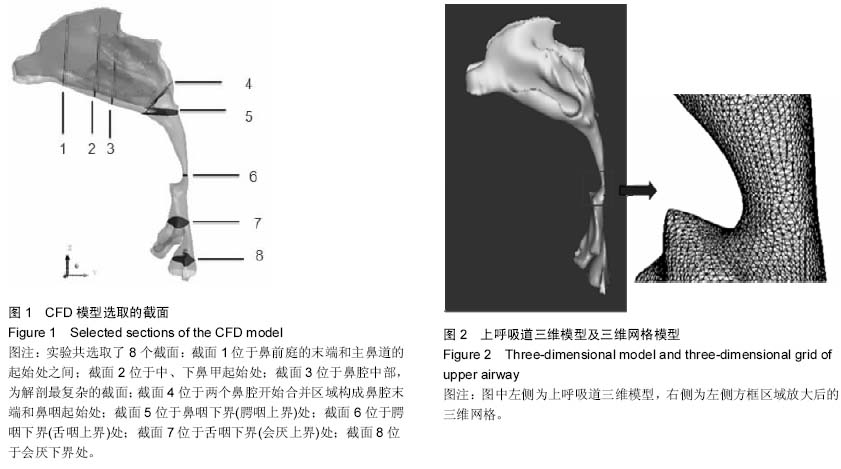
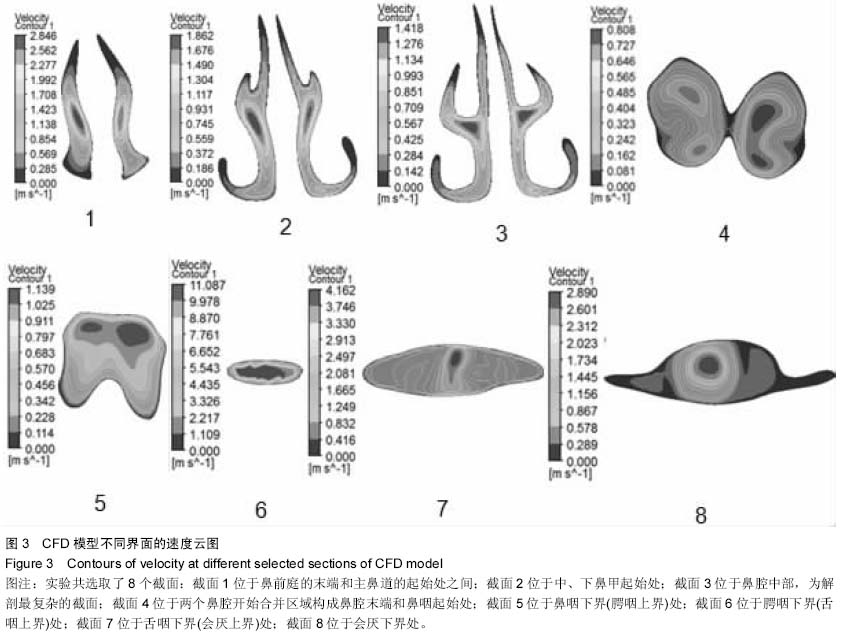
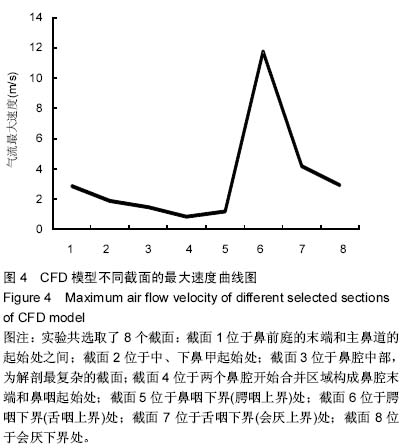
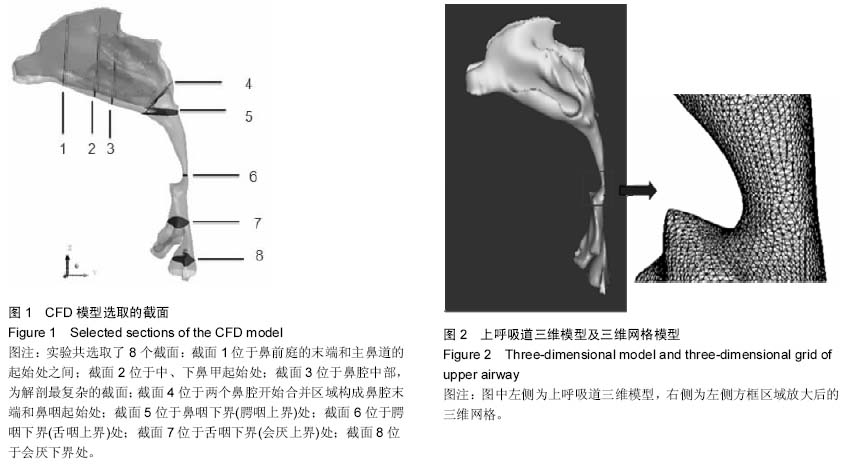
中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (20): 3211-3215.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.20.018
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征患者上气道流体动力学模型的建立
李三军1,李懿波2,李永明2
- 1陕西省商洛市妇幼保健医院口腔科,陕西省商洛市 726000;2解放军第四军医大学口腔医学院正畸科,陕西省西安市 710032
Establishment of three-dimensional computational fluid dynamics model of upper airway in patients with obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome
Li San-jun1, Li Yi-bo2, Li Yong-ming2
- 1Department of Stomatology, Shangluo Municipal Woman and Children’s Hospital, Shangluo 726000, Shaanxi Province, China; 2Department of Orthodontics, College of Stomatology, Fourth Military Medical University of Chinese PLA, Xi’an 710032, Shaanxi Province, China
摘要:
背景:对阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征患者上呼吸道内气体流动情况进行分析有助于进一步了解上呼吸道解剖结构与功能间的相互关系,从而认识阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征的发病机制。 目的:建立阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征患者上气道三维形态及流体动力学模型,为研究阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征患者上气道气流动力学特征,探讨其发病机制奠定基础。 方法:对1名男性中度阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征患者的上气道行CT扫描,将以DICOM格式存储的扫描数据导入Mimics 10.01软件中进行处理,得到上气道三维模型。通过ANSYS ICEM CFD14.0对三维模型进行网格划分后,用 ANSYS 14.0-Fluid Dynamics对上呼吸道内部流场进行数值模拟,获得上气道气流场相关信息。 结果与结论:建立了完整的上气道三维形态及流体动力学模型,共得到上气道网格数为1 751 940个单元,节点数为303 981个节点,上呼吸道内最大流速为11.087 m/s位于咽腔狭窄区域腭咽下界处。上气道流体动力学模型符合人体的生物力学特点,为以后进一步研究阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征患者上呼吸道气流动力学特征奠定了基础。
中图分类号: