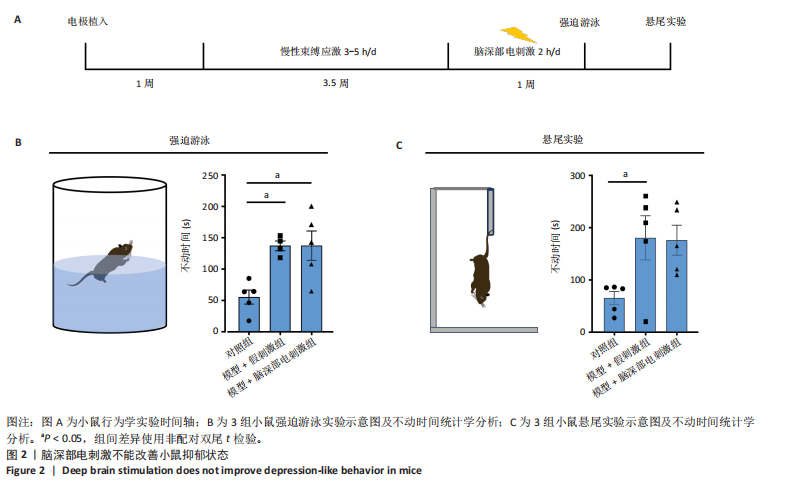
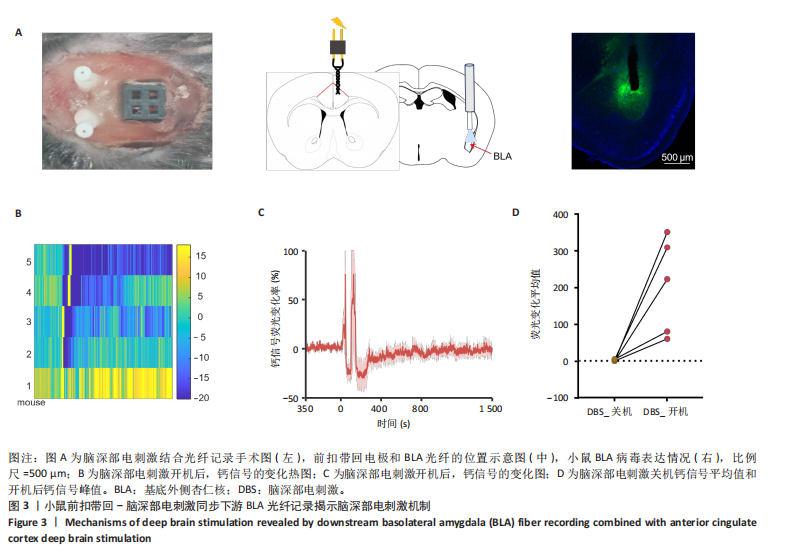
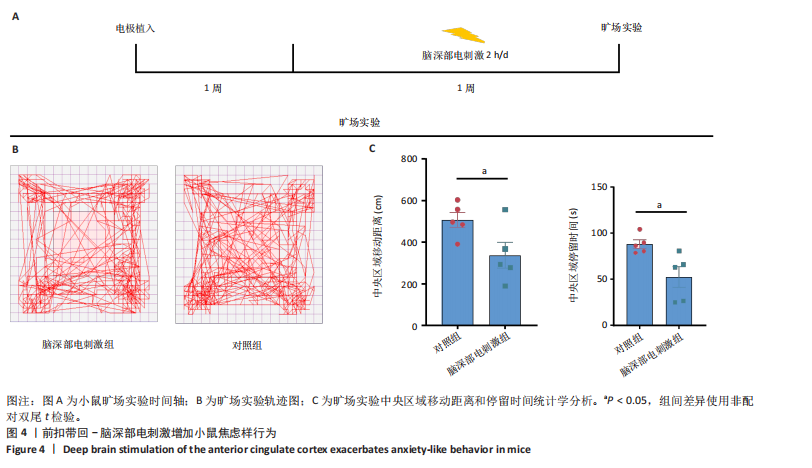
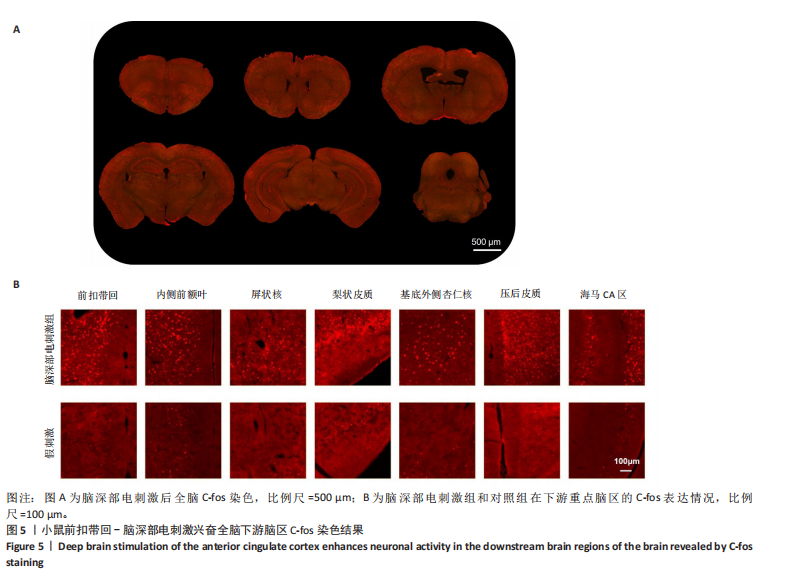
[1] BROMET E, ANDRADE LH, HWANG I, et al. Cross-national epidemiology of DSM-IV major depressive episode. BMC medicine. 2011;9:90.
[2] GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators.Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet (London, England). 2018;392(10159): 1789-1858.
[3] WALKER ER, MCGEE RE, DRUSS BG. Mortality in mental disorders and global disease burden implications: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. 2015;72(4):334-341.
[4] ROE-SEPOWITZ D. Adolescent female murderers: characteristics and treatment implications. Am J Orthop. 2007;77(3):489-496.
[5] GAYNES BN, LUX L, GARTLEHNER G, et al. Defining treatment-resistant depression. Depress Anxiety. 2020;37(2):134-145.
[6] MONCRIEFF J, COOPER R E, STOCKMANN T, et al. The serotonin theory of depression: a systematic umbrella review of the evidence. Molecular Psychiatry. 2023;28(8):3243-3256.
[7] SANDOVAL-PISTORIUS SS, HACKER ML, WATERS AC, et al. Advances in Deep Brain Stimulation: From Mechanisms to Applications. J Neurosci. 2023;43(45):7575-7586.
