| [1] Duffield JS, Lupher M, Thannickal V J, et al. Host responses in tissue repair and fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol.2013;8:241-276.[2] Rouabhia M, Park HJ, Zhang Z. Electrically Activated Primary Human Fibroblasts Improve In Vitro and In Vivo Skin Regeneration. J Cell Physiol. 2016;231(8):1814-1821.[3] Nithiananthan S, Crawford A, Knock JC, et al. Physiological Fluid Flow Moderates Fibroblast Responses to TGF-beta1. J Cell Biochem.2016.[4] Pilling D, Vakil V, Cox N, et al. TNF-alpha-stimulated fibroblasts secrete lumican to promote fibrocyte differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(38):11929-11934.[5] Alase AA, El-Sherbiny YM, Vital EM, et al.IFNlambda Stimulates MxA Production in Human Dermal Fibroblasts via a MAPK-Dependent STAT1-Independent Mechanism. J Invest Dermatol.2015;135(12):2935-2943.[6] Kendall RT, Feghali-Bostwick CA. Fibroblasts in fibrosis: novel roles and mediators. Front Pharmacol.2014;5:123.[7] Jang YH, Koo GB, Kim JY, et al.Prolonged activation of ERK contributes to the photorejuvenation effect in photodynamic therapy in human dermal fibroblasts. J Invest Dermatol.2013; 133(9):2265-2275.[8] Sriram G, Bigliardi PL, Bigliardi-Qi M. Fibroblast heterogeneity and its implications for engineering organotypic skin models in vitro. Eur J Cell Biol. 2015;94(11):483-512.[9] Takashima A. Establishment of fibroblast cultures. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2001;Chapter 2:1-2.[10] Nahm WK, Zhou L, Falanga V. Sustained ability for fibroblast outgrowth from stored neonatal foreskin: a model for studying mechanisms of fibroblast outgrowth. J Dermatol Sci.2002; 28(2):152-158.[11] Hsia LT, Ashley N, Ouaret D, et al. Myofibroblasts are distinguished from activated skin fibroblasts by the expression of AOC3 and other associated markers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2016;113(15):E2162-E2171.[12] 张卓然. 培养细胞学与细胞培养技术[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2004.[13] 谭玉珍. 实用细胞培养技术[M].北京: 高等教育出版社, 2010.[14] 章静波. 组织和细胞培养技术[M]. 3版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2014.[15] 医疗机构管理条例[J]. 中华人民共和国国务院公报, 1994,(3): 83-89.[16] Pandamooz S, Hadipour A, Akhavan-Niaki H, et al. Short exposure to collagenase and coculture with mouse embryonic pancreas improve human dermal fibroblast culture. Biotechnol Appl Biochem.2012;59(3):254-261.[17] Attia-Vigneau J, Terryn C, Lorimier S, et al. Regeneration of human dermis by a multi-headed peptide. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134(1):58-67.[18] Myllyla RM, Haapasaari KM, Lehenkari P, et al. Bone morphogenetic proteins 4 and 2/7 induce osteogenic differentiation of mouse skin derived fibroblast and dermal papilla cells. Cell Tissue Res.2014;355(2):463-470.[19] Wang H, Van Blitterswijk CA, Bertrand-De HM, et al.Improved enzymatic isolation of fibroblasts for the creation of autologous skin substitutes. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim.2004; 40(8-9):268-277.[20] 宋瑞,卞徽宁,赖文,等. 碱性成纤维细胞生长因子对增生性瘢痕与正常皮肤成纤维细胞胶原、纤维连接蛋白表达的影响(英文)[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(41):7784-7790.[21] Chang Y, Guo K, Li Q, et al. Multiple Directional Differentiation Difference of Neonatal Rat Fibroblasts from Six Organs. Cell Physiol Biochem.2016;39(1):157-171.