中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (11): 1712-1716.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.11.014
• 组织构建细胞学实验 cytology experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
草酸钙晶体刺激下人巨噬细胞高迁移率族蛋白B1的表达
黄 鹏,邓耀良,黎承杨,陶芝伟,王 翔,奉有才,吴 博
- 广西医科大学第一附属医院泌尿外科,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530021
Calcium oxalate crystals stimulate expression of high mobility group box-1 protein in human macrophages
Huang Peng, Deng Yao-liang, Li Cheng-yang, Tao Zhi-wei, Wang Xiang, Feng You-cai, Wu Bo
- Department of Urinary Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
背景:研究发现在肾结石模型中肾间质晶体周围存在大量单核/巨噬细胞浸润,显示巨噬细胞可能参与晶体在肾脏中的沉积过程,而巨噬细胞是人体重要的固有免疫细胞,在肾脏中沉积的大量的单核/巨噬细胞吞噬晶体,会产生一些炎症因子损伤和破坏肾小管上皮细胞,最终有利于结石的形成。
目的:探讨一水草酸钙晶体刺激人巨噬细胞后高迁移率族蛋白B1的表达水平。
方法:用100 mg/L的一水草酸钙刺激巨噬细胞,分别于刺激后0,6,12,24和36 h,用Western blot检测细胞总蛋白和细胞浆内高迁移率族蛋白B1的含量;用实时荧光定量PCR,检测细胞中高迁移率族蛋白B1 mRNA表达情况;分别于一水草酸钙刺激后0,1,2和4 h,用酶联免疫吸附实验测定细胞培养液上清中肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6的水平。
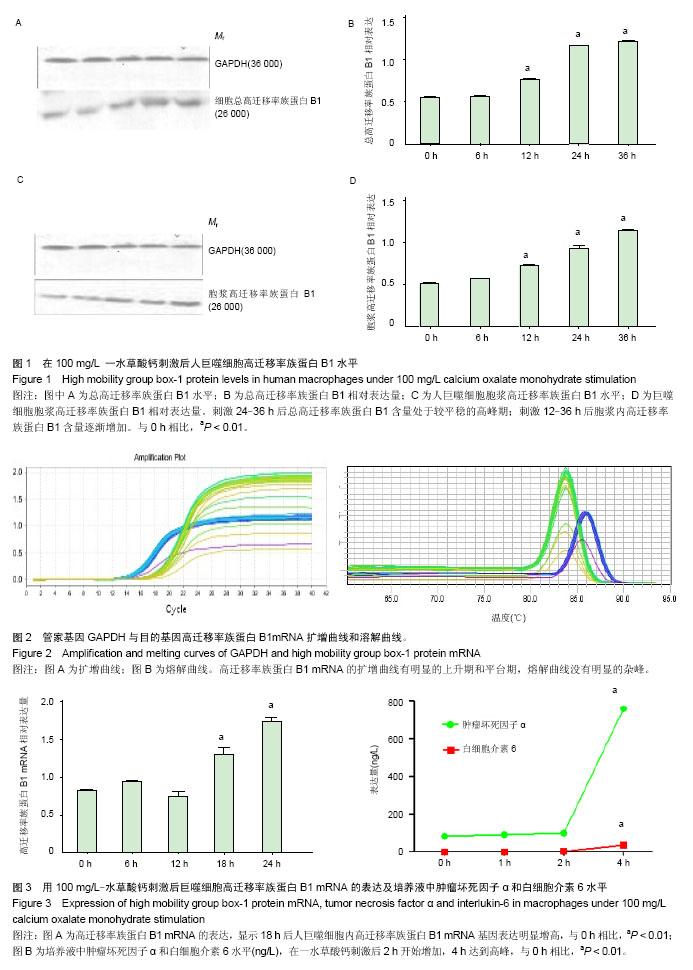
结果与结论:一水草酸钙刺激后0-6 h细胞浆内高迁移率族蛋白B1的含量较低,刺激后12-36 h细胞浆内高迁移率族蛋白B1逐渐增加。一水草酸钙刺激后0-6 h,巨噬细胞总蛋白中高迁移率族蛋白B1含量不高,在刺激后12 h细胞总蛋白高迁移率族蛋白B1的含量开始增加,并且在刺激后24-36 h保持在较高水平。RT-PCR结果显示,一水草酸钙刺激后0-12 h,培养细胞中高迁移率族蛋白B1的mRNA表达量无明显变化,刺激后18-24 h培养细胞中高迁移率族蛋白B1的mRNA表达量明显增加。ELISA结果显示,一水草酸钙刺激后2 h,细胞培养液上清中肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6表达和释放增加,4 h达到明显高峰。结果表明,一水草酸钙可以诱导人巨噬细胞高迁移率族蛋白B1的表达及mRNA表达增加;诱导人巨噬细胞内肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6的表达增加,且高迁移率族蛋白B1表达的时间明显晚于肿瘤坏死因子a和白细胞介素6的释放时间。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)