中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (16): 2489-2495.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0819
• 软骨组织构建 cartilage tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
工程化软骨几何形状对缺损修复区力学行为的影响
赵永政1,2,刘海英1,2,张春秋1,2,胡亚辉1,2
- 1天津市先进机电系统设计与智能控制重点实验室,天津市 300384;2机电工程国家级实验教学示范中心(天津理工大学),天津市 300384
Geometric shapes of tissue-engineered cartilage exert effects on mechanical behaviors of a defected area
Zhao Yong-zheng1, 2, Liu Hai-ying1, 2, Zhang Chun-qiu1, 2, Hu Ya-hui1, 2
- 1Tianjin Key Laboratory of Advanced Mechatronic System Design and Intelligent Control, Tianjin 300384, China; 2National Demonstration Center for Experimental Mechanical and Electrical Engineering Education (Tianjin University of Technology), Tianjin 300384, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
数值模拟:也叫计算机模拟。依靠电子计算机,结合有限元或有限容积的概念,通过数值计算和图像显示的方法,达到对工程问题和物理问题乃至自然界各类问题研究的目的。
三维模型:①通常用计算机或者其它视频设备进行显示物体的多边形表示,显示的物体可以是现实世界的实体,也可以是虚构的物体;②任何物理自然界存在的东西都可以用三维模型表示;③三维模型经常用三维建模工具这种专门的软件生成,但是也可以用其它方法生成;④作为点和其它信息集合的数据,三维模型可以手工生成,也可以按照一定的算法生成;⑤尽管通常按照虚拟的方式存在于计算机或者计算机文件中,但是在纸上描述的类似模型也可以认为是三维模型。
