中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (31): 4610-4615.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.31.007
• 脊柱植入物 spinal implant • 上一篇 下一篇
脊髓内移后路矫形内固定修复伴神经损害的脊柱侧后凸畸形:神经电生理及功能的改善
李 平1,2,孙建民1,王 彤3
- 1山东大学附属省立医院脊柱外科,山东省济南市 250021;2菏泽市单县东大医院骨科,山东省菏泽市 274300;3南京医科大学骨科,江苏省南京市 210029
Transvertebral transposition of the spinal cord and posterior correction in patients suffering from neurologic deficit secondary to angular kyphoscoliosis: improvement of electrophysiology and function
Li Ping1, 2, Sun Jian-min1, Wang Tong3
- 1Department of Spinal Surgery, Affiliated Provincial Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan 250021, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Heze Shanxian Dong Da Hospital, Heze 274300, Shandong Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
脊柱侧后凸畸形:是一种由于各种原因(先天性、特发性和神经肌源性脊柱侧凸长期未经治疗引起)导致的脊柱侧凸,且长期未得到良好的治疗而引起的严重脊柱矢状面和冠状面的畸形。随着后路全脊椎截骨在临床上的广泛应用,显著提高了重度脊柱侧后凸畸形的矫正率,但是单纯的行后路全脊椎截骨术却并不能显著性的改善脊髓神经功能,甚至可能进一步使神经功能损害加重。
体感诱发电位:在临床得到广泛应用主要是由于该方法的敏感性(对术中脊髓的牵拉、缺血以及压迫均较敏感)和具备连续检测的功能。虽然运动诱发电位监测脊髓神经损害的特异性和敏感性均较高,但是对直接反映脊髓感觉功能和连续性的监测无法满足,所以对脊髓神经功能监测时采用体感诱发电位及运动诱发电位联合监测的方法可以提高准确性和可靠性。
摘要
背景:有文献报道,采用脊髓内移术修复伴有脊髓神经受压的脊柱侧后凸畸形,术后大部分患者的神经功能可以达到不同程度的恢复,但该方案改善术后神经功能的有效性机制仍不明确。
目的:观察脊髓内移后路矫形内固定修复伴神经损害的脊柱侧后凸畸形后神经功能的改善情况。
方法:选择脊柱侧后凸畸形同时伴神经损害患者18例,经检查确诊后,行脊髓内移后路矫形内固定治疗。所有患者均在术前和术后1周行体感诱发电位检测,术中监测其运动诱发电位和体感诱发电位。在MRI上测定椎管内缘至顶椎区凸侧脊髓外缘之间的距离,并计算脊髓内移的距离。
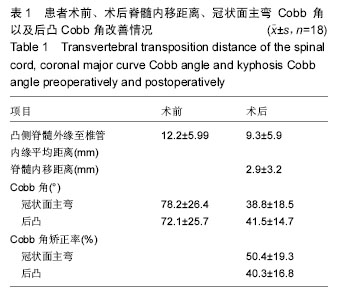
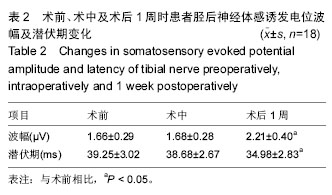
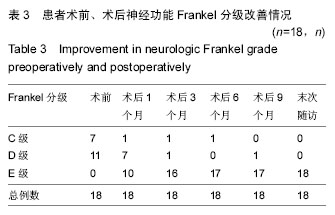
结果与结论:①术前胫后神经体感诱发电位检测到P40的波幅(1.66±0.29) μV、峰潜伏期为(39.25±3.02) ms;术中胫后神经体感诱发电位检测到P40的波幅和峰潜伏期的值分别(1.68±0.28) μV、和(38.68±2.67) ms,术中与术前的波幅与峰潜伏期比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);②术后冠状面主弯Cobb 角矫正率以及后凸Cobb角矫正率分别为(51.1±21.2)%以及(38.9±18.1)%;顶椎区脊髓位置在术后平均内移距离为(2.4±1.7) mm;③胫后神经体感诱发电位检测到P40的波幅与潜伏期在术后1周时分别为(2.21±0.40) μV和(34.98±2.83) ms,较术前有显著改善,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);④结果提示,脊髓内移后路矫形内固定可明显改善伴神经损害脊柱侧后凸畸形患者的神经电生理指标及神经功能。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-5826-3872(李平)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)