Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (12): 1864-1871.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.12.012
Previous Articles Next Articles
Nano-collagen artificial bone for alveolar ridge preservation in the Kazakh from Xinjiang Tacheng Region
Wang Cheng-yue1, Zhao Yuan2, Yang Man2, Wang Shu-feng3
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou 121000, Liaoning Province, China
2School of Graduate, Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou 121000, Liaoning Province, China
3Department of Prosthodontics, Stomatology Hospital of Xuzhou City, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Revised:2015-02-15Online:2015-03-19Published:2015-03-19 -
Contact:Wang Cheng-yue, Department of Prosthodontics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou 121000, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Wang Cheng-yue, M.D., Associate chief physician, Department of Prosthodontics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou 121000, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the Scientific Research and Technological Development Project in Tacheng Region, No. 2013406
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Cheng-yue, Zhao Yuan, Yang Man, Wang Shu-feng. Nano-collagen artificial bone for alveolar ridge preservation in the Kazakh from Xinjiang Tacheng Region[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(12): 1864-1871.
share this article
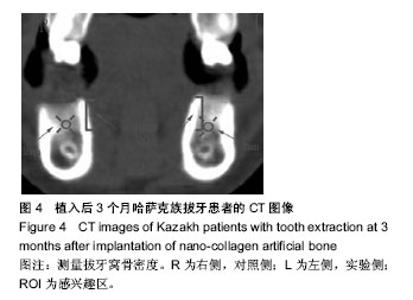
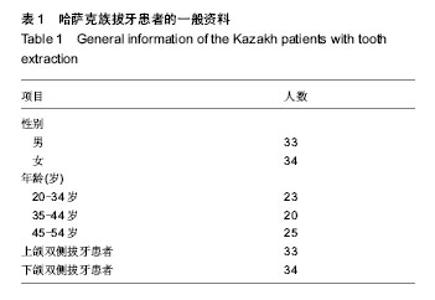
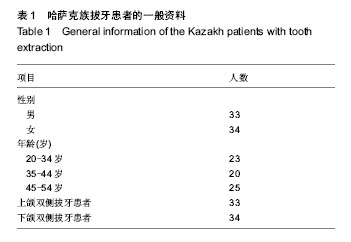
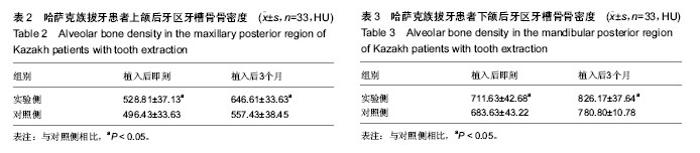
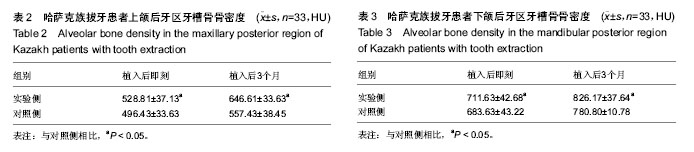
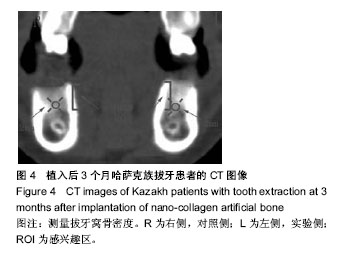
2.2 随访情况 1例患者因去哈萨克斯坦失访。大多数哈萨克族患者拔牙区伤口无感染,愈合良好,患者无不良反应。1例哈萨克族患者植入后1周,因食烤馕,奶疙瘩伤口裂开,重新缝合后Ⅱ期愈合。植入后3个月,拔牙区处表面的黏膜颜色正常。 2.3 上下颌后牙区牙槽骨骨密度 实验侧和对照侧植入后即刻,可见拔牙窝清晰的轮廓,牙槽间隔可见(图2E)。植入后3个月,对照侧和实验侧CT图像显示拔牙窝牙槽间隔影像模糊,CT值与周围牙槽突CT值接近,但实验侧植骨区骨充盈(图4)。 表2显示,33例双侧上颌拔牙患者后牙区牙槽骨植入后即刻实验侧骨密度高于对照侧(P < 0.05);植入后3个月实验侧骨密度仍高于对照侧(P < 0.05)。 表3显示,34例双侧下颌拔牙患者后牙区牙槽骨植入后即刻实验侧骨密度高于对照侧(P < 0.05);植入后3个月实验侧骨密度仍高于对照侧(P < 0.05)。 2.4 不良反应 材料植入后均无不良反应出现。"
| [1] 阿利•阿布塔里普,汪玺,张德罡,等.哈萨克族的草原游牧文化(Ⅳ)—哈萨克族的衣、食、住、行及婚丧等生活文化[J].草原与草坪,2013,33(1):76-82. [2] Kotsakis G, Chrepa V, Marcou N, et al. Flapless alveolar ridge preservation utilizing the "socket-plug" technique: clinical technique and review of the literature. J Oral Implantol. 2014;40(6):690-698. [3] Borg TD, Mealey BL. Histologic healing following tooth extraction with ridge preservation using mineralized versus combined mineralized-demineralized freeze-dried bone allograft: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Periodontol. 2015;86(3):348-355. [4] Kim Y, Leem DH. Post traumatic immediate GBR: alveolar ridge preservation after a comminuted fracture of the anterior maxilla. Dent Traumatol. 2015;31(2):156-159. [5] Etoz OA, Demetoglu U, Ocak H. New method to increase inter-alveolar height with preservation of crestal cortical bone for implant treatment. J Oral Implantol. 2014;40(5): 601-602. [6] Pang C, Ding Y, Zhou H, et al. Alveolar ridge preservation with deproteinized bovine bone graft and collagen membrane and delayed implants. J Craniofac Surg. 2014;25(5):1698-1702. [7] Saund D, Dietrich T. Minimally-invasive tooth extraction: doorknobs and strings revisited! Dent Update. 2013;40(4): 325-326, 328-330. [8] Cucchi A, Ghensi P. Vertical Guided Bone Regeneration using Titanium-reinforced d-PTFE Membrane and Prehydrated Corticocancellous Bone Graft. Open Dent J. 2014;8:194-200. [9] Quaranta A, Andreana S, Pompa G, et al. Active implant peri-apical lesion: a case report treated via guided bone regeneration with a 5-year clinical and radiographic follow-up. J Oral Implantol. 