| [1] 朱玉珍,张庆文.神经元钙传感蛋白研究前沿与热点分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(42):6856-6862.[2] 朱玉珍,邹昱,张庆文.将分子动力学模拟方法引入体育领域研究的可行性分析--以肌动蛋白、肌球蛋白和人类神经元钙传感蛋白为例[J],体育科学,2017,37(1):90-97.[3] 朱玉珍,张庆文.分子动力学模拟:神经元钙传感蛋白生理机制研究的新方向[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(20):3224-3233.[4] Drumond LE, Mourao FA, Leite HR, et al. Differential effects of swimming training on neuronal calcium sensor-1 expression in rat hippocampus/cortex and in object recognition memory tasks. Brain Res bulletin.2012;88:385-391.[5] White LJ, Castellano V. Exercise and brain health--implications for multiple sclerosis: Part 1-neuronal growth factors.Sports medicine. 2008;38: 91-100.[6] Saab BJ,Georgiou J,Nath A,et al.NCS-1 in the dentate gyrus promotes exploration, synaptic plasticity, and rapid acquisition of spatial memory. Neuron.2009;63: 643-656.[7] Dason JS,Romero-Pozuelo J,Atwood HL, et al. Multiple roles for frequenin/NCS-1 in synaptic function and development.Molecular neurobiology.2012;45: 388-402.[8] Ardoy DN,Fernandez-Rodriguez JM,Jimenez-Pavon D,et al.A Physical Education trial improves adolescents' cognitive performance and academic achievement:the EDUFIT study. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2014;24(1):e52-61[9] Pongs O,Lindemeier J,Zhu XR,et al.Frequenin--a novel calcium-binding protein that modulates synaptic efficacy in the Drosophila nervous system.Neuron.1993;11: 15-28.[10] Hilfiker S.Neuronal calcium sensor-1: a multifunctional regulator of secretion.Biochem Soc Trans. 2003;31:828-832.[11] Burgoyne RD.Neuronal calcium sensor proteins: generating diversity in neuronal Ca2+ signalling. Nat Rev Neurosci.2007;8: 182-193.[12] Martin VM,Johnson JR,Haynes LP,et al.Identification of key structural elements for neuronal calcium sensor-1 function in the regulation of the temperature-dependency of locomotion in C. elegans.Mol Brain.2013;6: 39.[13] Zhu Y, Ma B, Qi R, Nussinov R, et al.Temperature-Dependent Conformational Properties of Human Neuronal Calcium Sensor-1 Protein Revealed by All-Atom Simulations.J Phys Chem B.2016; 120:3551-3559.[14] 郭浙斌.低氧下运动及补液对集体体液平衡和有氧运动能力的影响[D].华南师范大学,2007.[15] Heidarsson PO,Bjerrum-Bohr IJ,Jensen GA,et al.The C-terminal tail of human neuronal calcium sensor 1 regulates the conformational stability of the Ca 2+- activated state.J Mol Biol. 2012;417: 51-64.[16] Bourne Y,Dannenberg J,Pollmann V,et al.Immunocytochemical localization and crystal structure of human frequenin (neuronal calcium sensor 1).J Biol Chem.2001;276: 11949-11955.[17] Zhu Y, Wu Y, Luo Y, et al.R102Q mutation shifts the salt-bridge network and reduces the structural flexibility of human neuronal calcium sensor-1 protein.J Phys Chem B.2014;118: 13112-13122.