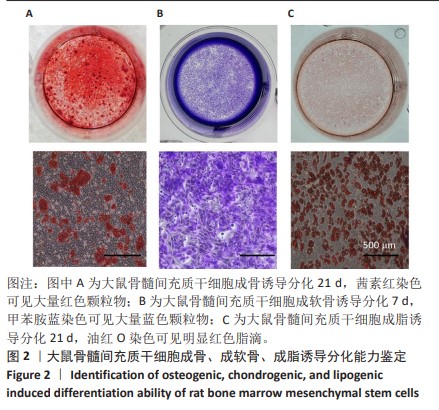
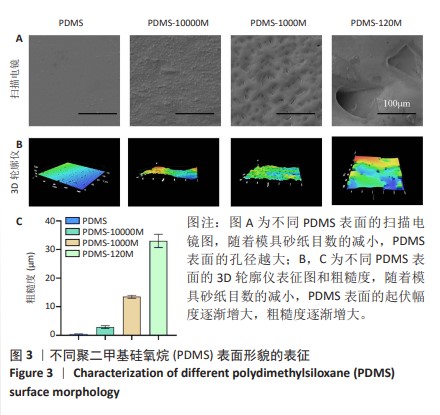
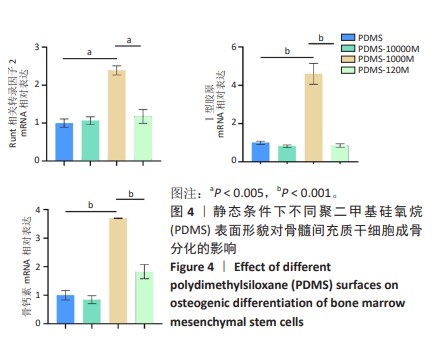
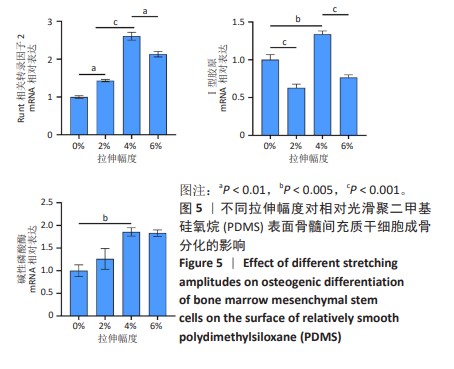
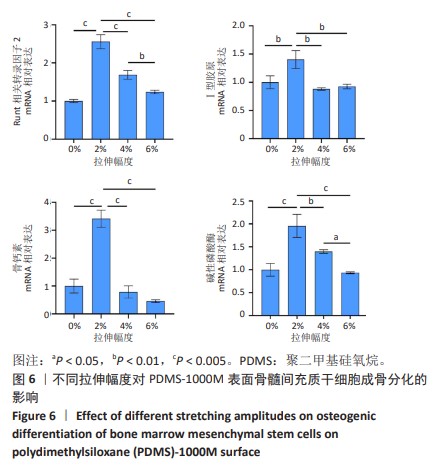
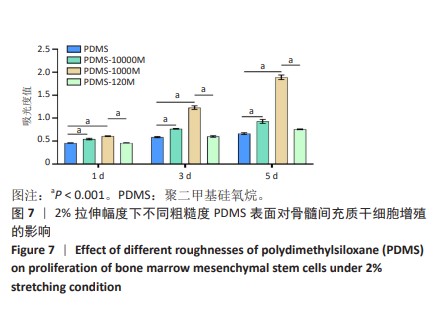
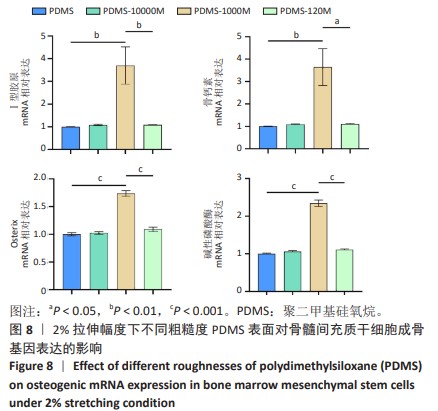
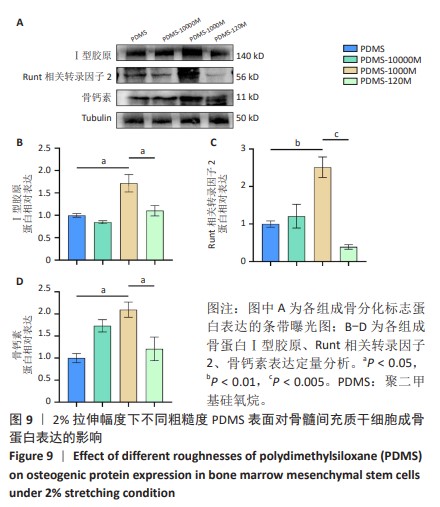
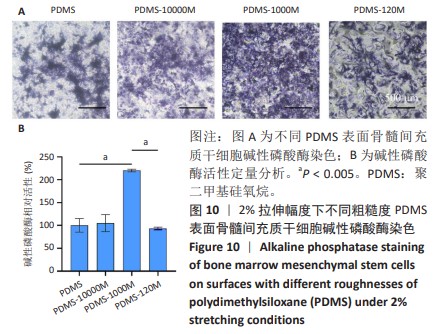
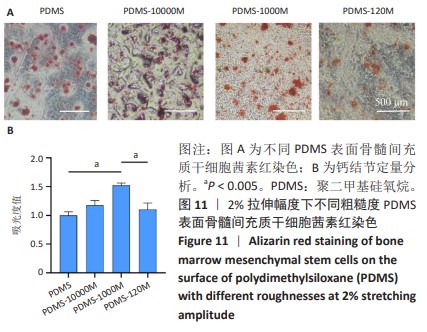
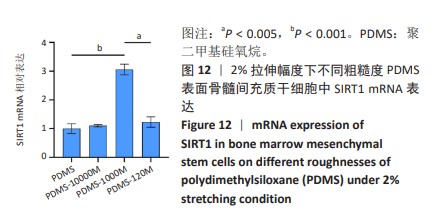
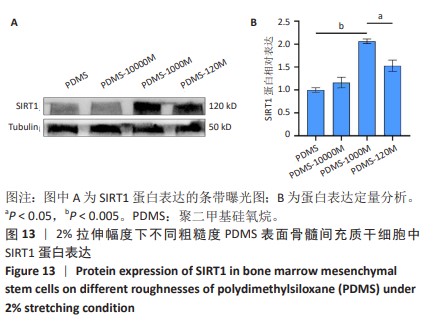
[1] CHEN Q, SHOU P, ZHENG C, et al. Fate decision of mesenchymal stem cells: adipocytes or osteoblasts? Cell Death Differ. 2016;23(7): 1128-1139.
[2] CHEN D, LIU S, CHU X, et al. Osteogenic Differentiation Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using Single Cell Multiomic Analysis. Genes (Basel). 2023;14(10):1871.
[3] GAO H, DONG H, ZHENG J, et al. LINC01119 negatively regulates osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells via the Wnt pathway by targeting FZD4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):43.
[4] LIU Y, PENG L, LI L, et al. 3D-bioprinted BMSC-laden biomimetic multiphasic scaffolds for efficient repair of osteochondral defects in an osteoarthritic rat model. Biomaterials. 2021;279:121216.
[5] ARTHUR A, GRONTHOS S. Clinical Application of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells to Repair Skeletal Tissue. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(24):9759.
[6] ERENAY B, SAĞLAM ASY, GARIPCAN B, et al. Bone surface mimicked PDMS membranes stimulate osteoblasts and calcification of bone matrix. Biomater Adv. 2022;142:213170.
[7] GUO Q, LIU Y, SUN R, et al. Mechanical stimulation induced osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs through TWIST/E2A/p21 axis. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(5):BSR20193876.
