中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (35): 5596-5601.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1004
• 人工假体 artificial prosthesis • 上一篇 下一篇
膝关节置换后患者的三维步态特征
黄 萍1,陈 博1,刘志宏1,许 萍2
- 1上海市伤骨科研究所,上海市中西医结合防治骨与关节病损重点实验室,上海交通大学医学院附属瑞金医院,上海市 200025;2上海健康医学院,上海市 201318
Three-dimensional gait characteristics of patients after knee arthroplasty
Huang Ping1, Chen Bo1, Liu Zhihong1, Xu Ping2
- 1Shanghai Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics, Shanghai Key Laboratory for Prevention and Treatment of Bone and Joint Diseases with Integrated Chinese-Western Medicine, Ruijin Hospital of Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China; 2Shanghai University of Medicine & Health Sciences, Shanghai 201318, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
膝关节置换:指用生物相容性与机械性能良好的金属材料制成的一种类似人体骨关节的人工膝关节假体。用手术方法将假体置换被疾病或损伤所破坏的膝关节面,其目的是切除病灶、缓解疼痛、恢复关节的活动与原有的功能。尽管人工膝关节假体的寿命达到15-20年,但是磨损和松动等临床问题依然制约着人工膝关节的使用寿命。而体内膝关节运动、动力学承载等情况与人工膝关节假体的失效有着直接的关系。
三维步态分析:三维步态分析是现代实验室所采用的数字化、高科技的步态分析系统,由一组通过网络将三维运动捕捉系统、三维测力台等连接起来,获取运动学和动力学等数据,对人类行走状态进行分析的一种生物力学研究方法。三维步态分析能够提供一系列时间、几何、力学等参数值和曲线,能够客观定量地评定人体步行功能。
摘要
背景:膝关节置换后患者的步态越来越受到临床医生和研究者关注。
目的:定量评价膝关节置换后患者的步行功能和膝关节生物力学变化,评定手术疗效,探索最佳的治疗策略和置换后康复方案。
方法:采用英国Vicon三维运动捕捉系统对膝关节炎双膝关节置换后患者12例(试验组)和12例相匹配的健康志愿者(对照组)进行步态测试,以Polygon软件分析受试者步行能力和膝关节三维运动学及动力学特征。
结果与结论:①时空参数(步频、双足支撑期、对侧足跟着地比、对侧足尖离地比、单足支撑期、步长、一步时间、步宽、步幅、步行周期、步速):2组相比差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05);②角度:试验组膝关节屈曲角度峰值、内翻角度峰值、冠状面上最大活动范围均减小,与对照组相比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);③角速度和角加速度:试验组膝关节角速度峰值、角速度平均值、角加速度峰值、角加速度平均值均减小,与对照组相比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);④力矩:试验组膝关节伸展力矩峰值减小,与对照组相比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。⑤地面反力:试验组Y轴和Z轴方向地面反作用力峰值减小,与对照组相比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);⑥结果表明,试验组患者和正常人在平地步行中时空参数没有明显差别,提示人工膝关节置换是改善下肢步行功能极为重要的治疗方法。但是结果也显示置换后患者假体关节存在一些运动和运动力学的异常,膝关节的生物力学没有完全达到正常水平,这些变化是人工膝关节置换后的运动生物力学特征,可能是影响患者长期疗效的重要因素。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-8732-8452(许萍)
中图分类号:
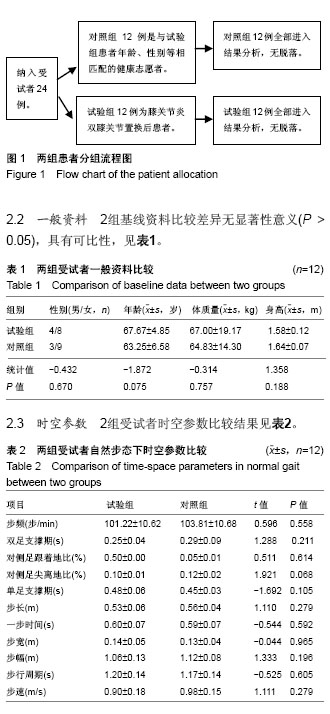
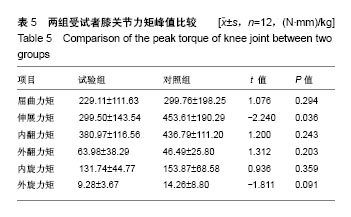
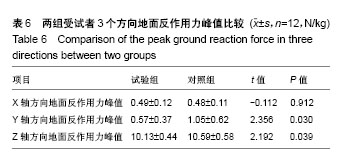
.jpg)