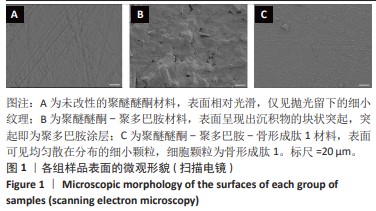
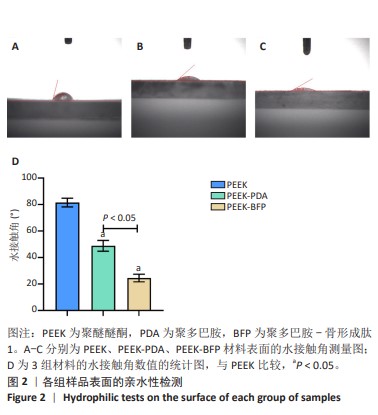
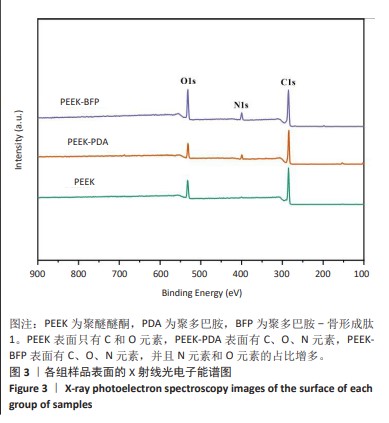
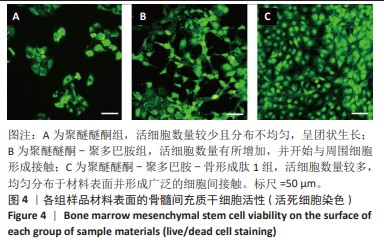
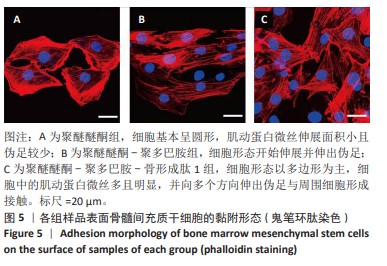
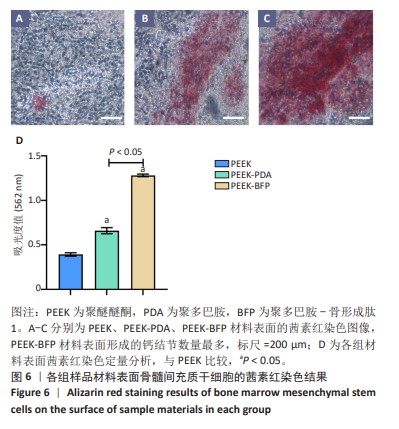
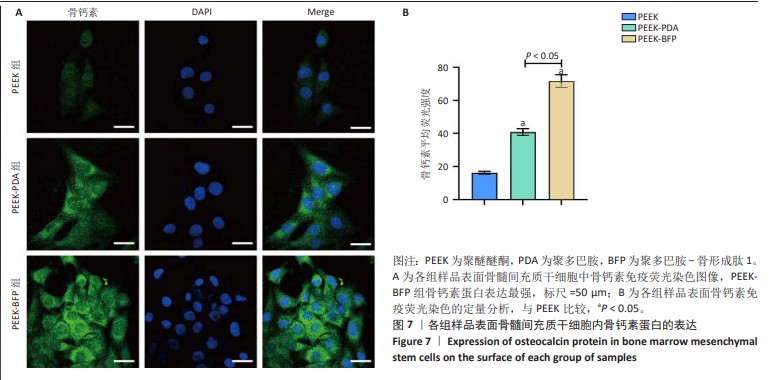
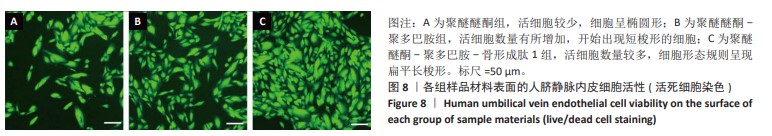
[1] HOTCHKISS KM, REDDY GB, HYZY SL, et al. Titanium surface characteristics, including topography and wettability, alter macrophage activation. Acta Biomater. 2016;31:425-434.