[8] ZHANG R, WAN J, WANG H. Mechanical strain triggers differentiation of dental mesenchymal stem cells by activating osteogenesis-specific biomarkers expression. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(1):233-244.
[9] LIN S, LI J, SHAO J, et al. Anisotropic magneto-mechanical stimulation on collagen coatings to accelerate osteogenesis. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022;210:112227.
[10] SALIFU AA, OBAYEMI JD, UZONWANNE VO, et al. Mechanical stimulation improves osteogenesis and the mechanical properties of osteoblast-laden RGD-functionalized polycaprolactone/hydroxyapatite scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2020;108(12):2421-2434.
[11] SUMANASINGHE RD, BERNACKI SH, LOBOA EG. Osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells in collagen matrices: effect of uniaxial cyclic tensile strain on bone morphogenetic protein (BMP-2) mRNA expression. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(12):3459-3465.
[12] DONG L, SONG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Mechanical stretch induces osteogenesis through the alternative activation of macrophages. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(9):6376-6390.
[13] ZHANG D, ZHANG R, SONG X, et al. Uniaxial Cyclic Stretching Promotes Chromatin Accessibility of Gene Loci Associated With Mesenchymal Stem Cells Morphogenesis and Osteogenesis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:664545.
[14] MAEDA E, ATSUMI Y, ISHIGURO M, et al. Shape-dependent regulation of differentiation lineages of bone marrow-derived cells under cyclic stretch. J Biomech. 2019;96:109371.
[15] BAO M, XIE J, HUCK WTS. Recent Advances in Engineering the Stem Cell Microniche in 3D. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2018;5(8):1800448.