[8] GILBERT Z, MASON X, SEBASTIAN R, et al. A review of neurophysiological effects and efficiency of waveform parameters in deep brain stimulation. Clin Neurophysiol. 2023;152:93-111.
[9] JOHNSON KA, OKUN MS, SCANGOS KW, et al. Deep brain stimulation for refractory major depressive disorder: a comprehensive review. Mol Psychiatry. 2024;29(4):1075-1087.
[10] MAYBERG HS, LOZANO AM, VOON V, et al. Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Neuron. 2005;45(5):651-660.
[11] HOLTZHEIMER PE, HUSAIN MM, LISANBY SH, et al. Subcallosal cingulate deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: a multisite, randomised, sham-controlled trial. lancet Psychiatry. 2017;4(11):839-849.
[12] RAMASUBBU R, ANDERSON S, HAFFENDEN A, et al. Double-blind optimization of subcallosal cingulate deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: a pilot study. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2013;38(5):325-332.
[13] UDUPA K, CHEN R. The mechanisms of action of deep brain stimulation and ideas for the future development. Prog Neurobiol. 2015;133:27-49.
[14] KRAUSS JK, LIPSMAN N, AZIZ T, et al. Technology of deep brain stimulation: current status and future directions. Nat Rev Neurol. 2021;17(2):75-87.