[18] 朱玉珍,张庆文.神经元钙传感蛋白R102Q 突变体的动力学构象特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(2):225-230.[19] 朱玉珍.神经元钙传感蛋白构象动力学及调控机制研究[D].上海体育学院.2016.[20] Gifford JL,Walsh MP, Vogel, HJ.Structures and metal-ion-binding properties of the Ca2+-binding helix-loop-helix EF-hand motifs. Biochem J.2007;405: 199-221.[21] Hess B, Kutzner C, van der Spoel D,et al.GROMACS 4: Algorithms for highly efficient, load-balanced, and scalable molecular simulation.J Chem Theory Comput.2008;4: 435-447.[22] Bjelkmar P, Larsson P, Cuendet MA, et al.Implementation of the CHARMM force field in GROMACS: analysis of protein stability effects from correction maps, virtual interaction sites, and water models.J Chem Theory Comput.2010;6:459-466.[23] Bussi G,Donadio D,Parrinello M.Canonical sampling through velocity rescaling.J Chem Phys. 2007;126: 014101.[24] Parrinello M, Rahman A. Polymotphic transitions in single-crystals-a new molecular-dynamics method.J Appl Phys.1981;52: 7182-7190.[25] Berk Hess,Hemk Bekker,Herman J.C.Berendsen,et al. LINCS: A linear constraint solver for molecular simulations.J Comput Chem.1997;18: 1463-1472.[26] Shuichi Miyamoto,Peter A.Kollman.Settle- an analytical version of the shake and rattle algorithm for rigid water models.J Comput Chem.1992;13: 952-962.[27] Kabsch W, Sander C.Dictionary of potein secondary structure - pattern -recognition of hydrogen -bonded and geometrical features. Biopolymers.1983;22:2577-2637.[28] Humphrey W,Dalke A,Schulten K.VMD: visual molecular dynamics. Journal of molecular graphics. 1996;14:33-38,27-28.[29] Eargle J, Luthey-Schulten Z.NetworkView: 3D display and analysis of protein.RNA interaction networks.Bioinformatics. 2012;28: 3000-3001.[30] Zhu Y, Yang S, Qi R, et al.Effects of the C-Terminal Tail on the Conformational Dynamics of Human Neuronal Calcium Sensor-1 Protein.J Phys Chem B.2015;119:14236-14244.[31] Sethi A,Eargle J,Black AA,et al.Dynamical networks in tRNA:protein complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(16):6620-6625.[32] Girvan M,Newman ME.Community structure in social and biological networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(12): 7821-7826[33] Strahl T,Huttner IG,Lusin JD,et al.Structural insights into activation of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase (Pik1) by yeast frequenin (Frq1).J Biol Chem.2007;282(42):30949-30959.[34] Hendricks KB,Wang BQ,Schnieders EA,et al.Yeast homologue of neuronal frequenin is a regulator of phosphatidylinositol-4-OH kinase.Nat Cell Biol.1999;1(4):234-241.