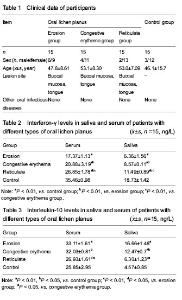
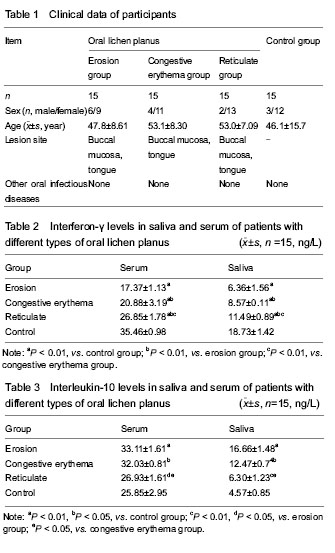
| [1] Lodi G, Scully C, Carrozzo M, et al. Current controversies in oral lichen planus: report of an international consensus meeting. Part 2. Clinical management and malignant transformation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005;100(2):164-178.
[2] Femiano F, Cozzolino F, Gaeta GM, et al. Recent advances on the pathogenesis of oral lichen planus (OLP). The adhesion molecules. Minerva Stomatol. 1999;48(4): 151-159.
[3] Sugerman PB, Savage NW, Walsh LJ, et al. The pathogenesis of oral lichen planus. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2002;13(4):350-365.
[4] Billiau A, Heremans H, Vermeire K, et al. Immunomodulatory properties of interferon-gamma. An update. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998;856:22-32.
[5] Chen QM, Zhou ZT. Oral Mucosal Diseases. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2012:103-110.
[6] Moore KW, de Waal Malefyt R, Coffman RL, et al. Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:683-765.
[7] Han YP. Investigation of the pathogenesis of oral lichen planus: role of Th1/Th2 cell and its cytokines. Fuzhou: Fujian Medical University, 2011.
[8] Garza KM, Chan SM, Suri R, et al. Role of antigen-presenting cells in mediating tolerance and autoimmunity. J Exp Med. 2000;191(11):2021-2027.
[9] Zhu JH, Yan XL, Gao CY, et al. Expression and correlation of IL-10 in serum and saliva of patients with oral lichen planus. Linchuang Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi. 2014, 30(4): 221-223.
[10] Iijima W, Ohtani H, Nakayama T, et al. Infiltrating CD8+ T cells in oral lichen planus predominantly express CCR5 and CXCR3 and carry respective chemokine ligands RANTES/CCL5 and IP-10/CXCL10 in their cytolytic granules: a potential self-recruiting mechanism. Am J Pathol. 2003;163(1):261-268.
[11] Zhou G, Fan MW, Liu JY. Effects of glucocorticoids on T helper cells balance in oral lichen planus. Zhonghua Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi. 2005;40(2):98-101.
[12] Liu W, Dan H, Wang Z, et al. IFN-gamma and IL-4 in saliva of patients with oral lichen planus: a study in an ethnic Chinese population. Inflammation. 2009;32(3):176-181.
[13] Kelso A. Th1 and Th2 subsets: paradigms lost? Immunol Today. 1995;16(8):374-379.
[14] Scully C, Carrozzo M. Oral mucosal disease: Lichen planus. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;46(1):15-21.
[15] Jungell P, Konttinen YT, Nortamo P, et al. Immunoelectron microscopic study of distribution of T cell subsets in oral lichen planus. Scand J Dent Res. 1989;97(4):361-367.
[16] Wang XJ, Liu Q, Gu Y. Treatment of oral lichen planus with epidermal transfer factor. Shiyong Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi. 2008;24(5):717.
[17] Gong FL. Medical Immunology. Beijing: Science Press. 2008.
[18] Fromowitz FB, Viola MV, Chao S, et al. ras p21 expression in the progression of breast cancer. Hum Pathol. 1987; 18(12):1268-1275.
[19] Li BQ. Oral Mucosal Diseases. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2006:83-87.
[20] Lai HC, Cao HK. Mechanism and progress of lichen planus cell infiltration. Shanghai Kouqiang Yixue. 1995;4(1):46-48,50.
[21] Deng GH, Chen ZL, Chen HB, et al. Significance of cell immunoreactions and cell apoptosis in oral lichen planus. Huaxi Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi. 2009;27(3):256-259.
[22] Zhou G. CD4+T Lymphocyte Subsets and Th1/Th2 Polarization in Oral Lichen Planus. Wuhan: Wuhan University. 2004.
[23] Deng GH, Han YP, Wang HR, et al. The role of IL-2/IL-10 cell in the pathogenesis of oral lichen planus. Linchuang Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi. 2012;28(12):715-718.
[24] Edgar WM. Saliva: its secretion, composition and functions. Br Dent J. 1992;172(8):305-312.
[25] Nagler RM, Hershkovich O, Lischinsky S, et al. Saliva analysis in the clinical setting: revisiting an underused diagnostic tool. J Investig Med. 2002;50(3):214-225. |