文题释义:
数值模拟:也叫计算机模拟。依靠电子计算机,结合有限元或有限容积的概念,通过数值计算和图像显示的方法,达到对工程问题和物理问题乃至自然界各类问题研究的目的。
三维模型:①通常用计算机或者其它视频设备进行显示物体的多边形表示,显示的物体可以是现实世界的实体,也可以是虚构的物体;②任何物理自然界存在的东西都可以用三维模型表示;③三维模型经常用三维建模工具这种专门的软件生成,但是也可以用其它方法生成;④作为点和其它信息集合的数据,三维模型可以手工生成,也可以按照一定的算法生成;⑤尽管通常按照虚拟的方式存在于计算机或者计算机文件中,但是在纸上描述的类似模型也可以认为是三维模型。
.jpg) 文题释义:
数值模拟:也叫计算机模拟。依靠电子计算机,结合有限元或有限容积的概念,通过数值计算和图像显示的方法,达到对工程问题和物理问题乃至自然界各类问题研究的目的。
三维模型:①通常用计算机或者其它视频设备进行显示物体的多边形表示,显示的物体可以是现实世界的实体,也可以是虚构的物体;②任何物理自然界存在的东西都可以用三维模型表示;③三维模型经常用三维建模工具这种专门的软件生成,但是也可以用其它方法生成;④作为点和其它信息集合的数据,三维模型可以手工生成,也可以按照一定的算法生成;⑤尽管通常按照虚拟的方式存在于计算机或者计算机文件中,但是在纸上描述的类似模型也可以认为是三维模型。
文题释义:
数值模拟:也叫计算机模拟。依靠电子计算机,结合有限元或有限容积的概念,通过数值计算和图像显示的方法,达到对工程问题和物理问题乃至自然界各类问题研究的目的。
三维模型:①通常用计算机或者其它视频设备进行显示物体的多边形表示,显示的物体可以是现实世界的实体,也可以是虚构的物体;②任何物理自然界存在的东西都可以用三维模型表示;③三维模型经常用三维建模工具这种专门的软件生成,但是也可以用其它方法生成;④作为点和其它信息集合的数据,三维模型可以手工生成,也可以按照一定的算法生成;⑤尽管通常按照虚拟的方式存在于计算机或者计算机文件中,但是在纸上描述的类似模型也可以认为是三维模型。摘要
背景:关节软骨损伤修复结果的不确定性与修复区的力学行为有关,缺损修复的形状、层深及载荷特性均不同程度地改变修复区的力学环境。
目的:通过有限元仿真分析在生理载荷作用下关节软骨缺损修复区的力学行为。
方法:应用有限元软件ABAQUS建立基于横观各向同性的关节软骨损伤与修复的轴对称模型。分析在压缩载荷作用下,软骨不同修复形状(圆柱、圆台、正棱柱、椭圆柱形)和深度对缺损软骨修复区力学行为的影响。
