Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (12): 1924-1930.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.12.023
Previous Articles Next Articles
Timed morphological changes of human hepatocytes L-02 cultured at high density by the support of spherical porous chitosan microcarriers
Zhang Rui, Liu Ming
- Department of General Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010050, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Revised:2015-02-17Online:2015-03-19Published:2015-03-19 -
Contact:Liu Ming, Chief physician, Department of General Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010050, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zhang Rui, M.D., Chief physician, Department of General Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010050, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program), No. 2007AA02Z487; the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 30672043, 30772105, 20074031; the General Program of the Science and Technology Department of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, No. 2012MS1124; the Scientific Research Program in High Education of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, No. NJSZY11128
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Rui, Liu Ming. Timed morphological changes of human hepatocytes L-02 cultured at high density by the support of spherical porous chitosan microcarriers[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(12): 1924-1930.
share this article
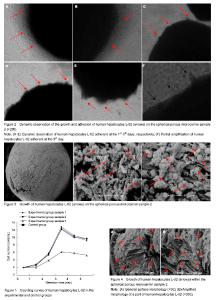
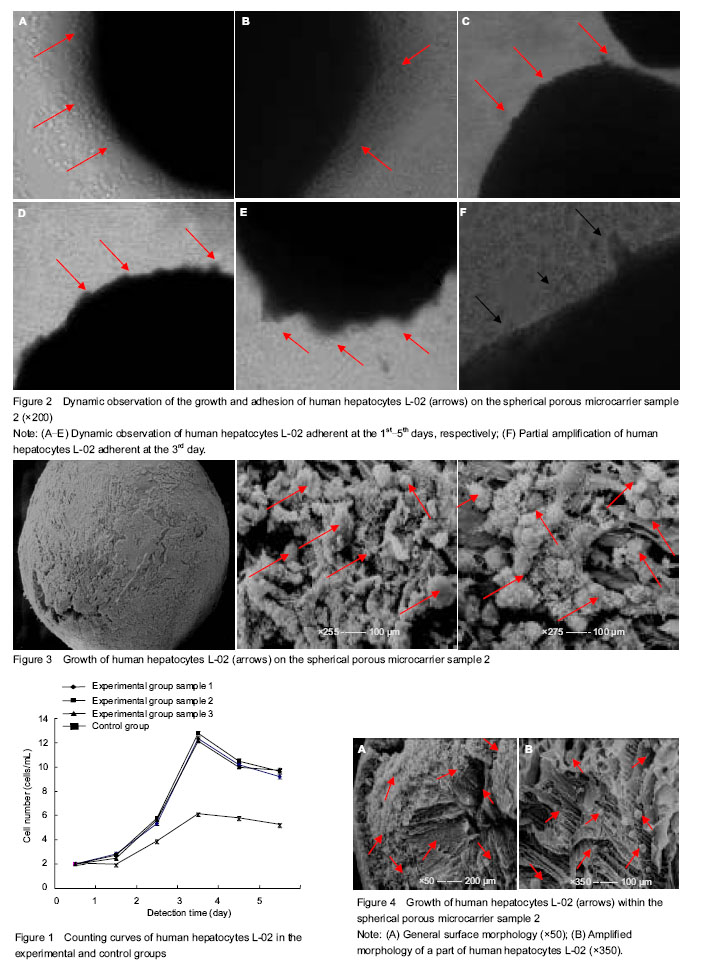
Cell counting of cultured human hepatocytes L-02 The number of cells in the two groups showed an increasing trend in the first 3 days of culture and reached peak at day 3, followed by a downward trend at days 4, 5 days. The largest increase in the cell amount was visible within 2-3 days. The cell number in the experimental group was significantly higher than that in the control group from beginning to end (P < 0.05), but there was no difference among different samples in the experimental group (P > 0.05). Experimental results showed that compared with the control group, the spherical porous chitosan microcarrier as a scaffold was better to generate a larger number of hepatocytes (Figure 1). Dynamic observation results of human hepatocytes L-02 under the inverted phase contrast microscope (Figure 2) Seen in Figure 2, in the experimental group, a few of scattered hepatocytes were adhered to the microcarriers at days 1-5 of culture under the inverted phase contrast microscope, and the vast majority of cells still suspended in the culture media. At the 1st day of culture, many human hepatocytes L-02 showed adherent growth on microcarrier samples 1, 2, 3. At the 2nd day, the cells adherent to the microcarriers were increased gradually in number, and most of the cells became a little oblate from the spherical shape, to form the clear cell contact with nuclear clearly visible. At the 3rd day, there were many cell masses on the surface of most of the microcarriers, adherent cells were in spherical or irregular polygonal shape that was similar to the morphology of epithelioid cells, merged into pieces and spread over the surface of the microcarriers, on which, villous protuberances changed slightly. Most of hepatocytes were directly or indirectly firmly adhesive to the microcarriers. On the locally enlarged microcarriers, clusters or projections formed on the surface of microcarriers were caused by a large amount of adherent cells which were mostly seen in a viable state. At the 4th and 5th days, the morphological changes proceeded, but hepatocyte necrosis, loss and floating were increase locally on the microcarriers and in the media. These above-mentioned morphological manifestations were observed from human hepatocytes L-02 cultured on the microcarrier 2 as an example. In addition, human hepatocytes cultured on the microcarrier samples 1, 2, 3 in the experimental group and in the control group for 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 days were sampled for overall survival assessment, including the cells adherent to the microcarriers and suspending in the culture medium). The overall survival rates were all over 90%, and hepatocytes maintained a good morphological structure. Ultrastructural changes of cultured human hepatocytes L-02 Based on the cell counting and microscopic observations at different periods, cultured human hepatocytes L-02 showed a good number and growth condition at day 3 of culture. Therefore, at the 3rd day of culture, on the clean bench, two or three samples from each of