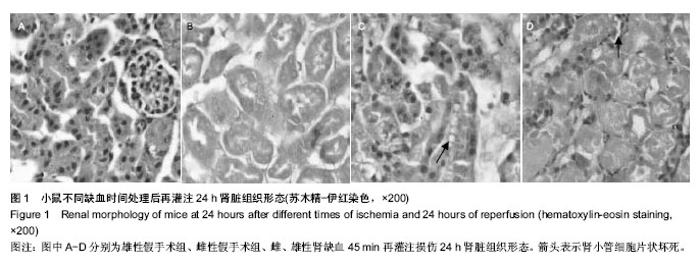
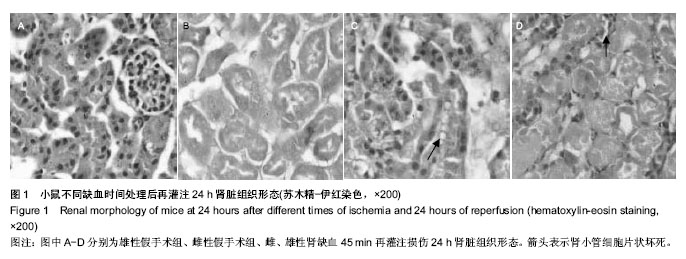
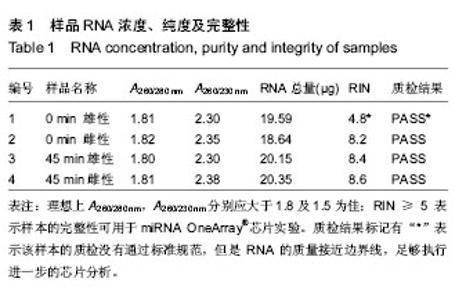
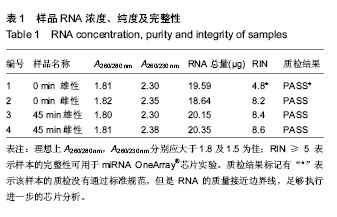
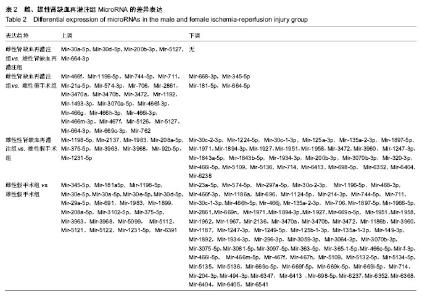
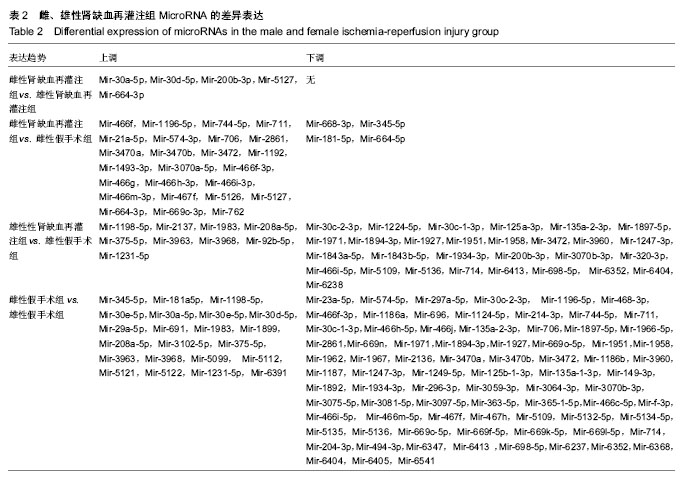
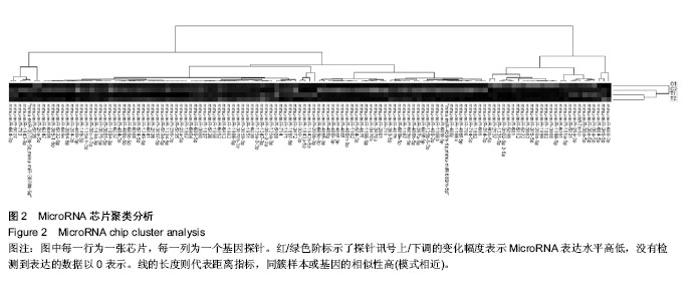
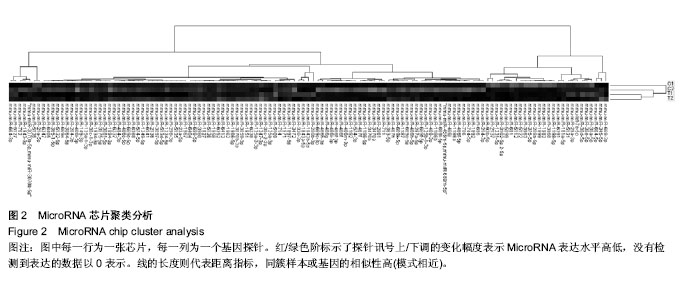
| [1] TanakaR, Tsutsui H, Ohkita M, et al. Sex differences in ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury are dependent on the renal sympathetic nervous system. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013;714(1-3):397-404.