2014;40(3):313-319. [10] Wang CY, Wang SF, Yao YS, et al. Study on vertical mandibular distraction osteogenesis using magnesium alloy on canine. Prog Nat Sci Mater Int. 2014;24(5):446-451. [11] Ma J, Both SK, Yang F, et al. Concise review: cell-based strategies in bone tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2014;3(1):98-107. [12] Cui FZ, Li Y, Ge J. Self-assembly of mineralized collagen composites. Mater Sci Eng R Rep. 2007;57(1-6):1-27. [13] Li X, Wang L, Fan Y, et al. Nanostructured scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101(8): 2424-2435. [14] 王程越,姚玉胜,艾红军,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/胶原对富血小板血浆促进骨髓基质干细胞成骨向分化的影响[J].口腔医学研究,2007, 23(3):241-244. [15] 王程越,王伟,张力,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/月交原/聚乳酸复合物与骨髓间充质干细胞修复兔下颌骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(49):9762-9765. [16] 王程越,姚玉胜,王树峰,等.组织工程骨修复兔下颌骨缺损的实验研究[J].口腔医学研究,2012,28(3):213-217. [17] 崔福斋.骨组织工程的发展趋势[J].中国医疗器械信息,2011,16(2): 16-21. [18] 胡良平.统计学三型理论在实验设计中的应用[M].北京:人民军医出版社,2006:24-26. [19] 温宇,陆怀秀,王忠义,等.拔牙后牙槽骨骨密度变化的影响[J].口腔医学,2000,20(2):64-65. [20] 魏宁,朱国威.拔牙后牙槽骨愈合的影响因素[J].遵义医学院学报, 2008,31(6):631-634. [21] 宋军,雷建伟.偏侧咀嚼对下颌骨骨密度及面部影响的研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2005,21(6):849-850. [22] 赵效国,刘文亚,邓晓帆,等.不同民族及部分生活因子对骨密度的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2003,9(3):193-195. [23] 卢贤欣,张凤,王劲茗,等.微创拔牙后牙槽窝愈合的临床研究[J].广东牙病防治.2010,18(2):90-92. [24] Hargreaves KM, Berman LH. Cohen's Pathways of the Pulp Expert Consult. Mosby: Elsevier Medicine. 2010:14-20. [25] Park HS, Lee YJ, Jeong SH, et al. Density of the alveolar and basal bones of the maxilla and the mandible. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2008;133(1):30-37. [26] 胡明华,米丛波,聂晶,等.上下颌牙槽骨不同部位骨密度的螺旋CT研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2011,17(2):145-149. [27] Joo NS, Yang SW, Song BC, et al. Vitamin A Intake, Serum Vitamin D and Bone Mineral Density: Analysis of the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES, 2008-2011). Nutrients. 2015;7(3):1716-1727. [28] Edmonds SW, Cram P, Lu X, et al. Improving bone mineral density reporting to patients with an illustration of personal fracture risk. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2014;14(1):101. [29] 郑旭,林久祥.牙槽骨密度定量测量系统的建立及测量精确性、有效性的检验[J].北京大学学报,2008,40(4):431-436. [30] 李升,杨明华,宋仁波,等.计算机灰度法对牙槽骨密度变化的初步评价[J].现代生物医学进展,2006,6(8):40-41. [31] 吴贾涵,杨萍.测量牙槽骨密度方法的研究进展[J].中国现代医生, 2014,52(3):158-160. [32] Wada M, Andoh T, Gonda T, et al. Implant placement with a guided surgery system based on stress analyses utilizing the bone density: a clinical case report. J Oral Implantol. 2014; 40(5):603-606. [33] Panmekiate S, Ngonphloy N, Charoenkarn T, et al. Comparison of mandibular bone microarchitecture between micro-CT and CBCT images. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2015:20140322. [34] 郑旭,林久祥.计算机辅助的牙槽骨密度定量测量系统准确性和灵敏度的研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2009,27(3):305-309. [35] 杨烁,徐淑兰,肖希娟,等.计算机灰度法对可降解珊瑚羟基磷灰石与脱矿无机牛骨在上颌窦提升中改变的对比研究[J].广东医学, 2013,34(6):891-893. [36] 金超岭,王猛,李红磊,等.双能X线骨密度仪精密度和准确度的研究[J].中华创伤杂志,2014,30(1):41-43. [37] 李韶伟,王国世,魏明贵,等.基于三维重建对牙种植骨移植材料的定量研究[J].广东牙病防治,2014,22(1):6-10. [38] 冯力,张国权,张国志,等.X线、螺旋CT及双能X线骨密度测量仪对拔牙窝骨密度测量的评价[J].海南医学,2006,17(8):124-125. [39] 柴娟,常晓峰.螺旋CT骨密度测定对种植前牙槽骨骨质的评价[J].西安交通大学学报,2011,32(4):504-507. [40] 马绪臣.口腔颌面锥形束CT的临床应用[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2010:10-11. [41] 谢彬,麦理想,蔡斌,等.青少年下颌后牙区牙槽骨和基骨骨皮质密度的锥形束CT测量[J].