[35] Kabbani N,Negyessy L,Lin R,et al.Interaction with neuronal calcium sensor NCS-1 mol/Lediates desensitization of the D2 dopamine receptor. J Neurosci. 2002 Oct 1;22(19):8476-8486.[36] Kumar S, Ma B, Tsai CJ, et al.Folding funnels and binding mechanisms.Protein eng.1999;12 (9):713-720.[37] Waldburger CD, Schildbach JF, Sauer RT. Are buried salt bridges important for protein stability and conformational specificity? Nat Struct Biol.1995;2: 122-128.[38] Tissot AC, Vuilleumier S, Fersht AR. Importance of two buried salt bridges in the stability and folding pathway of barnase. Biochemistry.1996;35: 6786-6794.[39] Makhatadze GI,Loladze VV,Ermolenko DN,et al.Contribution of surface salt bridges to protein stability: guidelines for protein engineering.J Mol Biol.2003;327: 1135-1148.[40] Ibarra-Molero B,Zitzewitz JA, Matthews CR.Salt-bridges can stabilize but do not accelerate the folding of the homodimeric coiled-coil peptide GCN4-p1.J Mol Biol.2004;336: 989-996.[41] Bellucci L,Corni S,Di Felice R,et al.The structure of neuronal calcium sensor-1 in solution revealed by molecular dynamics simulations.PLoS One.2013;8: e74383. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
神经元钙传感蛋白:是一种能够触发信号转导的蛋白,在学习、记忆、行为探索和物体识别中起到重要的作用,而且在不同的大脑区域、不同环境中表现出不同的生理功能,还能够通过运动训练调节特定的认知过程。
神经元钙传感蛋白分子结构:神经元钙传感蛋白分子结构中包含190个氨基酸,主要由9个α-螺旋(H1-H9)、3个环形结构(L1-L3)和4个EF-hand(EF1-EF4)组成,是一个含有高电荷的蛋白,其中正电荷氨基酸有24个,负电荷氨基酸有33个。
文题释义:
神经元钙传感蛋白:是一种能够触发信号转导的蛋白,在学习、记忆、行为探索和物体识别中起到重要的作用,而且在不同的大脑区域、不同环境中表现出不同的生理功能,还能够通过运动训练调节特定的认知过程。
神经元钙传感蛋白分子结构:神经元钙传感蛋白分子结构中包含190个氨基酸,主要由9个α-螺旋(H1-H9)、3个环形结构(L1-L3)和4个EF-hand(EF1-EF4)组成,是一个含有高电荷的蛋白,其中正电荷氨基酸有24个,负电荷氨基酸有33个。.jpg) 文题释义:
神经元钙传感蛋白:是一种能够触发信号转导的蛋白,在学习、记忆、行为探索和物体识别中起到重要的作用,而且在不同的大脑区域、不同环境中表现出不同的生理功能,还能够通过运动训练调节特定的认知过程。
神经元钙传感蛋白分子结构:神经元钙传感蛋白分子结构中包含190个氨基酸,主要由9个α-螺旋(H1-H9)、3个环形结构(L1-L3)和4个EF-hand(EF1-EF4)组成,是一个含有高电荷的蛋白,其中正电荷氨基酸有24个,负电荷氨基酸有33个。
文题释义:
神经元钙传感蛋白:是一种能够触发信号转导的蛋白,在学习、记忆、行为探索和物体识别中起到重要的作用,而且在不同的大脑区域、不同环境中表现出不同的生理功能,还能够通过运动训练调节特定的认知过程。
神经元钙传感蛋白分子结构:神经元钙传感蛋白分子结构中包含190个氨基酸,主要由9个α-螺旋(H1-H9)、3个环形结构(L1-L3)和4个EF-hand(EF1-EF4)组成,是一个含有高电荷的蛋白,其中正电荷氨基酸有24个,负电荷氨基酸有33个。

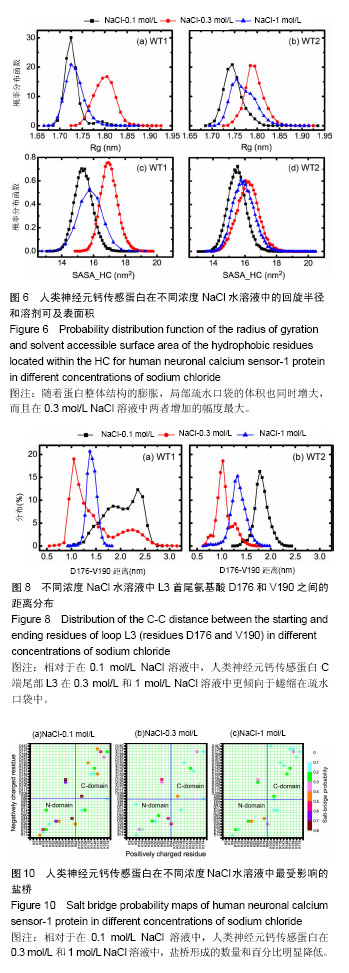
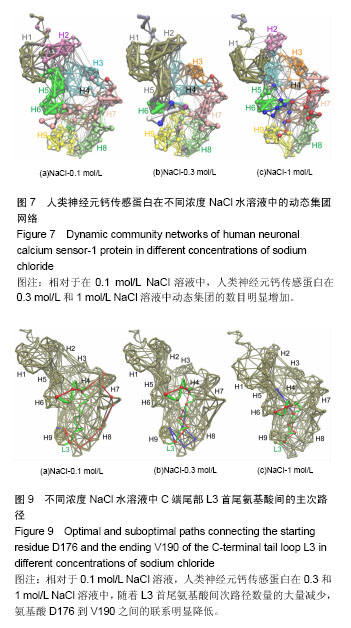
.jpg) 文题释义:
神经元钙传感蛋白:是一种能够触发信号转导的蛋白,在学习、记忆、行为探索和物体识别中起到重要的作用,而且在不同的大脑区域、不同环境中表现出不同的生理功能,还能够通过运动训练调节特定的认知过程。
神经元钙传感蛋白分子结构:神经元钙传感蛋白分子结构中包含190个氨基酸,主要由9个α-螺旋(H1-H9)、3个环形结构(L1-L3)和4个EF-hand(EF1-EF4)组成,是一个含有高电荷的蛋白,其中正电荷氨基酸有24个,负电荷氨基酸有33个。
文题释义:
神经元钙传感蛋白:是一种能够触发信号转导的蛋白,在学习、记忆、行为探索和物体识别中起到重要的作用,而且在不同的大脑区域、不同环境中表现出不同的生理功能,还能够通过运动训练调节特定的认知过程。
神经元钙传感蛋白分子结构:神经元钙传感蛋白分子结构中包含190个氨基酸,主要由9个α-螺旋(H1-H9)、3个环形结构(L1-L3)和4个EF-hand(EF1-EF4)组成,是一个含有高电荷的蛋白,其中正电荷氨基酸有24个,负电荷氨基酸有33个。