[15] CHIKEN S, NAMBU A. Mechanism of Deep Brain Stimulation: Inhibition, Excitation, or Disruption? Neuroscientist. 2016;22(3):313-322.
[16] SHARIM J, POURATIAN N. Anterior Cingulotomy for the Treatment of Chronic Intractable Pain: A Systematic Review. Pain Physician. 2016; 19(8): 537-550.
[17] BARTHAS F, HUMO M, GILSBACH R, et al. Cingulate Overexpression of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Phosphatase-1 as a Key Factor for Depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2017;82(5):370-379.
[18] KIM KS, HAN PL. Optimization of chronic stress paradigms using anxiety- and depression-like behavioral parameters. J Neurosci Res. 2006;83(3):497-507.
[19] LI Y, ZHONG W, WANG D, et al. Serotonin neurons in the dorsal raphe nucleus encode reward signals. Nat Commun. 2016;7:10503.
[20] HAMANI C, MAYBERG H, STONE S, et al. The subcallosal cingulate gyrus in the context of major depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2011;69(4):301-308.
[21] CAI X, PADOA-SCHIOPPA C. Neuronal encoding of subjective value in dorsal and ventral anterior cingulate cortex. J Neurosci. 2012; 32(11):3791-3808.
[22] PALOMERO-GALLAGHER N, HOFFSTAEDTER F, MOHLBERG H, et al. Human Pregenual Anterior Cingulate Cortex: Structural, Functional, and Connectional Heterogeneity. Cereb Cortex. 2019;29(6):2552-2574.
[23] YUAN Z, QI Z, WANG R, et al. A corticoamygdalar pathway controls reward devaluation and depression using dynamic inhibition code. Neuron. 2023;111(23):3837-53.e5.
[24] GAO Y, GAO D, ZHANG H, et al. BLA DBS improves anxiety and fear by correcting weakened synaptic transmission from BLA to adBNST and CeL in a mouse model of foot shock. Cell Rep. 2024; 43(2):113766.
[25] LOWET E, KONDABOLU K, ZHOU S, et al. Deep brain stimulation creates informational lesion through membrane depolarization in mouse hippocampus. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):7709.
[26] PUIGDEMONT D, PéREZ-EGEA R, PORTELLA MJ, et al. Deep brain stimulation of the subcallosal cingulate gyrus: further evidence in treatment-resistant major depression. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012;15(1):121-133.
[27] LIN ZJ, GU X, GONG WK, et al. Stimulation of an entorhinal-hippocampal extinction circuit facilitates fear extinction in a post-traumatic stress disorder model. J Clin Invest. 2024;134(22):e181095.
[28] SONG N, LIU Z, GAO Y, et al. NAc-DBS corrects depression-like behaviors in CUMS mouse model via disinhibition of DA neurons in the VTA. Mol Psychiatry. 2024;29(5):1550-1566.
[29] ASHKAN K, ROGERS P, BERGMAN H, et al. Insights into the mechanisms of deep brain stimulation. Nat Rev Neurol. 2017;13(9):548-554.
[30] PIALLAT B, CHABARDèS S, DEVERGNAS A, et al. Monophasic but not biphasic pulses induce brain tissue damage during monopolar high-frequency deep brain stimulation. Neurosurgery. 2009;64(1):156-162; discussion 62-63.
[31] BÜHNING F, MIGUEL TELEGA L, TONG Y, et al. Electrophysiological and molecular effects of bilateral deep brain stimulation of the medial forebrain bundle in a rodent model of depression. Exp Neurol. 2022;355:114122.
[32] DOURNES C, BEESKÉ S, BELZUNG C, et al. Deep brain stimulation in treatment-resistant depression in mice: comparison with the CRF1 antagonist, SSR125543.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2013;40:213-220.
[33] ZHANG Y, MA L, ZHANG X, et al. Deep brain stimulation in the lateral habenula reverses local neuronal hyperactivity and ameliorates depression-like behaviors in rats. Neurobiol Dis. 2023;180:106069.