中华口腔医学研究杂志(电子版),2013, 7(2):134-139. [42] Turkyilmaz I, Tözüm TF, Tumer C. Bone density assessments of oral implant sites using computerized tomography. J Oral Rehabil. 2007;34(4):267-272. [43] 王勤涛.牙周病学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2011:261-262. [44] 王春萍,修桂英.健康人群骨密度测定及骨密度影响因素分析[J].吉林医学,2014,35(1):116-117. [45] 温宁,陆怀秀,王忠义,等.拔牙后牙槽骨愈合速度及骨密度变化的横向研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2000,16(6):430-431. [46] Albanese A, Licata ME, Polizzi B, et al. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) in dental and oral surgery: from the wound healing to bone regeneration. Immun Ageing. 2013;10(1):23. [47] Sun Z, Herring SW, Tee BC, et al. Alveolar ridge reduction after tooth extraction in adolescents: an animal study. Arch Oral Biol. 2013;58(7):813-825. [48] Tomlin EM, Nelson SJ, Rossmann JA. Ridge preservation for implant therapy: a review of the literature. Open Dent J. 2014; 8:66-76. [49] Kim YK, Yun PY, Um IW, et al. Alveolar ridge preservation of an extraction socket using autogenous tooth bone graft material for implant site development: prospective case series. J Adv Prosthodont. 2014;6(6):521-527. [50] Hansson S, Halldin A. Alveolar ridge resorption after tooth extraction: A consequence of a fundamental principle of bone physiology. J Dent Biomech. 2012;3:1758736012456543. [51] Li B, Wang Y. Contour changes in human alveolar bone following tooth extraction of the maxillary central incisor. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2014;15(12):1064-1071. [52] Chen ST, Buser D. Esthetic outcomes following immediate and early implant placement in the anterior maxilla--a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2014; 29 Suppl:186-215. [53] Alsamak S, Psomiadis S, Gkantidis N. Positional guidelines for orthodontic mini-implant placement in the anterior alveolar region: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2013;28(2):470-479. [54] Hämmerle CH, Araújo MG, Simion M, et al. Evidence-based knowledge on the biology and treatment of extraction sockets. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012;23 Suppl 5:80-82. [55] Chen ST, Wilson TG Jr, Hämmerle CH. Immediate or early placement of implants following tooth extraction: review of biologic basis, clinical procedures, and outcomes. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2004;19 Suppl:12-25. [56] Iizuka T, Miller SC, Marks SC Jr. Alveolar bone remodeling after tooth extraction in normal and osteopetrotic (ia) rats. J Oral Pathol Med. 1992;21(4):150-155. [57] Aghaloo TL, Moy PK. Which hard tissue augmentation techniques are the most successful in furnishing bony support for implant placement? Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2007;22 Suppl:49-70. [58] 王勤涛.牙周病学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2011:192-193. [59] Campana V, Milano G, Pagano E, et al. Bone substitutes in orthopaedic surgery: from basic science to clinical practice. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014;25(10):2445-2461. [60] Kaiser MG, Groff MW, Watters WC 3rd, et al. Guideline update for the performance of fusion procedures for degenerative disease of the lumbar spine. Part 16: bone graft extenders and substitutes as an adjunct for lumbar fusion. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;21(1):106-132. [61] Zwingenberger S, Nich C, Valladares RD, et al. Recommendations and considerations for the use of biologics in orthopedic surgery. BioDrugs. 2012;26(4):245-256. [62] Roffi A, Filardo G, Kon E, et al. Does PRP enhance bone integration with grafts, graft substitutes, or implants? A systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013;14:330. [63] Janicki P, Schmidmaier G. What should be the characteristics of the ideal bone graft substitute? Combining scaffolds with growth factors and/or stem cells. Injury. 