结果与结论:①模拟结果表明,不同形状、层深的工程化软骨对软骨修复区力学行为影响规律不同;②中间层缺损修复时应力集中现象最显著,深(全)层缺损修复时应力分布较合理;③圆柱形工程化软骨修复时的应力场及液相流场分布规律与无损软骨最为接近;临床上,可以选用圆柱形或圆台形工程化软骨进行修复,且尽量避免中间层修复。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-4888-3338(赵永政)
中图分类号:
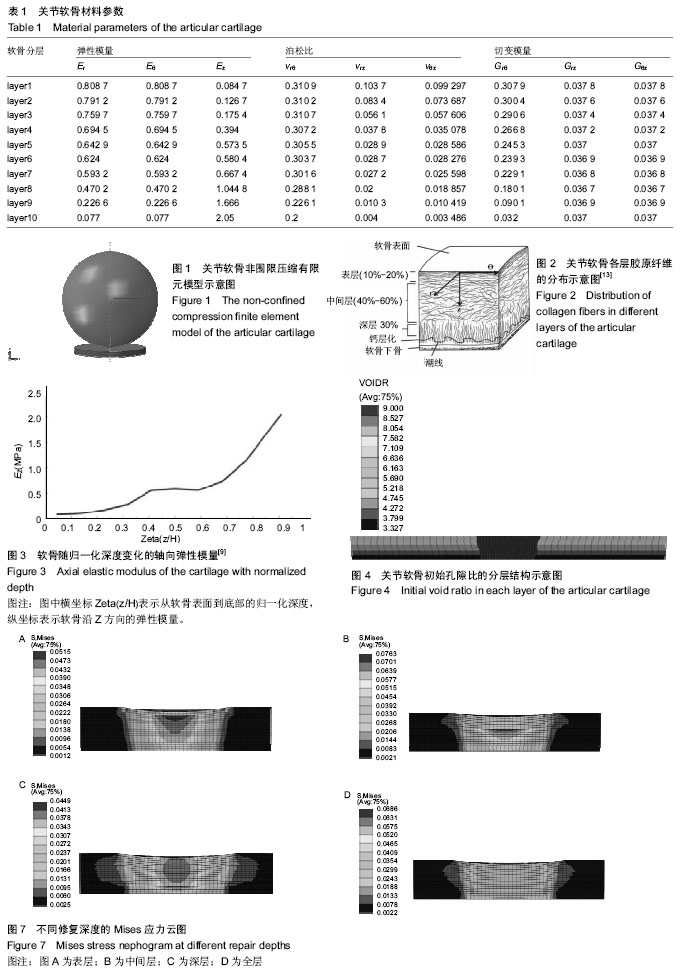
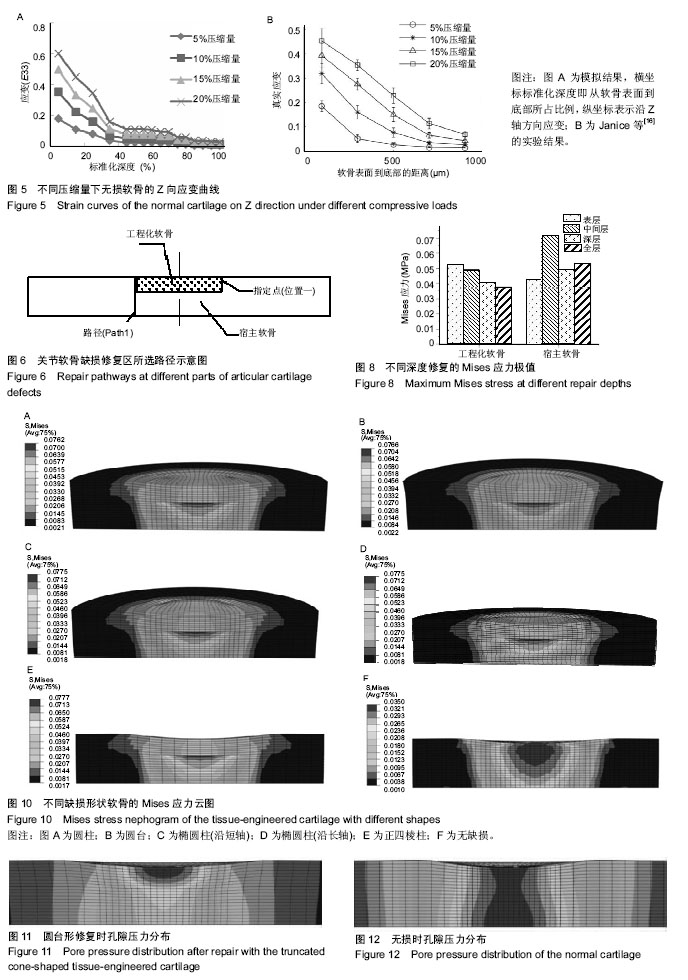
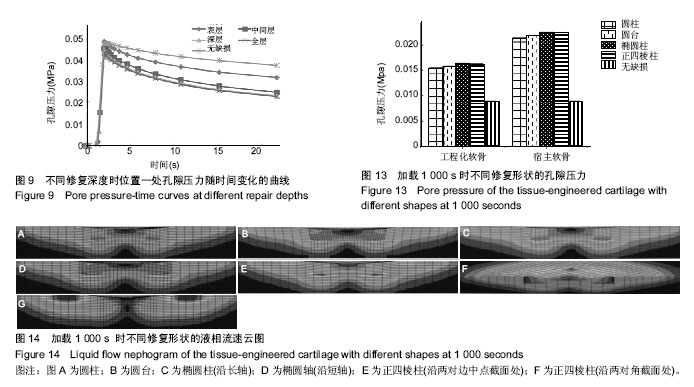
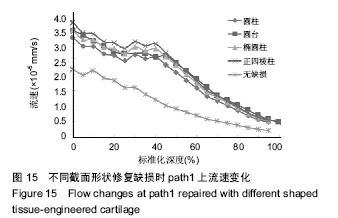
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
数值模拟:也叫计算机模拟。依靠电子计算机,结合有限元或有限容积的概念,通过数值计算和图像显示的方法,达到对工程问题和物理问题乃至自然界各类问题研究的目的。
三维模型:①通常用计算机或者其它视频设备进行显示物体的多边形表示,显示的物体可以是现实世界的实体,也可以是虚构的物体;②任何物理自然界存在的东西都可以用三维模型表示;③三维模型经常用三维建模工具这种专门的软件生成,但是也可以用其它方法生成;④作为点和其它信息集合的数据,三维模型可以手工生成,也可以按照一定的算法生成;⑤尽管通常按照虚拟的方式存在于计算机或者计算机文件中,但是在纸上描述的类似模型也可以认为是三维模型。
文题释义:
数值模拟:也叫计算机模拟。依靠电子计算机,结合有限元或有限容积的概念,通过数值计算和图像显示的方法,达到对工程问题和物理问题乃至自然界各类问题研究的目的。
三维模型:①通常用计算机或者其它视频设备进行显示物体的多边形表示,显示的物体可以是现实世界的实体,也可以是虚构的物体;②任何物理自然界存在的东西都可以用三维模型表示;③三维模型经常用三维建模工具这种专门的软件生成,但是也可以用其它方法生成;④作为点和其它信息集合的数据,三维模型可以手工生成,也可以按照一定的算法生成;⑤尽管通常按照虚拟的方式存在于计算机或者计算机文件中,但是在纸上描述的类似模型也可以认为是三维模型。