[22] Stenn KS, Link R,Moellmann G,et al.Dispase, a neutral protease from Bacillus polymyxa, is a powerful fibronectinase and type IV collagenase. J Invest Dermatol.1989;93(2): 287-290.[23] Yamato M, Utsumi M, Kushida A, et al. Thermo-responsive culture dishes allow the intact harvest of multilayered keratinocyte sheets without dispase by reducing temperature. Tissue Eng.2001;7(4):473-480.[24] Schaefer BM, Wallich R,Schmolke K, et al. Immunohistochemical and molecular characterization of cultured keratinocytes after dispase-mediated detachment from the growth substratum. Exp Dermatol.2000;9(1):58-64.[25] 陆新,韩春茂.皮肤组织工程进展[J].中华烧伤杂志, 2003,19(z1): 72-74.[26] 李伟,伍津津,吴国选,等. 人角质形成细胞库的建立[J]. 第三军医大学学报, 2004,26(11):987-989.[27] 毛一雷,徐海峰. 创口的处理与难点[J].中国实用外科杂志, 2011, 31(1):69-71.[28] Patriota LL, Procopio TF, de Souza MF, et al. A Trypsin Inhibitor from Tecoma stans Leaves Inhibits Growth and Promotes ATP Depletion and Lipid Peroxidation in Candida albicans and Candida krusei. Front Microbiol.2016;7:611.[29] 王志强,梁锐,陈明清,等. 胰蛋白酶消化法和组织块法原代培养人包皮成纤维细胞的比较[J]. 生命科学研究, 2012,16(3): 242-247.[30] Sinclair JA, Henderson C, Tettey JN, et al.The influence of the choice of digestion enzyme used to prepare rat hepatocytes on xenobiotic uptake and efflux. Toxicol In Vitro.2013;27(1): 451-457.[31] Agley CC, Rowlerson AM, Velloso CP, et al.Isolation and quantitative immunocytochemical characterization of primary myogenic cells and fibroblasts from human skeletal muscle.J Vis Exp.2015;(95):52049. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
胶原酶:按其存在的方式不同可分为人体内源性胶原酶和药用胶原酶两种。人体内源性胶原酶是指人体内部本身所具有的胶原酶,如牙龈、触膜等上皮组织和关节滑膜、椎间盘内都不同程度的存在着这种胶原酶,它在体内胶原蛋白的分解过程中发挥着不可或缺的作用。药用胶原酶是指利用生物制药的高科技手段从溶组织梭状芽孢杆菌的发酵液中提取、纯化并精制而得的白色或类白色无菌冻干粉针生物制剂。
酶消化法:酶消化法是指利用蛋白酶,通过消化分解组织块,从而得到单个细胞的方法,是目前科学研究中最常用的提取原代细胞和将融合细胞分离为单个细胞的方法。
文题释义:
胶原酶:按其存在的方式不同可分为人体内源性胶原酶和药用胶原酶两种。人体内源性胶原酶是指人体内部本身所具有的胶原酶,如牙龈、触膜等上皮组织和关节滑膜、椎间盘内都不同程度的存在着这种胶原酶,它在体内胶原蛋白的分解过程中发挥着不可或缺的作用。药用胶原酶是指利用生物制药的高科技手段从溶组织梭状芽孢杆菌的发酵液中提取、纯化并精制而得的白色或类白色无菌冻干粉针生物制剂。
酶消化法:酶消化法是指利用蛋白酶,通过消化分解组织块,从而得到单个细胞的方法,是目前科学研究中最常用的提取原代细胞和将融合细胞分离为单个细胞的方法。.jpg) 文题释义:
胶原酶:按其存在的方式不同可分为人体内源性胶原酶和药用胶原酶两种。人体内源性胶原酶是指人体内部本身所具有的胶原酶,如牙龈、触膜等上皮组织和关节滑膜、椎间盘内都不同程度的存在着这种胶原酶,它在体内胶原蛋白的分解过程中发挥着不可或缺的作用。药用胶原酶是指利用生物制药的高科技手段从溶组织梭状芽孢杆菌的发酵液中提取、纯化并精制而得的白色或类白色无菌冻干粉针生物制剂。
酶消化法:酶消化法是指利用蛋白酶,通过消化分解组织块,从而得到单个细胞的方法,是目前科学研究中最常用的提取原代细胞和将融合细胞分离为单个细胞的方法。
文题释义:
胶原酶:按其存在的方式不同可分为人体内源性胶原酶和药用胶原酶两种。人体内源性胶原酶是指人体内部本身所具有的胶原酶,如牙龈、触膜等上皮组织和关节滑膜、椎间盘内都不同程度的存在着这种胶原酶,它在体内胶原蛋白的分解过程中发挥着不可或缺的作用。药用胶原酶是指利用生物制药的高科技手段从溶组织梭状芽孢杆菌的发酵液中提取、纯化并精制而得的白色或类白色无菌冻干粉针生物制剂。
酶消化法:酶消化法是指利用蛋白酶,通过消化分解组织块,从而得到单个细胞的方法,是目前科学研究中最常用的提取原代细胞和将融合细胞分离为单个细胞的方法。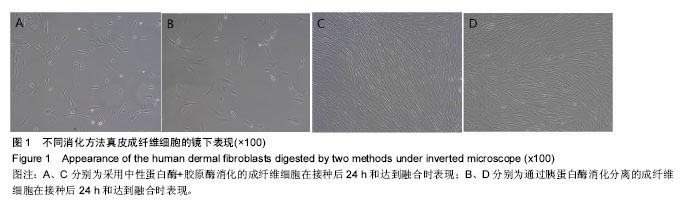


.jpg) 文题释义:
胶原酶:按其存在的方式不同可分为人体内源性胶原酶和药用胶原酶两种。人体内源性胶原酶是指人体内部本身所具有的胶原酶,如牙龈、触膜等上皮组织和关节滑膜、椎间盘内都不同程度的存在着这种胶原酶,它在体内胶原蛋白的分解过程中发挥着不可或缺的作用。药用胶原酶是指利用生物制药的高科技手段从溶组织梭状芽孢杆菌的发酵液中提取、纯化并精制而得的白色或类白色无菌冻干粉针生物制剂。
酶消化法:酶消化法是指利用蛋白酶,通过消化分解组织块,从而得到单个细胞的方法,是目前科学研究中最常用的提取原代细胞和将融合细胞分离为单个细胞的方法。
文题释义:
胶原酶:按其存在的方式不同可分为人体内源性胶原酶和药用胶原酶两种。人体内源性胶原酶是指人体内部本身所具有的胶原酶,如牙龈、触膜等上皮组织和关节滑膜、椎间盘内都不同程度的存在着这种胶原酶,它在体内胶原蛋白的分解过程中发挥着不可或缺的作用。药用胶原酶是指利用生物制药的高科技手段从溶组织梭状芽孢杆菌的发酵液中提取、纯化并精制而得的白色或类白色无菌冻干粉针生物制剂。
酶消化法:酶消化法是指利用蛋白酶,通过消化分解组织块,从而得到单个细胞的方法,是目前科学研究中最常用的提取原代细胞和将融合细胞分离为单个细胞的方法。