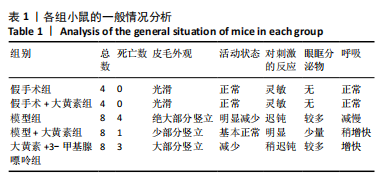
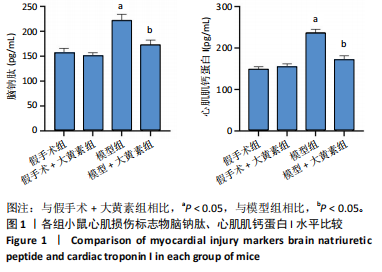
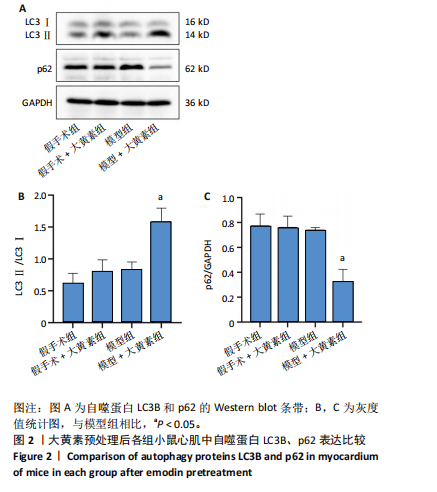
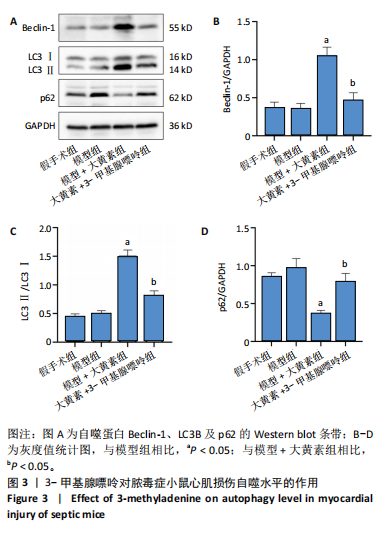
[1] PÓVOA P, COELHO L, DAL-PIZZOL F, et al. How to use biomarkers of infection or sepsis at the bedside: guide to clinicians. Intensive Care Med. 2023;49(2):142-153.
[2] LI Y, ZHANG L, ZHANG P, et al. Dehydrocorydaline Protects Against Sepsis-Induced Myocardial Injury Through Modulating the TRAF6/NF-κB Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:709604.
[3] WANG Z, QIANG X, PENG Y, et al. Design and synthesis of salidroside analogs and their bioactivity against septic myocardial injury. Bioorg Chem. 2023;138:106609.
[4] FRENCKEN JF, VAN SMEDEN M, VAN DE GROEP K, et al. Etiology of Myocardial Injury in Critically Ill Patients with Sepsis: A Cohort Study. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2022;19(5):773-780.
[5] BI CF, LIU J, YANG LS, et al. Research Progress on the Mechanism of Sepsis Induced Myocardial Injury. J Inflamm Res. 2022;15:4275-4290.
[6] GAO Y, LIU J, LI K, et al. Metformin Alleviates Sepsis-Associated Myocardial Injury by Enhancing AMP-Activated Protein Kinase/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Signaling Pathway-Mediated Autophagy. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2023;82(4):308-317.
[7] KLIONSKY DJ, PETRONI G, AMARAVADI RK, et al. Autophagy in major human diseases. EMBO J. 2021;40(19):e108863.
[8] SUN Y, CAI Y, ZANG QS. Cardiac Autophagy in Sepsis. Cells. 2019;8(2): 141.
[9] CAO W, LI J, YANG K, et al. An overview of autophagy: Mechanism, regulation and research progress. Bull Cancer. 2021;108(3):304-322.
[10] IRIONDO MN, ETXANIZ A, VARELA YR, et al. LC3 subfamily in cardiolipin-mediated mitophagy: a comparison of the LC3A, LC3B and LC3C homologs. Autophagy. 2022;18(12):2985-3003.
[11] SUN Y, YAO X, ZHANG QJ, et al. Beclin-1-Dependent Autophagy Protects the Heart During Sepsis. Circulation. 2018;138(20):2247-2262.
[12] SHU X, SUN Y, SUN X, et al. The effect of fluoxetine on astrocyte autophagy flux and injured mitochondria clearance in a mouse model of depression. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(8):577.
[13] HO J, YU J, WONG SH, et al. Autophagy in sepsis: Degradation into exhaustion? Autophagy. 2016;12(7):1073-1082.
[14] ZHANG P, LI Y, FU Y, et al. Inhibition of Autophagy Signaling via 3-methyladenine Rescued Nicotine-Mediated Cardiac Pathological Effects and Heart Dysfunctions. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(8):1349-1362.
[15] BARICHELLO T, GENEROSO JS, SINGER M, et al. Biomarkers for sepsis: more than just fever and leukocytosis-a narrative review. Crit Care. 2022;26(1):14.
[16] MCDONALD SJ, VANDERVEEN BN, VELAZQUEZ KT, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Emodin for Gastrointestinal Cancers. Integr Cancer Ther. 2022;21:15347354211067469.
[17] QIN B, ZENG Z, XU J, et al. Emodin inhibits invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via regulating autophagy-mediated degradation of snail and β-catenin. BMC Cancer. 2022;22(1):671.