[2] SOUZA JCM, SORDI MB, KANAZAWA M, et al. Nano-scale modification of titanium implant surfaces to enhance osseointegration. Acta Biomater. 2019;94:112-131.
[3] PANAYOTOV IV, ORTI V, CUISINIER F, et al. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) for medical applications. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016;27(7):118.
[4] KATZER A, MARQUARDT H, WESTENDORF J, et al. Polyetheretherketone--cytotoxicity and mutagenicity in vitro. Biomaterials. 2002;23(8):1749-1759.
[5] FENG P, WU P, GAO C, et al. A Multimaterial Scaffold With Tunable Properties: Toward Bone Tissue Repair. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2018;5(6):1700817.
[6] YIN J, HAN Q, ZHANG J, et al. MXene-Based Hydrogels Endow Polyetheretherketone with Effective Osteogenicity and Combined Treatment of Osteosarcoma and Bacterial Infection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020; 12(41):45891-45903.
[7] WIESLI MG, ÖZCAN M. High-Performance Polymers and Their Potential Application as Medical and Oral Implant Materials: A Review. Implant Dent. 2015;24(4):448-457.
[8] KHATAYEVICH D, GUNGORMUS M, YAZICI H, et al. Biofunctionalization of materials for implants using engineered peptides. Acta Biomater. 2010; 6(12):4634-4641.
[9] YAKUFU M, WANG Z, WANG Y, et al. Covalently functionalized poly(etheretherketone) implants with osteogenic growth peptide (OGP) to improve osteogenesis activity. RSC Adv. 2020;10(17):9777-9785.
[10] LI M, BAI J, TAO H, et al. Rational integration of defense and repair synergy on PEEK osteoimplants via biomimetic peptide clicking strategy. Bioact Mater. 2022;8:309-324.
[11] SENATOV F, MAKSIMKIN A, CHUBRIK A, et al. Osseointegration evaluation of UHMWPE and PEEK-based scaffolds with BMP-2 using model of critical-size cranial defect in mice and push-out test. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021;119:104477.
[12] ANUSUYA GS, KANDASAMY M, JACOB RAJA SA, et al. Bone morphogenetic proteins: Signaling periodontal bone regeneration and repair. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2016;8(Suppl 1):S39-s41.
[13] SUN Z, OUYANG L, MA X, et al. Controllable and durable release of BMP-2-loaded 3D porous sulfonated polyetheretherketone (PEEK) for osteogenic activity enhancement. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;171:668-674.
[14] SAMPATH TK, VUKICEVIC S. Biology of bone morphogenetic protein in bone repair and regeneration: A role for autologous blood coagulum as carrier. Bone. 2020;141:115602.
[15] KIM HK, KIM JH, PARK DS, et al. Osteogenesis induced by a bone forming peptide from the prodomain region of BMP-7. Biomaterials. 2012;33(29): 7057-7063.
[16] XIANG M, ZHU M, YANG Z, et al. Dual-Functionalized Apatite Nanocomposites with Enhanced Cytocompatibility and Osteogenesis for Periodontal Bone Regeneration. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(3):1704-1714.
[17] WANG H, CHENG H, TANG X, et al. The synergistic effect of bone forming peptide-1 and endothelial progenitor cells to promote vascularization of tissue engineered bone. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(4):1008-1021.
[18] HONG CA, SON HY, NAM YS. Layer-by-layer siRNA/poly(L-lysine) Multilayers on Polydopamine-coated Surface for Efficient Cell Adhesion and Gene Silencing. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):7738.
[19] WANG H, LIN C, ZHANG X, et al. Mussel-Inspired Polydopamine Coating: A General Strategy To Enhance Osteogenic Differentiation and Osseointegration for Diverse Implants. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019; 11(7):7615-7625.
