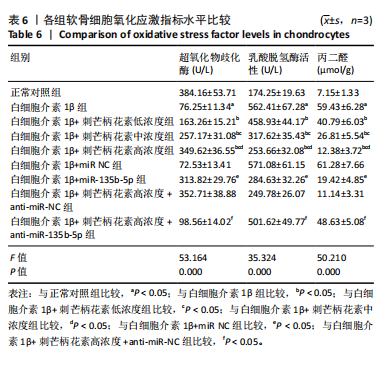
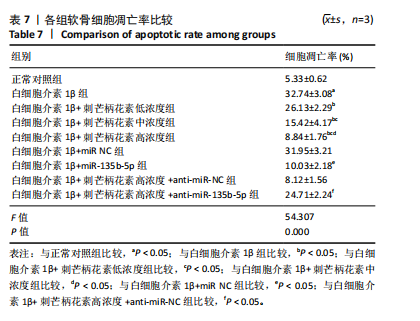
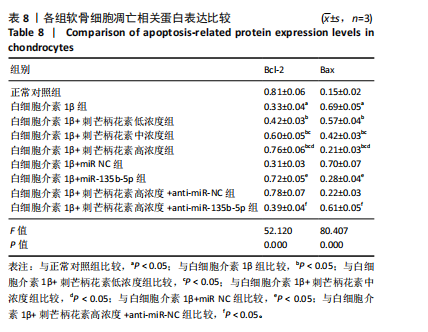
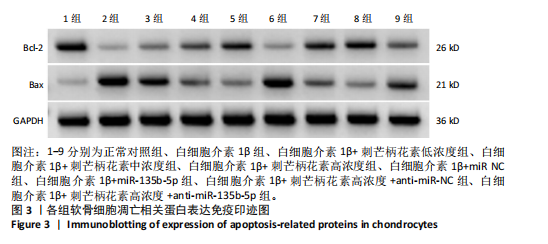
[1] LIU C, WANG B, XIAO L, et al. Protective effects of the pericellular matrix of chondrocyte on articular cartilage against the development of osteoarthritis. Histol Histopathol. 2018;33(8):757-764.
[2] 汪博,张明焕.CIRC_0044235靶向miR-574-5p减轻IL-1β诱导的人软骨细胞损伤[J].基础医学与临床,2023,43(3):419-426.
[3] JENEI-LANZL Z, MEURER A, ZAUCKE F. Interleukin-1β signaling in osteoarthritis - chondrocytes in focus. Cell Signal. 2019;53(1):212-223.
[4] CHANG Q, LI C, HU J, et al. Protective effects of hsa_circ_0072568 on interleukin‑1β‑stimulated human chondrocytes are mediated via the miR-382-5p/TOP1 axis. Exp Ther Med. 2023;26(2):383-391.
[5] 周海银,罗兰,陈艳瑛,等.刺芒柄花素通过调控SIRT1/PGC-1α通路对脓毒症诱导的大鼠急性肾损伤的影响[J].中医药导报,2022, 28(1):6-11.
[6] 张春华,胡凌云,解云,等.刺芒柄花素通过阻断海马组织NF-κB通路抑制炎症因子释放改善慢性轻度不可预见性应激老龄大鼠认知行为[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2023,39(7):610-616.
[7] SHAH R, YERI A, DAS A, et al. Small RNA-seq during acute maximal exercise reveal RNAs involved in vascular inflammation and cardiometabolic health: brief report. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017;313(6):H1162-H1167.
[8] 李坤,张育民,王亚康,等.上调microRNA-543表达对大鼠骨关节炎软骨细胞的保护作用[J].中国临床医学,2018,25(2):239-243.
[9] XU J, QIAN X, DING R. MiR-24-3p attenuates IL-1β-induced chondrocyte injury associated with osteoarthritis by targeting BCL2L12. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):371-380.
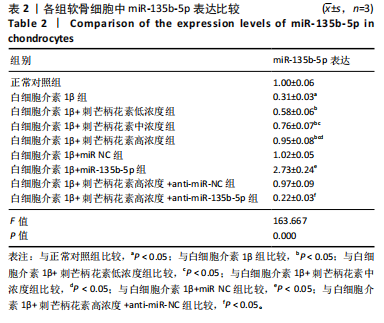
10] DUAN Q, SUN W, YUAN H, et al. MicroRNA-135b-5p prevents oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation-induced neuronal injury through regulation of the GSK-3β/Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. Arch Med Sci. 2018;14(4):735-744.