[34] SCHOR JS, GONZALEZ MONTALVO I, SPRATT PWE, et al. Therapeutic deep brain stimulation disrupts movement-related subthalamic nucleus activity in parkinsonian mice. Elife. 2022;11:e75253.
[35] VAN DEN BOOM BJG, ELHAZAZ-FERNANDEZ A, RASMUSSEN PA, et al. Unraveling the mechanisms of deep-brain stimulation of the internal capsule in a mouse model. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):5385.
[36] GONG W K, LI X, WANG L, et al. Prefrontal FGF1 Signaling is Required for Accumbal Deep Brain Stimulation Treatment of Addiction. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025;12(16):e2413370.
[37] SPIX TA, NANIVADEKAR S, TOONG N, et al. Population-specific neuromodulation prolongs therapeutic benefits of deep brain stimulation. Science. 2021;374(6564):201-206.
[38] MIGUEL TELEGA L, ASHOURI VAJARI D, STIEGLITZ T, et al. New Insights into In Vivo Dopamine Physiology and Neurostimulation: A Fiber Photometry Study Highlighting the Impact of Medial Forebrain Bundle Deep Brain Stimulation on the Nucleus Accumbens. Brain Sci. 2022;12(8):1105.
[39] SCHOR JS, NELSON AB. Multiple stimulation parameters influence efficacy of deep brain stimulation in parkinsonian mice. J Clin Invest. 2019;129(9):3833-3838.
[40] PAULK AC, ZELMANN R, CROCKER B, et al. Local and distant cortical responses to single pulse intracranial stimulation in the human brain are differentially modulated by specific stimulation parameters.Brain Stimul. 2022;15(2):491-508.
[41] MURPHY KR, FARRELL JS, BENDIG J, et al. Optimized ultrasound neuromodulation for non-invasive control of behavior and physiology. Neuron. 2024;112(19):3252-66.e5.
[42] VALVERDE S, VANDECASTEELE M, PIETTE C, et al.Deep brain stimulation-guided optogenetic rescue of parkinsonian symptoms. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):2388.
[43] ALEXANDER L, JELEN LA, MEHTA MA, et al. The anterior cingulate cortex as a key locus of ketamine’s antidepressant action. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021;127:531-554.
[44] DIENER C, KUEHNER C, BRUSNIAK W, et al. A meta-analysis of neurofunctional imaging studies of emotion and cognition in major depression. NeuroImage. 2012;61(3):677-685.
[45] HOLMES SE, HINZ R, CONEN S, et al. Elevated Translocator Protein in Anterior Cingulate in Major Depression and a Role for Inflammation in Suicidal Thinking: A Positron Emission Tomography Study. Biol Psychiatry. 2018;83(1):61-69.
[46] SELLMEIJER J, MATHIS V, HUGEL S, et al. Hyperactivity of Anterior Cingulate Cortex Areas 24a/24b Drives Chronic Pain-Induced Anxiodepressive-like Consequences. J Neurosci. 2018;38(12):3102-3115.
[47] MAYBERG HS, LIOTTI M, BRANNAN SK, et al. Reciprocal limbic-cortical function and negative mood: converging PET findings in depression and normal sadness. Am J Psychiatry. 1999;156(5):675-682.
[48] PALOMERO-GALLAGHER N, EICKHOFF SB, HOFFSTAEDTER F, et al. Functional organization of human subgenual cortical areas: Relationship between architectonical segregation and connectional heterogeneity. Neuroimage. 2015;115:177-190.
[49] KISEL YS, LI A, WARREN N, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of deep brain stimulation for depression. Depress Anxiety. 2018;35(5):468-480.
[50] MAYBERG HS.Targeted electrode-based modulation of neural circuits for depression. J Clin Invest. 2009;119(4):717-725.
[51] CROWELL AL, RIVA-POSSE P, HOLTZHEIMER PE, et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Subcallosal Cingulate Deep Brain Stimulation for Treatment-Resistant Depression. Am J Psychiatry. 2019;176(11):949-956.
|