[18] 徐瑞明,邵峥谊,王大为,等.大黄素对脓毒症大鼠心肌损伤的保护作用 [J].西部医学,2020,32(10):1443-1446.
[19] 田勇,周颖,古雍翔,等.二甲双胍预处理诱导心脏自噬减轻脓毒症小鼠的心肌损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(28):4469-4476.
[20] GAO LL, WANG ZH, MU YH, et al. Emodin Promotes Autophagy and Prevents Apoptosis in Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy through Activating BDNF/TrkB Signaling. Pathobiology. 2022;89(3):135-145.
[21] 田勇,周颖,古雍翔,等.二甲双胍诱导心肌细胞自噬对脓毒症小鼠心肌损伤的保护机制[J].安徽医科大学学报,2024,59(1):92-98.
[22] PEI XB, LIU B. Research Progress on the Mechanism and Management of Septic Cardiomyopathy: A Comprehensive Review. Emerg Med Int. 2023;2023:8107336.
[23] ZOU HX, QIU BQ, ZHANG ZY, et al. Dysregulated autophagy-related genes in septic cardiomyopathy: Comprehensive bioinformatics analysis based on the human transcriptomes and experimental validation. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:923066.
[24] TANG R, JIA L, LI Y, et al. Narciclasine attenuates sepsis-induced myocardial injury by modulating autophagy. Aging (Albany NY). 2021; 13(11):15151-15163.
[25] WONG SQ, KUMAR AV, MILLS J, et al. Autophagy in aging and longevity. Hum Genet. 2020;139(3):277-290.
[26] GROSS AS, GRAEf M. Mechanisms of Autophagy in Metabolic Stress Response. J Mol Biol. 2020;432(1):28-52.
[27] LIU C, LIU Y, CHEN H, et al. Myocardial injury: where inflammation and autophagy meet. Burns Trauma. 2023;11:tkac062.
[28] DU J, ZHOU Y. Propofol reduces lipopolysaccharide‑induced cardiomyocyte injury in sepsis by activating SIRT1‑mediated autophagy. Exp Ther Med. 2023;25(4):187.
[29] WANG X, XIE D, DAI H, et al. Clemastine protects against sepsis-induced myocardial injury in vivo and in vitro. Bioengineered. 2022;13(3): 7134-7146.
[30] QIN GW, LU P, PENG L, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 Inhibits Cardiomyocyte Autophagy via PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway and Reduces Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Am J Chin Med. 2021;49(8): 1913-1927.
[31] WANG X, YANG S, LI Y, et al. Role of emodin in atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases: Pharmacological effects, mechanisms, and potential therapeutic target as a phytochemical. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;161:114539.
[32] SU J, ZHOU F, WU S, et al. Research Progress on Natural Small-Molecule Compounds for the Prevention and Treatment of Sepsis. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(16):12732.
[33] CUI Y, CHEN LJ, HUANG T, et al. The pharmacology, toxicology and therapeutic potential of anthraquinone derivative emodin. Chin J Nat Med. 2020;18(6):425-435.
[34] DAI S, YE B, CHEN L, et al. Emodin alleviates LPS-induced myocardial injury through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Phytother Res. 2021;35(9):5203-5213.
[35] TU YJ, TAN B, JIANG L, et al. Emodin Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation by Activating Autophagy in RAW 264.7 Cells. Chin J Integr Med. 2021;27(5):345-352.
[36] LIU H, WANG Q, SHI G, et al. Emodin Ameliorates Renal Damage and Podocyte Injury in a Rat Model of Diabetic Nephropathy via Regulating AMPK/mTOR-Mediated Autophagy Signaling Pathway. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021;14:1253-1266.
[37] WU P, XIAO Y, QING L, et al. Emodin activates autophagy to suppress oxidative stress and pyroptosis via mTOR-ULK1 signaling pathway and promotes multi-territory perforator flap survival. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024;704:149688.
[38] SHE H, TAN L, DU Y, et al. VDAC2 malonylation participates in sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction via mitochondrial-related ferroptosis. Int J Biol Sci. 2023;19(10):3143-3158.
[39] SHEN XD, ZHANG HS, ZHANG R, et al. Progress in the Clinical Assessment and Treatment of Myocardial Depression in Critically Ill Patient with Sepsis. J Inflamm Res. 2022;15:5483-5490.
[40] LIU FJ, GU TJ, WEI DY. Emodin alleviates sepsis-mediated lung injury via inhibition and reduction of NF-kB and HMGB1 pathways mediated by SIRT1. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2022;38(3):253-260.
[41] GUO R, LI Y, HAN M, et al. Emodin attenuates acute lung injury in Cecal-ligation and puncture rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;85:106626.
[42] DONG Y, ZHANG L, JIANG Y, et al. Emodin reactivated autophagy and alleviated inflammatory lung injury in mice with lethal endotoxemia. Exp Anim. 2019;68(4):559-568.
[43] CHANG X, HE Y, WANG L, et al. Puerarin Alleviates LPS-Induced H9C2 Cell Injury by Inducing Mitochondrial Autophagy. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2022;80(4):600-608.
[44] ZHANG W, ZHANG J. Semaglutide Pretreatment Induces Cardiac Autophagy to Reduce Myocardial Injury in Septic Mice. Discov Med. 2023;35(178):853-860.
[45] WU B, SONG H, FAN M, et al. Luteolin attenuates sepsis‑induced myocardial injury by enhancing autophagy in mice. Int J Mol Med. 2020;45(5):1477-1487. |