[11] 赵晓东,王磊.miR-135b-5p对IL-1β诱导软骨细胞损伤的影响及机制研究[J].河北医药,2021,43(8):1136-1141.
[12] 林燕云,游纯秋,蒋擎,等.独活寄生汤抑制白细胞介素-1β诱导的软骨细胞凋亡的作用机制[J].中国老年学杂志,2019,39(7):1702-1705.
[13] 高莉晶,李婷,原丽,等.刺芒柄花素对高糖诱导的H902心肌细胞损伤的作用机制[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2022,38(23):2820-2824.
[14] 徐翀,申利民,苑文杰.当归多糖通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路抑制骨关节炎软骨细胞氧化应激损伤与炎症反应[J].陕西中医,2022, 43(6):700-703,770.
[15] 李伟,黄耀凯,王洪林,等.槲皮素通过下调MALAT1抑制膝骨关节炎小鼠软骨损伤及软骨细胞凋亡的相关机制[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2023,16(1):33-40.
[16] ALADAILEH SH, HUSSEIN OE, ABUKHALIL MH, et al. Formononetin Upregulates Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling and Prevents Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Kidney Injury in Methotrexate-Induced Rats. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019;8(10):430.
[17] 郝炎,李治成,陈越,等.刺芒柄花素对顺铂所致大鼠急性肾损伤的保护作用及其机制[J].川北医学院学报,2022,37(3):279-284.
[18] 胡志平,马俊,陈彦蓉,等.刺芒柄花素激活脑外伤小鼠Nrf2/HO-1通路减轻脑水肿并改善行为障碍[J]. 中国实验诊断学,2021, 25(6):887-893.
[19] YU L, ZHANG Y, CHEN Q, et al. Formononetin protects against inflammation associated with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by targeting the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;149(1):1-9.
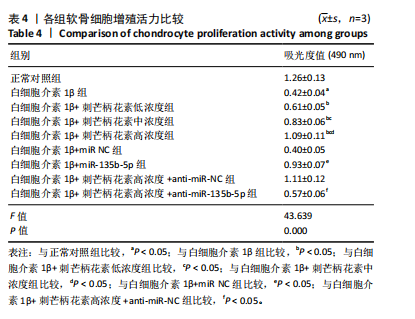
[20] JIANG Y. Osteoarthritis year in review 2021: biology. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(2):207-215.
[21] LIANG L, ZHANG F, FENG N, et al. IRE1α protects against osteoarthritis by regulating progranulin-dependent XBP1 splicing and collagen homeostasis. Exp Mol Med. 2023;55(11):2376-2389.
[22] PAN D, YIN P, LI L, et al. Holomycin, a novel NLRP3 inhibitor, attenuates cartilage degeneration and inflammation in osteoarthritis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023;657(21):59-68.
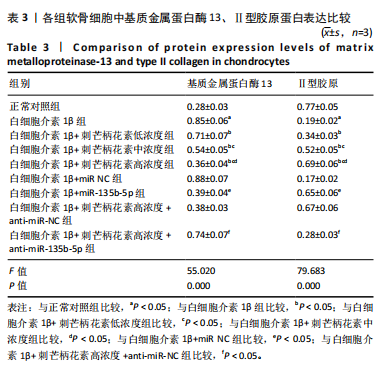
[23] Li Y, Tang L, Duan Y, et al. Upregulation of MMP-13 and TIMP-1 expression in response to mechanical strain in MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells. BMC Res Notes. 2010;17(3):309-321.
[24] Lan Q, Lu R, Chen H, et al. MMP-13 enzyme and pH responsive theranostic nanoplatform for osteoarthritis. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020;18(1):117-131.
[25] MAO J, ZHANG L. MiR-320a upregulation improves IL-1β-induced osteoarthritis via targeting the DAZAP1 and MAPK pathways. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):541-253.
[26] HORVÁTH E, SÓLYOM Á, SZÉKELY J, et al. Inflammatory and Metabolic Signaling Interfaces of the Hypertrophic and Senescent Chondrocyte Phenotypes Associated with Osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(22):16468-16579.