2011;42 Suppl 2: S77-81. [64] Grabowski G, Cornett CA. Bone graft and bone graft substitutes in spine surgery: current concepts and controversies. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2013;21(1):51-60. [65] 胡堃,刘斌.骨移植材料发展趋势[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究, 2010,7(3):32-38. [66] 王月升,王春兰,赵彤,等.纳米胶原基骨治疗牙周病骨缺损疗效观察[J].山东医药,2012, 52(10):87-88. |
| [1] | Shen Jinbo, Zhang Lin. Micro-injury of the Achilles tendon caused by acute exhaustive exercise in rats: ultrastructural changes and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1190-1195. |
| [2] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [3] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [4] | Yang Weiqiang, Ding Tong, Yang Weike, Jiang Zhengang. Combined variable stress plate internal fixation affects changes of bone histiocyte function and bone mineral density at the fractured end of goat femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 890-894. |
| [5] | Liu Liu, Zhou Qingzhu, Gong Zhuo, Liu Boyan, Yang Bin, Zhao Xian. Characteristics and manufacturing techniques of collagen/inorganic materials for constructing tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 607-613. |
| [6] | Xu Xiaoming, Chen Yan, Song Qian, Yuan Lu, Gu Jiaming, Zhang Lijuan, Geng Jie, Dong Jian. Human placenta derived mesenchymal stem cell gel promotes the healing of radiation skin damage in SD rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3976-3980. |
| [7] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [8] | Chen Lei, Zheng Rui, Jie Yongsheng, Qi Hui, Sun Lei, Shu Xiong. In vitro evaluation of adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction combined with osteochondral integrated scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3487-3492. |
| [9] | Huo Hua, Cheng Yuting, Zhou Qian, Qi Yuhan, Wu Chao, Shi Qianhui, Yang Tongjing, Liao Jian, Hong Wei. Effects of drug coating on implant surface on the osseointegration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3558-3564. |
| [10] | Yang Li, Li Xueli, Song Jinghui, Yu Huiqian, Wang Weixia. Effect of cryptotanshinone on hypertrophic scar of rabbit ear and its related mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3150-3155. |
| [11] | Liu Zhendong, Wang Rui, Li Xiaolei, Wang Jingcheng. Review of interferon alpha-2b inhibiting scar formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 317-321. |
| [12] | Chen Siyu, Li Yannan, Xie Liying, Liu Siqi, Fan Yurong, Fang Changxing, Zhang Xin, Quan Jiayu, Zuo Lin. Thermosensitive chitosan-collagen composite hydrogel loaded with basic fibroblast growth factor retards ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2472-2478. |
| [13] | Chen Liang, Meng Shu, Cheng Guoping, Ding Yi . Effects of fish scale collagen membrane on adhesion, proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2494-2499. |
| [14] | Zhang Hui, Wang Shaohua, Wang Qian, Wang Hui, Gan Hongquan, Cui Yishuang, Li Qijia, Wang Zhiqiang. Porous tantalum coated with RGD polypeptide can activate the integrin/focal adhesion kinase signaling pathway of MG63 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2535-2540. |
| [15] | Li Shao, Liang Yongkang, Gao Yi, Peng Qing. Establishment and functional in vitro characteristics of three-dimensional collagen HepaRG microsphere [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2541-2547. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||