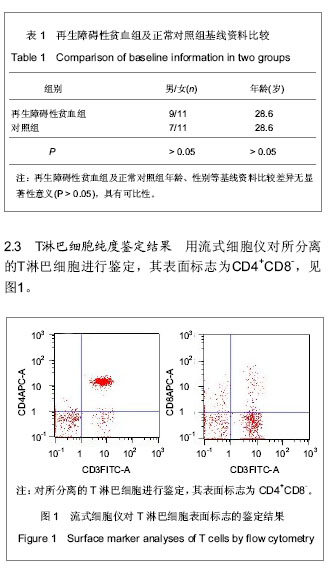
| [1] |
Wang Jian-ji, Yang Long, Li Jing, Sun Qi, Zuo Wei-min, Ren Qi-feng, Sun Yu, Wu Zhan-yu, Zou Qiang, Ma Min-xian, Ye Chuan.
Development and application of special-purpose grafter by femoral head decompression combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplantation based on three-dimensional printing technology
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(44): 6636-6642.
|
| [2] |
Zhou Chang-yan, Zhou Qing-huan, Bian Jing, Chen Ke, Chen Wen.
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with calcium phosphate cement to repair articular cartilage defects in rabbits
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(8): 1195-1199.
|
| [3] |
Xu Xiang, Yin He-ping.
Platelet-rich plasma accelerates the proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2144-2148.
|
| [4] |
Ma Fa-ku, Wang Huan, Liu Bin, Yang Yan-li, Su Qin-jun, Qian Zhen, Dong Liang.
Expression of CD44+/C-myc+ cancer stem cells and its relationship with the prognosis of patients in colorectal tumors
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2161-2166.
|
| [5] |
Chen Ping, Wang Jian.
Enrichment of lung cancer stem cells and expression of related markers
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2167-2171.
|
| [6] |
Fan Zhi-gang, Fan Hong-liang.
Oxidative stress response in diabetic nephropathy rats following injection of embryonic stem cells via the tail vein
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2199-2204.
|
| [7] |
Wang Yong, Zhao Wei, Feng Jian-zhou, Chen Xiao-chun.
Nerve growth factor-modified adipose derived stem cells for repair of spinal cord injury
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2224-2229.
|
| [8] |
Sha Wen-qiong, She Rui-lian, Wang Zi-neng, Ke Ru.
Ultrastructure and phagocytotic function of human placental mesenchymal stem cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2230-2235.
|
| [9] |
Du Qing-hua, Cao Jun-kai, Dong Xi-xi, E Ling-ling, Wei Li-jun.
Osteogenic differentiation of pluripotent stem cells induced by akermanite extracts
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2236-2242.
|
| [10] |
Wu Yan, Huang Lan .
Bone morphogenetic protein 9-induced osteogenic differentiation of dental follicle cells in vitro
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2255-2260.
|
| [11] |
Rao Li-jia, Li Qi-meng, Li Jin-ling, Xu Qiong.
Expression pattern of ten-eleven translocation family during differentiation of human dental pulp cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2261-2266.
|
| [12] |
Gao Zhuo-yue, Liu Yong-qi, He Jian-xin, Wu Zhi-wei, Luo Ya-li, Su Yun, Zhang Li-ying, Zhang Qi, Wu You-ming, Zhou Ni-na.
Regulatory effects of warming yang and invigorating qi treatment on the inflammatory balance and genetic stability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under tumor microenvironment
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2267-2272.
|
| [13] |
Wang Fang, Chen Shao-wei.
In vitro culture of embryos and establishment of embryonic stem cell lines
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2273-2277.
|
| [14] |
Du Wei-bin, Quan Ren-fu, Zheng Xuan, Wang Tuo.
Hair follicle stem cells promote the healing of skin wound
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2278-2282.
|
| [15] |
Du Hua, Shi Ying-xu .
Bone marrow microenvironment controls the “fate” of hematopoietic stem cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2283-2290.
|