[2] 徐青云,邵凤民.性别差异在肾脏缺血再灌注损伤中的作用机制[J].实用诊断与治疗杂志,2007,21(5):362-364
[3] Park KM, Kim JI, Ahn Y, et al. Testosterone is responsible for enhanced susceptibility of males to ischemic renal injury. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(50):52282-52292.
[4] Wei Q, Wang MH, Dong Z, et al. Differential gender differences in ischemic and nephrotoxic acute renal failure. Am J Nephrol. 2005;25(5):491-499.
[5] Bartel B, Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: at the root of plant development? Plant Physiol. 2003;132(2):709-717.
[6] Lim LP, Glasner ME, Yekta S, et al. Vertebrate microRNA genes. Science. 2003;299(5612):1540.
[7] Hwang HW, Mendell JT. MicroRNAs in cell proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis.Br J Cancer. 2006;94(6):776-780.
[8] Croce CM, Calin GA. miRNAs, cancer, and stem cell division. Cell. 2005;122(1):6-7.
[9] Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, Weinberg RA. Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nature. 2007;449(7163):682-688.
[10] Tavazoie SF, Alarcón C, Oskarsson T, et al. Endogenous human microRNAs that suppress breast cancer metastasis. Nature. 2008;451(7175):147-152.
[11] Ren A, Yan X ,Lu H, et al. Antagonism of endothelin-1inhibits hypoxia-induced apoptosis in cardiomyocytes. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008;86:536-540.
[12] Xu C, Lu Y, Pan Z, et al. The muscle-specific microRNAs miR-1 and miR-133 produce opposing effects on apoptosis by targeting HSP60 HSP70 and caspase-9 in cardiomyocytes. J Cell Sci. 2007;120(Pt 17):3045-3052.
[13] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30.
[14] 胡红林,王共先,邹丛.BALB/c小鼠肾缺血再灌注损伤模型的建立与评价[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(5):870-873.
[15] Rabb H, Mendiola CC, Dietz J, et al. Role of CD11a and CD11b in ischemic acute renal failure in rats.Am J Physiol. 1994;267(6 Pt 2):F1052-F1058.
[16] Wei Q, Wang MH, Dong Z. Differential gender differences in ischemic and nephrotoxic acute renal failure. Am J Nephrol. 2005;25(5):491-499.
[17] Kittikulsuth W, Sullivan JC, Pollock DM. ET-1 actions in the kidney: evidence for sex differences. Pharmacology. 2013; 168: 318-326.
[18] Fukuda K, Yao H, Ibayashi S, et al. Ovariectomy exacerbates and estrogen replacement attenuates photothrombotic focal ischemic brain injury in rats. Stroke. 2000;31:155-160.
[19] Sugden PH, Clerk A. Akt like a woman: gender differences in susceptibility to cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 2001;88: 975-977.
[20] Muller V. Losonczy G. Heemann U. et al. Sexual dimorphism in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats: possible role of endothelin. Kidney Int. 2002;62:1364-1371.
[21] Park KM, Kim JI, Ahn Y, et al. Testosterone is responsible for enhanced susceptibility ofmales to ischemic renal injury. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(50):52282-52292.
[22] Fekete A, Vannay A, Tulassay T, et al. Sex difference in the alterations of Na(+), K(+)-ATPase following ischemia- reperfusion injury in the rat kidney. J Physiol 2004;555(2): 471-480.
[23] 肖占琴,陶树新,陈阳美. microRNA 在神经系统疾病发病机制中的作用[J].中华神经医学杂志,2011,10(2):204-206.
[24] 雷平,李耀华,杨树源,等. microRNA 在神经系统中的作用研究进展[J].中华神经医学杂志,2010,9(2):203-207.
[25] 谭健,肖健,王志农.MicroRNA在大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤中表达谱的变化[J].实用医学杂志,2013,28(2):199-201.
[26] Jia P, Teng J, Zou J, et al. miR-21 contributes to xenon-conferred amelioration of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice.Anesthesiology. 2013;119(3):621-630.
[27] Kaucsár T, Révész C, Godó M, et al. Activation of the miR-17 family and miR-21 during murine kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2013;23(5):344-354.
[28] Saikumar J, Hoffmann D, Kim TM, et al. Expression, circulation, and excretion profile of microRNA-21, -155, and -18a following acute kidney injury. Toxicol Sci. 2012;129(2): 256-267.
[29] Zhang Q, Xiao X, Li M, et al. Acarbose reduces blood glucose by activating miR-10a-5p and miR-664 in diabetic rats. PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e79697.
[30] Wang JF, Zha YF, Li HW, et al. Screening plasma miRNAs as biomarkers for renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Med Sci Monit. 2014;20:283-289. |