中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (7): 940-946.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.07.004
• 软骨组织构建 cartilage tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
MicroRNAs在缺氧诱导因子1α缺失椎间盘组织中的差异性表达
孟祥超,刘卓超,王 君,周 琦,齐 进,张兴凯
- 上海交通大学医学院附属瑞金医院骨科,上海市伤骨科研究所,上海市 200025
Differential expression of microRNAs in the intervertebral disc of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha deficient mice
Meng Xiang-chao, Liu Zhuo-chao, Wang Jun, Zhou Qi, Qi Jin, Zhang Xing-kai
- Department of Orthopedics, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai Institute of Traumatology and Orthopaedics, Shanghai 200025, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
缺氧诱导因子1α:是一种真核转录因子,由α和β两个亚基组成,其可通过诱导多种缺氧相关反应基因的转录,起到促进机体新血管生成、维持细胞能量代谢的重要作用。
microRNAs(miRNAs):是一种小的,类似于siRNA的分子,由高等真核生物基因组编码,miRNA通过和靶基因mRNA碱基配对引导沉默复合体(RISC)降解mRNA或阻碍其翻译。miRNAs在物种进化中相当保守,在植物、动物和真菌中发现的miRNAs只在特定的组织和发育阶段表达,miRNA组织特异性和时序性,决定组织和细胞的功能特异性,表明miRNA在细胞生长和发育过程的调节过程中起多种作用。
背景:MicroRNAs在椎间盘退变的疾病中起重要作用,缺氧诱导因子缺失可加速椎间盘的退变。
目的:检测缺氧诱导因子1α后小鼠椎间盘内microRNAs的变化情况,探究microRNAs与椎间盘退变的关系及缺氧诱导因子1α调控椎间盘退变机制和通路。
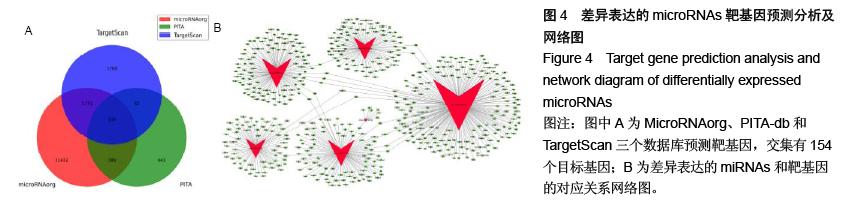
方法:通过前期构建的条件性敲除髓核细胞缺氧诱导因子1α基因的小鼠,分别取基因敲除组与正常对照组4周龄小鼠的椎间盘组织进行组织学染色观察;通过提取标本的总RNAs,从中分离microRNAs,荧光标记后与微阵列芯片杂交,扫描检测后数据经分析处理,筛选椎间盘组织中microRNA差异表达谱。采用实时荧光定量RT-PCR技术验证在椎间盘组织中均存在显著差异表达的microRNAs。分析差异表达microRNAs的靶基因及通路,预测其在椎间盘退变中的作用。
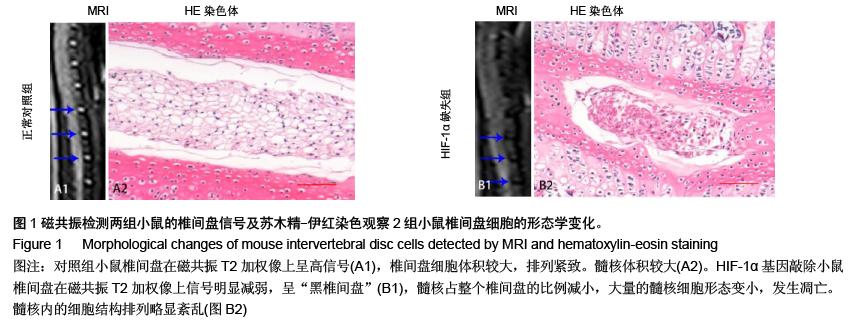
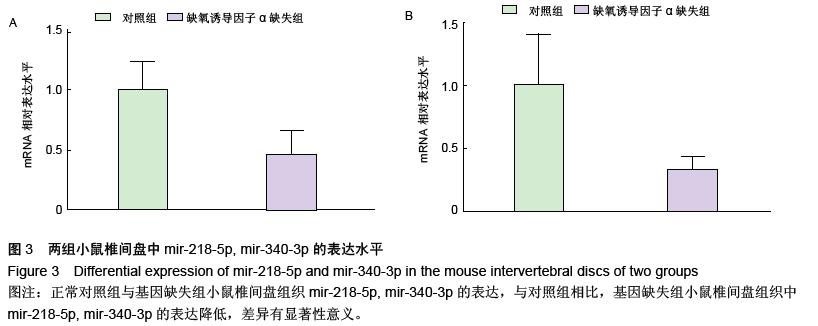
结果与结论:缺氧诱导因子1α基因缺失小鼠椎间盘髓核细胞数量减少,细胞形态变小,细胞质着色加深;两组小鼠椎间盘中的microRNAs的芯片筛选结果中,10个microRNAs发生了明显的差异表达,其中有7个microRNAs发生上调,3个microRNAs发生下调。结果提示缺氧诱导因子1α缺失后可能引起某些重要的microRNAs调节失衡,引起椎间盘髓核细胞大量的死亡,加速椎间盘的退变。
ORCID: 0000-0002-0621-2499(张兴凯)

.jpg)
.jpg)