| [1] AsallaraT, MuroharaT, Sullivan A, et al. Isolation of putative endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science. 1997;275(5302): 964-967.
[2] Peichev M, Naiyer AJ, Pereira D, et al. Expression of VEGFR-2 and AC133 by circulating human CD34(+)cells identifies a population of functional endothelial precrsors. Blood. 2000;95(3):952-958.
[3] Gill M, Dias S, Hattori K, et al. Vascular trauma induces rapid but transient mobilization of VEGF2(+)AC133(+)endothelial precursor cells. Circ Res. 2001;88(2):167-174.
[4] Hill JM, Zalos G, Halcox JP, et al. Circulating endothelial progenitor cells,vascular function,and cardiovascular risk. N EngI J Med. 2003;348(7):593-600.
[5] Walter DH, Rittig K, Bahlmann FH, et al. Statin therapy accelerates reendothelialization: a novel effect involving mobilization and incorporation of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells. Circulation. 2002;105(25): 3017-3024.
[6] Kocher AA, Schuster MD, Szabolcs MJ, et al. Neovascularization of ischemic myocardium by human bone-marrow-derived angioblasts prevents cardiomyocyte apoptosis, reduce remodeling and improves cardiac function. Nat Med. 2001;7(4):430-436.
[7] Takahashi T, Kalka C, Masnda H, et al. Ischemia-and cytokine- induced mobilization of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells for neovascularization. Nat Med. 1999;5(4): 434-438.
[8] Asahara T, Masuda H, Takahashi T, et al. Bone marrow origin of endothelial progenitor cells responsible for postnatal vasculogenesis in physiological and pathological neovascularization. Circ Res. 1999;85(3):221-228.
[9] Murayama T, Tepper OM, Silver M, et al. Determination of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cell significance in angiogenic growth factor-induced neovascularization in vivo. Exp Hematol. 2002;30(8):967-972.
[10] Suzuki T, Nishida M, Futami S, et al. Neoendothelialization after peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in humans:a case report of a Tokaimura nuclear accident victim. Cardiovasc Res. 2003;58(2):487-492.
[11] 彭艳,程培,徐勇,等.脐血内皮祖细胞尾静脉与局部注射治疗糖尿病下肢缺血[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(19): 3499-3502.
[12] Giannotti G, Doerries C, Mocharla PS, et al. Impaired endothelial repair capacity of early endothelial progenitor cells in prehypertension: relation to endothelial dysfunction. Hypertension. 2010;55(6):1389-1397.
[13] Chen LL, Liao YF, Zeng TS, et al. Number and function of circulating endothelial progenitor cell in diabetics with different vascular complications. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2009;89(18): 1234-1239.
[14] Maitra B, Szekely E, Gjini K, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells support unrelated donor hematopoietic stem cells and suppress T-cell activation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2004;33: 597-604.
[15] Rocha V, Wagner JE Jr, Sobocinski KA, et al. Graft-versus-host disease in children who have received a cord-blood or bone marrow transplant from an HLA-identical sibling. Eurocord and International Bone Marrow Transplant Registry Working Committee on Alternative Donor and Stem Cell Sources. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(25):1846-1854.
[16] Teleron AA, Carlson B, Young PP. Blood donor white blood cell reduction filter as a source of human peripheral blood-derived endohelial progenitor cell. Transfusion. 2005; 45(1):21-25.
[17] Eggermann J, Kliche S, Hoffmann K, et al. Endothelial progenitor cell culture and differentiation in vitro: a methodological comparison using human umbilical cord blood.Cardiovasc Res. 2003;58(2):478-486.
[18] Fadini GP, Albiero M, Cignarella A, et al. Effects of androgens on endothelial progenitor cells in vitro and in vivo.Clin Sci (Lond). 2009;117(10):355-364.
[19] Hur J, Yoon CH, Kim HS, et al. Characterization of two types of endothelial progenitor cells and their different contributions to neovasculogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004; 24(2):288-293.
[20] Chivu M, Diaconu CC, Bleotu C, et al. The comparison of different protocols forexpansion of umbilical-cord hematopoietic stem cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2004;8(2): 223-231.
[21] Reyftmann L, Dechaud H, Hamamah S, et al. Fetal and umbilical blood cord stem cells:a room for the obstetrician and gynaecologist. Part two, Gynecol Obstel Fertil. 2004;3(11): 969-975.
[22] 方立建,宋鄂,栾瑛,等.人脐血内皮祖细胞体外培养和鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,45(14):8450-8454.
[23] 徐燕,孟恒星,于珍,等.不同来源内皮祖细胞培养及其生物学特性比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,23(14): 4309-4316.
[24] He T, Peterson TE, Holmuhamedov EL, et al. Human endothelial progenitor cells tolerate oxidative stress due to intrinsically high expression of manganese superoxide dismutase. Arterioscler Thromb vasc Biol. 2004;24(11): 2021-2027.
[25] Maitra B, Szekely E, Gjini K, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells support unrelated donor hematopoietic stem cells and suppress T-cell activation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2004; 33(6): 597-604.
[26] 周建良,邹明晖,陈义初,等.人脐血内皮祖细胞与血管内皮生长因子和碱性成纤维细胞生长因子共培养及其增殖和迁移能力[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(6):1000-1004.
[27] Kovacic JC, Moore J, Herbert A, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells, angioblasts, and angiogenesis--old terms reconsidered from acurrent perspective. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2008; 18(2): 45-51.
[28] Prater DN, Case J, Ingram DA, et al. Working hypothesis to redefine endothelial progenitor cells. Leukemia. 2007;21(6): 1141-1149.
[29] Hirschi KK, Ingram DA, Yoder MC. Assessing identity, phenotype,and fate of endothelial progenitor cells. Arterioscler Thromb VascBiol. 2008;28(9):1584-1595.
[30] 宋晓红,张罗,韩德民,等.鼠尾胶原为底物的人鼻腔纤毛上皮细胞培养模式的建立[J].中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科,2007,2(14):107- 111.
[31] 章必成,王俊,赵勇,等.以鼠尾胶为贴黏剂的小鼠淋巴管内皮细胞培养体系的建立[J].第四军医大学学报,2007,28(5):390-393. |


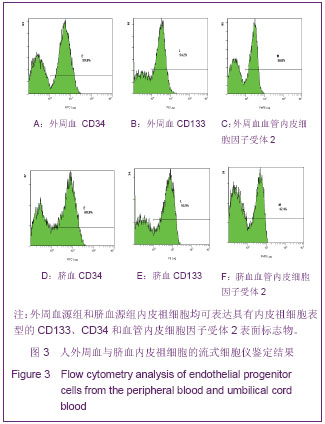
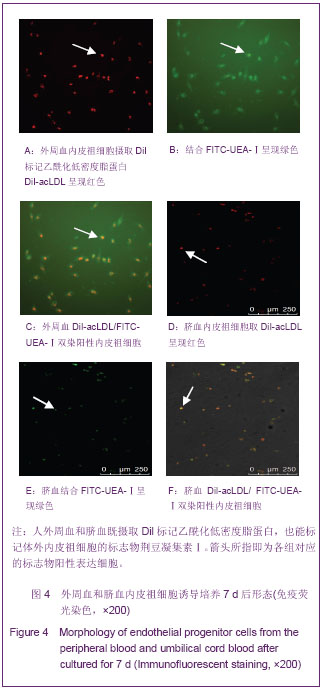
.jpg)