[16] LIU S, TAO R, WANG M, et al. Regulation of Cell Behavior by Hydrostatic Pressure. Appl Mech Rev. 2019;71(4):0408031-4080313.
[17] DE BRUYN H, CHRISTIAENS V, DOORNEWAARD R, et al. Implant surface roughness and patient factors on long-term peri-implant bone loss. Periodontol 2000. 2017;73(1):218-227.
[18] BOYAN BD, BERGER MB, NELSON FR, et al. The Biological Basis for Surface-dependent Regulation of Osteogenesis and Implant Osseointegration. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2022;30(13):e894-e898.
[19] LU T, SUN Z, JIA C, et al. Roles of irregularity of pore morphology in osteogenesis of Voronoi scaffolds: From the perspectives of MSC adhesion and mechano-regulated osteoblast differentiation. J Biomech. 2023;151:111542.
[20] MANIVASAGAM VK, POPAT KC. Hydrothermally treated titanium surfaces for enhanced osteogenic differentiation of adipose derived stem cells. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;128:112315.
[21] LOLLOBRIGIDA M, LAMAZZA L, CAPUANO C, et al. Physical Profile and Impact of a Calcium-Incorporated Implant Surface on Preosteoblastic Cell Morphologic and Differentiation Parameters: A Comparative Analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2016;31(1):223-231.
[22] LI Y, XIAO Y, LIU C. The Horizon of Materiobiology: A Perspective on Material-Guided Cell Behaviors and Tissue Engineering. Chem Rev. 2017;117(5):4376-4421.
[23] ZHU GY, LIU YH, LIU W, et al. Surface Epitaxial Nano-Topography Facilitates Biomineralization to Promote Osteogenic Differentiation and Osteogenesis. ACS Omega. 2021;6(33):21792-21800.
[24] MONTEIRO NO, CASANOVA MR, FANGUEIRO JF, et al. The biomimetic surface topography ofRubus fruticosusleaves stimulate the induction of osteogenic differentiation of rBMSCs. Biomed Mater. 2023;18(3). doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/acc55f.
[25] SARUTA J, SATO N, ISHIJIMA M, et al. Disproportionate Effect of Sub-Micron Topography on Osteoconductive Capability of Titanium. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(16):4027.
[26] 唐丽灵,潘君,王远亮,等.骨的应力集中效应 [J].医用生物力学, 2002,17(3):189-192.
[27] ZHANG L, ZHENG YL, WANG R, et al. Exercise for osteoporosis: A literature review of pathology and mechanism. Front Immunol. 2022; 13:1005665.
[28] CHEN X, YAN J, HE F, et al. Mechanical stretch induces antioxidant responses and osteogenic differentiation in human mesenchymal stem cells through activation of the AMPK-SIRT1 signaling pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2018;126:187-201.
[29] 熊婉琦,李振豪,崔焱,等.生物力学作用对成骨细胞生物特性的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(21):3407-3412.
[30] 聂文忠,蒋光普,韩笑,等.骨质疏松患者骨水泥强化内固定系统的生物力学特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(21):3287-3292.
[31] SAUVE AA, WOLBERGER C, SCHRAMM VL, et al. The biochemistry of sirtuins. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75:435-465.
[32] XU C, WANG L, FOZOUNI P, et al. SIRT1 is downregulated by autophagy in senescence and ageing. Nat Cell Biol. 2020;22(10): 1170-1179.
[33] HE F, LI Q, SHENG B, et al. SIRT1 Inhibits Apoptosis by Promoting Autophagic Flux in Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells in the Key Stage of Degeneration via ERK Signal Pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021: 8818713.
[34] RADA P, PARDO V, MOBASHER MA, et al. SIRT1 Controls Acetaminophen Hepatotoxicity by Modulating Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018;28(13):1187-1208.
[35] PARDO PS, MOHAMED JS, LOPEZ MA, et al. Induction of Sirt1 by mechanical stretch of skeletal muscle through the early response factor EGR1 triggers an antioxidative response. J Biol Chem. 2011; 286(4):2559-2566.
[36] YANG L, LI Y, GONG R, et al. The Long Non-coding RNA-ORLNC1 Regulates Bone Mass by Directing Mesenchymal Stem Cell Fate. Mol Ther. 2019;27(2):394-410.
[37] LEE SI, PARK KH, KIM SJ, et al. Mechanical stress-activated immune response genes via Sirtuin 1 expression in human periodontal ligament cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 2012;168(1):113-124.
[38] LU Y, MA ZX, DENG R, et al. The SIRT1 activator SRT2104 promotes BMP9-induced osteogenic and angiogenic differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells. Mech Ageing Dev. 2022;207:111724.
[39] ZHOU L, CHEN X, LIU T, et al. Melatonin reverses H2 O2 -induced premature senescence in mesenchymal stem cells via the SIRT1-dependent pathway. J Pineal Res. 2015;59(2):190-205. |