the three kinds of microcarriers were taken with a small sterile spoon followed by fixation, graded dehydration, drying, positioning and metal-spraying, and then the scanning electron microscope was used to observe the cell growth on these samples. There were sheets in mutual integration, unevenly covering the general surface of microcarrier samples 1, 2, 3, and villous projections could be seen faintly on the surface as well as the exposed surface pores. After local surface enlargement, there were many hepatocytes that were spherical and firmly adhered to the surface and pores of microcarriers. The number of hepatocytes on each microcarrier was varied and distributed unevenly, and the cell size was 20-30 μm. The hepatocyte surface was covered with microvilli, and there was a close interconnection between the cells. The spherical hepatocytes were interconnected by microvilli into a group, and local projection changes were visible on most of the cells. The above-mentioned results were observed from the human hepatocytes L-02 cultured on the microcarrier sample 3 as an example (Figure 3). Under the electron microscope, there were uneven and mutually fused sheets and microvilli covering the surface of microcarriers 1, 2, 3, and a lot of spherical hepatocytes were closely adherent to the pores inside the microcarriers. But the number of hepatocytes on each microcarrier was varied and distributed unevenly, and the cell size was 20-30 μm. The hepatocyte surface was full of microvilli. Some hepatocytes were interconnected by microvilli into a group or even locally aggregated in heaps that were more seen. These above-mentioned morphological manifestations were observed from human hepatocytes L-02 cultured on the microcarrier 2 as an example (Figure 4)."
| [1] Kang H, Lu S, Peng J, et al. Chondrogenic differentiation of human adipose?derived stem cells using microcarrier and bioreactor combination technique. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11(2): 1195-1199. [2] Zhang Z, Zhou HC, Li ZG, et al. Microgravity culture ofhepatocytes on cellulose/gelatin macroporous microcarrier. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2010;30(4): 704-707. [3] Jin ZK, Xu CX, Tian PX, et al. Immune monitoring in kidney transplant recipients could predict acute rejection by a new method: flow cytometric microcarrier assay. Transplant Proc. 2013;45(4):1508-1510. [4] Bock A, Schulze-Horsel J, Schwarzer J, et al. High-density microcarrier cell cultures for influenza virus production. Biotechnol Prog. 2011;27(1):241-250. [5] Yu P, Huang Y, Zhang Y, et al. Production and evaluation of a chromatographically purified Vero cell rabies vaccine (PVRV) in China using microcarrier technology. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2012;8(9):1230-1235. [6] Lam AT, Chen AK, Li J, et al. Conjoint propagation and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to cardiomyocytes in a defined microcarrier spinner culture. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(5):110. [7] Tashiro S, Tsumoto K, Sano E. Establishment of a microcarrier culture system with serial sub-cultivation for functionally active human endothelial cells. J Biotechnol. 2012;160(3-4):202-213. [8] Lai JY. Biofunctionalization of gelatin microcarrier with oxidized hyaluronic acid for corneal keratocyte cultivation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014;122:277-286. [9] Ting S, Chen A, Reuveny S, et al. An intermittent rocking platform for integrated expansion and differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells to cardiomyocytes in suspended microcarrier cultures. Stem Cell Res. 2014;13(2):202-213. [10] Rodrigues CA, Diogo MM, da Silva CL, et al. Microcarrier expansion of mouse embryonic stem cell-derived neural stem cells in stirred bioreactors. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2011; 58(4):231-242. [11] Abeille F, Mittler F, Obeid P, et al. Continuous microcarrier-based cell culture in a benchtop microfluidic bioreactor. Lab Chip. 2014;14(18):3510-3518. [12] Kim BJ, Zhao T, Young L, et al. Batch, fed-batch, and microcarrier cultures with CHO cell lines in a pressure-cycle driven miniaturized bioreactor. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2012; 109(1):137-145. [13] Hupfeld J, Gorr IH, Schwald C, et al. Modulation of mesenchymal stromal cell characteristics by microcarrier culture in bioreactors. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2014;111(11): 2290-2302. [14] Ning B, Liu HF, Gong WM, et al. The changes of extracellular matrix in adult degenerative nucleus pulposus cells with stiring microcarrier culture system in vitro. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013;51(5):432-436. [15] Lu SJ, Kelley T, Feng Q, et al. 3D microcarrier system for efficient differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into hematopoietic cells without feeders and serum. Regen Med. 2013;8(4):413-424. [16] Chen AK, Chen X, Choo AB, et al. Critical microcarrier properties affecting the expansion of undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Res. 2011;7(2):97-111. [17] Kurokawa M, Sato S. Growth and poliovirus production of Vero cells on a novel microcarrier with artificial cell adhesive protein under serum-free conditions. J Biosci Bioeng. 2011; 111(5): 600-604. [18] Goh TK, Zhang ZY, Chen AK, et al. Microcarrier culture for efficient expansion and osteogenic differentiation of human fetal mesenchymal stem cells. Biores Open Access. 2013;2(2):84-97. [19] Park Y, Subramanian K, Verfaillie CM, et al. Expansion and hepatic differentiation of rat multipotent adult progenitor cells in microcarrier suspension culture. J Biotechnol. 2010;150(1): 131-139. [20] Chen AK, Reuveny S, Oh SK. Application of human mesenchymal and pluripotent stem cell microcarrier cultures in cellular therapy: achievements and future direction. Biotechnol Adv. 2013;31(7):1032-1046. [21] Ning B, Liu H, Gong W, et al. Biological characteristics of adult degenerative nucleus pulposus cells in a three-dimensional microcarrier stirring culture system. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(6): 858-863. [22] Chang J, Lei H, Liu Q,et al. Optimization of culture of mesenchymal stem cells: a comparison of conventional plate and microcarrier cultures. Cell Prolif. 2012;45(5):430-437. [23] Bardy J, Chen AK, Lim YM, et al. Microcarrier suspension cultures for high-density expansion and differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells to neural progenitor cells. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2013;19(2):166-180. [24] Shakhbazau A, Shcharbin D, Bryszewska M, et al. Non-viral engineering of skin precursor-derived Schwann cells for enhanced NT-3 production in adherent and microcarrier culture. Curr Med Chem. 2012;19(32):5572-5579. [25] Lecina M, Ting S, Choo A, Reuveny S, et al. Scalable platform for human embryonic stem cell differentiation to cardiomyocytes in suspended microcarrier cultures. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2010;16(6):1609-1619. [26] Lippens E, Cornelissen M. Slow cooling cryopreservation of cell-microcarrier constructs. Cells Tissues Organs. 2010; 192(3): 177-186. [27] Justice C, Leber J, Freimark D, et al. Online- and offline- monitoring of stem cell expansion on microcarrier. Cytotechnology. 2011;63(4):325-335. [28] Surrao DC, Khan AA, McGregor AJ, et al. Can microcarrier-expanded chondrocytes synthesize cartilaginous tissue in vitro? Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(15-16): 1959-1967. [29] Schrobback K, Klein TJ, Schuetz M, et al. Adult human articular chondrocytes in a microcarrier-based culture system: expansion and redifferentiation. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(4): 539-546. [30] Leung HW, Chen A, Choo AB, et al. Agitation can induce differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells in microcarrier cultures. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2011;17(2):165-172. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Chen Jiming, Wu Xiaojing, Liu Tianfeng, Chen Haicong, Huang Chengshuo. Effects of silymarin on liver injury and bone metabolism induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1224-1228. |
| [3] | Wang Hanyue, Li Furong, Yang Xiaofei, Hu Chaofeng. Direct reprogramming hepatocytes into islet-like cells by efficiently targeting and activating the endogenous genes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1056-1063. |
| [4] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [5] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [6] | Liu Yang, Gong Yi, Fan Wei. Anti-hepatoma activity of targeted Pluronic F127/formononetin nanocomposite system in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 526-531. |
| [7] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [8] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [9] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [10] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [11] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [12] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [13] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [14] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [15] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||