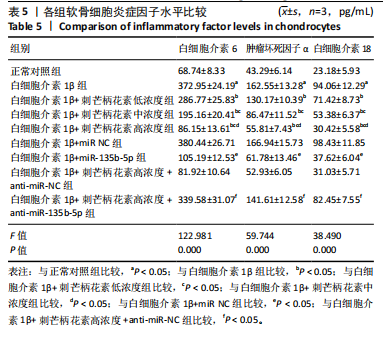
[27] 段大波,张树鹰.血清TGF-β1、TIMP-1、TNF-α及IL-17在膝关节骨性关节炎患者血清变化情况及其与病情严重程度的关系[J].中国实验诊断学,2023,27(7):825-828.
[28] 卞雅莉,陈晓宏,季晶俊,等.等速肌力训练联合时空针灸灵龟八法治疗老年肝肾亏虚型膝骨关节炎的疗效及对血清细胞因子的影响[J].现代生物医学进展,2022,22(7):1257-1261.
[29] TUDORACHI NB, TOTU EE, FIFERE A, et al. The Implication of Reactive Oxygen Species and Antioxidants in Knee Osteoarthritis. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021;10(6):985-997.
[30] LI J, DENG C, LIANG W, et al. Mn-containing bioceramics inhibit osteoclastogenesis and promote osteoporotic bone regeneration via scavenging ROS. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(11):3839-3850.
[31] 王翠平,梁翼,余文景,等.消增强骨片联合西药治疗对膝骨关节炎患者疼痛症状、关节功能及氧化应激的影响[J].成都医学院学报,2023,18(6):732-735.
[32] 裴珍珍,王革生,东潇博,等.益气通络方含药血清通过减弱氧化应激反应和激活PI3K/AKT信号通路对PC12细胞氧化应激损伤模型的保护作用[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2023,25(2):36-41.
[33] JING L, GAO R, ZHANG J, et al. Norwogonin attenuates hypoxia-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in PC12 cells. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021;21(1):18-31.
[34] 马天文,于跃,吕良钰,等.白果内酯对IL-1β诱导的ATDC5软骨细胞自噬、增殖和凋亡的影响[J].畜牧兽医学报,2023,54(2):837-846.
[35] RAJ SR, D ND, MONDAL S, et al. Expression analysis of pro-apoptotic BAX and anti-apoptotic BCL-2 genes in relation to lactation performance in Deoni and Holstein Friesian crossbred cows. Anim Biotechnol. 2023;34(4):1354-1361.
[36] XU K, LIU Z, PAN S, et al. BMSCs attenuate radiation-induced brain injury induced hippocampal neuronal apoptosis through a PI3K/Akt/Bax/Bcl-2 signaling pathway. Brain Res. 2024;15(1):1829-1842.
[37] LIU W, RONG Y, WANG J, et al. Exosome-shuttled miR-216a-5p from hypoxic preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells repair traumatic spinal cord injury by shifting microglial M1/M2 polarization. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):47-68.
[38] WANG C, GUO X, WANG Y, et al. Silencing of miR-324-5p alleviates rat spinal cord injury by Sirt1. Neurosci Res. 2021;173(4):34-43.
[39] zhao l, qi y, xu l, et al. MicroRNA-140-5p aggravates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by promoting myocardial oxidative stress via targeting Nrf2 and Sirt2. Redox Biol. 2018;5(1):284-296.
[40] LU K, WANG Q, HAO L, et al. miR-204 ameliorates osteoarthritis pain by inhibiting SP1-LRP1 signaling and blocking neuro-cartilage interaction. Bioact Mater. 2023;26(20):425-436.
[41] LIU Y, ZHANG Z, LU X, et al. Senescence-responsive miR-33-5p promotes chondrocyte senescence and osteoarthritis progression by targeting SIRT6. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;121(2):110506-11613.
[42] CHENG C, TIAN Y, YANG R, et al. miR-5581 Contributes to Osteoarthritis by Targeting NRF1 to Disturb the Proliferation and Functions of Chondrocytes. Am J Pathol. 2023;193(9):1234-1247.
[43] HUANG Y, WANG Y, OUYANG Y. Elevated microRNA-135b-5p relieves neuronal injury and inflammation in post-stroke cognitive impairment by targeting NR3C2. Int J Neurosci. 2022;132(1):58-66.
[44] 臧宾宾,李华,杨颖,等. miR-135b-5p抑制脓毒症引起的小鼠急性肺损伤(ALI)的作用及机制[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2022,38(4): 366-372. |