[20] GUO Q, CHEN J, WANG J, et al. Recent progress in synthesis and application of mussel-inspired adhesives. Nanoscale. 2020;12(3):1307-1324.
[21] BUSER D, SENNERBY L, DE BRUYN H. Modern implant dentistry based on osseointegration: 50 years of progress, current trends and open questions. Periodontol 2000. 2017;73(1):7-21.
[22] KAUSHIK N, NHAT NGUYEN L, KIM JH, et al. Strategies for Using Polydopamine to Induce Biomineralization of Hydroxyapatite on Implant Materials for Bone Tissue Engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(18): 6544.
[23] PANDEY C, ROKAYA D, BHATTARAI BP. Contemporary Concepts in Osseointegration of Dental Implants: A Review. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022: 6170452.
[24] ROMANOS GE, FISCHER GA, DELGADO-RUIZ R. Titanium Wear of Dental Implants from Placement, under Loading and Maintenance Protocols. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(3):1067.
[25] RAHMITASARI F, ISHIDA Y, KURAHASHI K, et al. PEEK with Reinforced Materials and Modifications for Dental Implant Applications. Dent J (Basel). 2017;5(4):35.
[26] ALFIERI ML, WEIL T, NG DYW, et al. Polydopamine at biological interfaces. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2022;305:102689.
[27] LEE H, RHO J, MESSERSMITH PB. Facile Conjugation of Biomolecules onto Surfaces via Mussel Adhesive Protein Inspired Coatings. Adv Mater. 2009;21(4):431-434.
[28] MENG X, ZHANG J, CHEN J, et al. KR-12 coating of polyetheretherketone (PEEK) surface via polydopamine improves osteointegration and antibacterial activity in vivo. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(44):10190-10204.
[29] WANG Y, ZHANG J, GAO T, et al. Covalent immobilization of DJK-5 peptide on porous titanium for enhanced antibacterial effects and restrained inflammatory osteoclastogenesis. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021;202: 111697.
[30] YANG X, WANG Q, ZHANG Y, et al. A dual-functional PEEK implant coating for anti-bacterial and accelerated osseointegration. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2023;224:113196.
[31] CHENG W, ZENG X, CHEN H, et al. Versatile Polydopamine Platforms: Synthesis and Promising Applications for Surface Modification and Advanced Nanomedicine. ACS Nano. 2019;13(8):8537-8565.
[32] LI N, BAI J, WANG W, et al. Facile and Versatile Surface Functional Polyetheretherketone with Enhanced Bacteriostasis and Osseointegrative Capability for Implant Application. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(50): 59731-59746.
[33] PARK JW, JANG JH, LEE CS, et al. Osteoconductivity of hydrophilic microstructured titanium implants with phosphate ion chemistry. Acta Biomater. 2009;5(6):2311-2321.
[34] 李雪菁,邱小亥,赵宝红.亲水种植体促进骨整合机制研究进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2020,13(8):501-505.
[35] LEE YJ, LEE JH, CHO HJ, et al. Electrospun fibers immobilized with bone forming peptide-1 derived from BMP7 for guided bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2013;34(21):5059-5069.
[36] KANCHANAWONG P, CALDERWOOD DA. Organization, dynamics and mechanoregulation of integrin-mediated cell-ECM adhesions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023;24(2):142-161.
[37] BERNAR A, GEBETSBERGER JV, BAUER M, et al. Optimization of the Alizarin Red S Assay by Enhancing Mineralization of Osteoblasts. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 24(1):723.
[38] FERRARA N. Vascular endothelial growth factor and the regulation of angiogenesis. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2000;55:15-36.
[39] ZHAO Z, MA S, WU C, et al. Chimeric Peptides Quickly Modify the Surface of Personalized 3D Printing Titanium Implants to Promote Osseointegration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(29):33981-33994.
[40] CHEN J, HU G, LI T, et al. Fusion peptide engineered “statically-versatile” titanium implant simultaneously enhancing anti-infection, vascularization and osseointegration. Biomaterials. 2021;264:120446. |